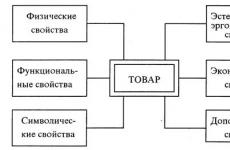
Burner designs. Gas burners, classification and characteristics A simple gas burner differs from one with a thermostat
Single-stage, two-stage and modulating burners for heating boilers. Review.
When choosing burners, consumers face a difficult task- which burner to choose . This choice allows them to make a small comparison of burners from different manufacturers according to the type of regulation and the level of automation of the burner device.
We invite you to get acquainted with the opinion of the specialists of our company, based on the experience of using Weishaupt, Elco, Cib Unigas and Baltur combined, oil and gas burners.
Let's define the basic requirements that apply to burners, depending on the application. Depending on the application, burners can be divided into groups.
Group 1. Burners for systems individual heating (in this group we include burners with a capacity of up to 500 - 600 kW, which are installed in boiler rooms of private houses, small industrial and commercial and administrative buildings).
When choosing burners for this group of consumers, it is necessary to take into account the wishes of the buyer in the level of automation of an individual boiler room:
if you do not show elevated technical requirements to the installed equipment and you want to have a reliable boiler room that does not require large initial financial investments, then you can opt for burners with single-stage, two-stage operating modes;
· if you want to build a heating system with a high level of automation, weather-dependent regulation, as well as low fuel and energy consumption, then you better apply modulating burners or burners with stepless two-stage regulation, which will provide the possibility of programming power and a wide operating range of burner control.
Group 2 Burners for heating systems of large residential complexes (in this group we include burners with a capacity of more than 600 kW for the needs of housing and communal services, central heating, as well as for the heat supply of large industrial and commercial and administrative buildings).
· Sliding two-stage or modulating burners are ideal for this group. This is due to: the large capacity of the boiler houses, the customer’s desire to build a boiler house with a high level of automation, the desire to ensure the lowest possible fuel and electricity consumption (use frequency control of the fan power), as well as to use equipment for automatic control of residual oxygen in flue gases (oxygen control).
Group 3. Burners for use on technological equipment (this group can include burners of any power, depending on the power of the process equipment).
For this group, preferred modulating burners. The choice of these burners is determined not so much by the wishes of the customer, but by the technological requirements of production. For example: in some production processes it is required to maintain a strictly defined temperature chart and prevent temperature fluctuations, otherwise it can lead to disruption of the technological process, product spoilage and, as a result, to significant financial losses. Staged burners can also be used in process plants, but only in those cases where slight temperature fluctuations are acceptable and do not entail negative consequences.
Brief description of the principle of operation of burners with different type regulation.
Single stage burners they work only in one power range, they work in a heavy mode for the boiler. During the operation of single-stage burners, frequent switching on and off of the burner occurs, which is regulated by the automation of the boiler unit.
Two stage burners , as the name implies, have two power levels. The first stage, as a rule, provides 40% of the power, and the second - 100%. The transition from the first stage to the second occurs depending on the controlled parameter of the boiler (heat carrier temperature or steam pressure), the on / off modes depend on the boiler automation.
Sliding two-stage burners allow for a smooth transition from the first stage to the second. This is a cross between a two-stage and a modulating burner.
Modulating burners heat the boiler continuously, increasing or decreasing power as necessary. Range of change of a mode of burning - from 10 to 100% of rated power.
Modulating burners are divided into three types according to the principle of operation of modulating devices:
1. burners with mechanical modulation system;
2. burners with pneumatic modulation system;
3. burners with electronic modulation.
Unlike burners with mechanical and pneumatic modulation, burners with electronic modulation provide the highest possible control accuracy, since mechanical errors in the operation of the burner devices are eliminated.
Price advantages and disadvantages
Of course, modulating burners are more expensive than stepped models, but they have a number of advantages over them. The smooth power control mechanism makes it possible to reduce the cycling of the boilers on and off to a minimum, which significantly reduces mechanical stresses on the walls and in the nodes of the boiler, which means it prolongs its “life”. Fuel economy in this case is at least 5%, and with proper tuning, you can achieve 15% or more. And, finally, the installation of modulating burners does not require the replacement of expensive boilers, if they function properly, while increasing the efficiency of the boiler.
Against the background of the disadvantages of stepped burners, the advantages of modulating burners are obvious. The only factor that makes managers opt for step models is their greater low price. But savings of this kind are deceptive: wouldn't it be better to spend a large sum at a time on more advanced, economical and environmentally friendly burners? Moreover, the costs will pay off in the next few years!
Many buyers understand the benefits of using modulating burners, and now they only have to choose the models they need. Which manufacturers are best to contact? Even with a superficial study of prices for imported and domestic burners, it is clear that the difference is very significant. Some models of foreign manufacturers are more expensive than products Russian production more than twice.
A detailed analysis of the market of burner manufacturers shows that Russian equipment is significantly inferior to imported analogues in terms of automation. In order to achieve high level automation of Russian-made burners, it is necessary to invest a lot of money to purchase the necessary automation systems and work on the installation and commissioning of equipment. Based on the results of all the work, it turns out that the cost of retrofitted Russian-made burners is close to the cost of imported burners. But at the same time, you will not have a 100% guarantee that the understaffed Russian burner will provide you with the desired result.
Conclusion of our experts
The right choice of burner is an important step in the construction or modernization of a boiler house. The further operation of the heating equipment depends on how responsibly you approached this issue. The stable operation of the burner, compliance with environmental regulations, longer service life of the boilers and the possibility of fully automating the operation of the thermal power plant speak of the significant advantages of using modulating burners in boiler rooms. And if the benefit from their exploitation is obvious, it is simply unreasonable not to use it.
Burners Weishaupt / Germany , Elco / Germany , Cib Unigas / Italy, Baltur / Italy have proven themselves as reliable and high-quality equipment. By choosing these burners, you get confidence and profit! In turn, we are ready to provide you with reasonable prices and the shortest delivery time for equipment.
Glossary of terms
Automatic boiling
The presence of the function of automatic boiling in electric stoves.
When using this function, you must set the desired power level for cooking. After that, the burner will start working at maximum power and will quickly heat the liquid to a boil. The power will then drop to the user-specified level and the boil will be maintained automatically. This function will facilitate and speed up the preparation of dishes, but its presence slightly increases the cost of the stove.
Oven door lock
Possibility to lock the oven door.
Some models have a door lock that is invisible to the eye, making it impossible to open the oven. This feature will be useful if there are small children in the house.
Control panel lock
The possibility of blocking the operation of the plate.
Some models have a security system that allows you to block the inclusion of burners and the oven. First of all, it serves to protect children from turning on the hob.
Rotisserie in the oven
Existence in a set of a cooker of a skewer for an oven.
The skewer is used in the preparation of barbecue, large pieces of meat, fish, poultry. It can be equipped with an electric motor. As a rule, a spit must be included with stoves equipped with a grill function ( see "Grill").
Air cooled case
Built-in cooling fan.
The built-in fan ensures efficient cooling of the oven door. He drives cool air through the cavities along the perimeter of the oven body, preventing heating of the surrounding furniture and electronics.
Pull-out oven trolley
Existence of the built-in sliding mechanism in a delivery set.
In some models, trays and trays are fixed on the door and automatically slide out with it when it is opened. This way you don't have to take out the trays with your hands to pour the sauce or brush over the cooking dish while it's cooking. This reduces the risk of hand burns and simplifies work in the kitchen - hands remain free. Cleaning is also made easier as the pull-out trolley is completely removable.
Height(from 5.0 to 98.0 cm)
The height of the cooker.
The standard height for stoves with ovens is 85 cm. Most stoves have this height.
Oven gas control
The presence of the function of controlling the gas supply in the oven.
The gas control of a gas oven is a safety system that automatically stops the gas supply if the flame goes out.
Gas control burners
The presence of the function of controlling the supply of gas in the burners of the stove.
Gas control of gas burners is a safety system that automatically stops the gas supply if the flame goes out for any reason.
Depth(from 20 to 100.0 cm)
Depth of the cooker body.
Most slabs have a standard depth of 60 cm. There are also models with a depth of 50 cm.
Grill
The presence of a grill function in the oven.
Grilling is a method of cooking food using heat radiation (similar to grilling food on charcoal). Suitable for cooking steaks, fish, toast, casseroles. Grilled food is considered healthier because it is prepared without the addition of oil or fat. Usually it has a delicious fried crust. There are electric, gas and infrared grills ( see "Grill type").
Display
The presence of a built-in display on the control panel of the stove.
It can display the current time, temperature, time remaining until the end of cooking, and other information.
Additional oven
The presence of an additional oven in the kitchen stove.
An additional oven can be located either above or below, or to the side of the main one. Compared to the main one, it has a smaller volume and, as a rule, not so rich functionality. Thanks to this design, you can cook several dishes at the same time (for example, bake meat in a larger oven and bake a cake in a smaller one). The presence of an additional oven leads to an increase in the dimensions of the stove compared to the classic dimensions, so if you have a small kitchen, it is better to choose a simpler model ( see "Additional oven location").
Safety shutdown
The presence of a protective device of self-shutdown.
This device turns off the burners or the entire stove after a certain time, if no other commands come from you. Some models have an additional safety thermostat that turns off the burner in case of overheating.
Residual heat indicators
Presence of indicators of residual heat.
Some ranges with electric hotplates (see "Type of hob") are equipped with residual heat indicators for the hotplates, which are designed to ensure user safety as well as to save energy. During operation of any of the burners, the corresponding residual heat indicator lights up, which continues to burn even after the burner is turned off until the temperature on the surface of the burner reaches a level that is safe for humans. Another significant advantage of the residual heat indicator is that with its help you can easily determine which of the burners has not cooled down yet, and, therefore, it can be used to keep the dish warm. This allows you to save energy.
Energy class
Stove energy class.
This characteristic allows you to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of its use. All modern stoves can have three classes: A, B or C, they are all quite economical.
Number of oven door glass
The number of glasses installed in the oven door.
In many models of modern stoves and ovens, the door has double (and sometimes even triple or four-layer) glass, which allows you to reduce heat outer surface practically to zero. All heat is stored inside the oven: for example, if inside the oven is 200 ° C, the temperature of the outer surface can reach a maximum of 40 degrees.
Convection in the oven
The presence of the convection function in the stove oven.
Convection - oven heating mode. The fan ensures constant air circulation throughout the entire volume of the oven, which allows the dish to bake evenly on all sides. With the help of convection, you can cook dishes on several levels at the same time.
Coup de feu burner
The presence of the Coup de feu panel in the gas stove.
This panel is a large, thick cast iron surface that is heated by a gas burner. The design allows you to cook both on the burner and on an open fire. Coup de Feu the best way suitable for making sauces, stewing, and can also be used as a plate warmer. This burner is found only in wide models of work surfaces and will be of interest primarily to professionals.
Fry top burner
The presence of a Fry-top burner in an electric stove.
It is a thick (usually 1.5-2 cm) flat stainless steel surface, under which are heating elements. Fry-top, due to its thickness, heats evenly and is ideal for natural cooking of vegetables, meat and fish, however, it takes up a lot of space, so it is installed only on wide models of cookers.
Burner with oval heating zone
The presence of a burner with an oval heating zone.
In some models of electric stoves there is a burner with an oval heating zone - when the switch is in the appropriate position, an additional segment of the heating element is turned on, turning the round burner into an oval one. Such burners are very convenient for cooking dishes in special dishes (for example, a duckling, a fish tray, etc.). The double expanded field gives the chance of cooking in ware as a round, and oval form.
Grill burner
Grill burner available.
As a rule, this is a thick ribbed surface or a grate with heating elements located below or a gas burner ( see "Type of hob"). Good for cooking meat, fish, vegetables without additional oil. Grill burners are installed only in wide stove models, because they take up a lot of space on the work surface.
Maximum power consumption(from 25 to 10900 W)
The value of the maximum power consumption.
The less the stove consumes electricity, the more economical it is, but at the same time it is also more expensive.
See also "Energy class".
For gas stoves ( see "Type") the power consumption of electrical equipment is indicated. For example, for stoves equipped with an electric oven ( see "Type of oven") power will be several kW, for models with gas oven, but electric ignition, display, etc. - 100 - 300 W.
Maximum temperature(from 200 to 360 °С)
The maximum operating temperature of the oven. For cooking most dishes, a temperature of 220-250 ° C is sufficient.
Oven volume(from 24.0 to 135.0 l)
Usable volume of the oven.
Useful is the volume that can be used to accommodate the prepared products. The total volume of the oven will always be slightly larger, as additional space is needed for the free circulation of air.
Silencing the beeper
Ability to turn off the sound signal of the timer.
In models with a timer, an audible signal will inform you in time that the dish has been cooked. Of course, this is very convenient, but in certain cases it may not be entirely appropriate (for example, at night, when you don’t want to disturb the sleep of loved ones). For such situations, some models provide the ability to turn off the sound.
Cleaning the oven
Method for cleaning the oven.
Purification can be conventional, pyrolytic or catalytic.
Traditional cleaning is carried out in the usual way, that is, manually, using detergents and a damp cloth.
Pyrolytic cleaning is a self-cleaning system in which grease and other contaminants on the interior surfaces of the oven are burned off at very high temperatures, turning into ash, which can be easily removed with a damp cloth. Pyrolytic self-cleaning is most effective, it makes the use of special detergents unnecessary. However, plates with pyrolytic cleaning are not cheap.
In plates with a catalytic cleaning system, the inner surfaces of the working chamber are covered with finely porous enamel with special catalytic properties that accelerate the process of fat oxidation and its splitting into water and carbon. Catalytic cleaning occurs during normal heating of the oven chamber to 200-250 °C. The catalytic method is convenient in that it is carried out automatically during cooking, but it is less efficient than the pyrolytic one. Therefore, from time to time, the camera, covered with catalytic enamel, still needs to be washed by hand.
Switches
Type of switches depending on the mechanism.
AT different models slabs can be controlled using rotary, touch, push-button or recessed switches.
As a rule, rotary switches (regular rotary knobs) are installed in inexpensive stoves.
Recessed switches are used in more expensive models and have several advantages over conventional rotary ones. They can only be "drowned" in the off position. This makes it impossible to accidentally turn on the stove (only the extended handles can be turned). In the "recessed" state, the switches fit harmoniously into the front panel, which makes it easier to clean the hob.
Management in expensive models is carried out using touch switches - just one touch is enough to turn on the burner, select the power level or heating zone. A mistake when turning on is almost impossible thanks to the light indication and the well-thought-out arrangement of the touch buttons. The only inconvenience: connoisseurs of impeccable cleanliness after manipulating the modes have to wipe the glass-ceramic panel, on the surface of which fingerprints remain.
The alternative is button control. It is almost as convenient as touch, but avoids noticeable marks on the surface.
Oven lighting
The presence of internal lighting of the oven.
By turning on the lamp installed inside the oven, you can see the interior without opening the door and without releasing heat from the working chamber.
Working surface
The material of the working panel of the stove.
The working surface of the stove, on which the burners are located, can be enameled, steel, glass-ceramic or tempered glass.
Enamelled surfaces are inexpensive, durable, can have any color in the richest color scheme. At the same time, cleaning the enamel from traces of runaway liquid, fat droplets and other cooking companions is quite laborious, and since scratches appear on the enamel over time, caring for it becomes even more difficult. In addition, the enamel is unstable to chipping.
Stainless steel plates are popular - polished or matte. Although they are easier to clean than enamelled ones, maintaining their permanent shine is not easy. Finger stains may remain on them. Stainless steel requires special cleaning products.
Glass ceramics is an expensive, but very beautiful and convenient material. The glass-ceramic surface is a panel under which heating elements (ceramic, halogen or induction hobs) are placed, as well as residual heat indicators. A unique feature of glass ceramics is the ability to transfer heat evenly and quickly to working area and, accordingly, in the dishes standing on it. Such a plate has a very strong, perfectly flat and smooth surface, the dishes on it will never tip over, and it is easy and simple to care for this stove. But with all its advantages, glass ceramics also has a number of disadvantages: with strong boiling, the “escaped” liquid spills over the entire surface and can flow over the sides or get onto the hot burner; requires the use of dishes with a completely flat and smooth bottom; has a low resistance to mechanical damage in comparison with metal surfaces.
It should also be noted the "gas on glass" option, when the hob on which the burners are installed is covered with a layer of glass-ceramic or tempered glass. Since there are no heat sources under this layer in such panels, the good thermal conductivity of glass-ceramic will not be required. Therefore, it is more expedient to pay attention to models with tempered glass, which looks almost the same as glass ceramics, but is somewhat cheaper. Such a plate is easy to clean, looks good, but requires careful handling - scratches will be quite noticeable.
Additional oven location
The location of the additional oven relative to the main one ( see "Additional oven").
Lateral arrangement is found in wide slabs (their width, as a rule, is not less than 90 cm). Ovens located one above the other are more often in models with a height greater than the standard 85 cm. However, you can also find options where the volume of the main oven is reduced to maintain the standard dimensions of the stove.
Timer
The presence of a built-in timer in the stove.
The timer helps you program the cooking time. As a rule, the timer can be used for counting time for any other purpose. Depending on the model, after the set time has elapsed, an audible signal sounds or the hob switches off automatically ( see "Timer type").
Thermostat
The presence of a temperature control system.
Maintains the temperature at a given level. For electric stoves, the presence of a thermostat is mandatory, but not all gas stoves are equipped with them ( see "Type of oven"). In the presence of a thermostat, the gas burner, when turned on, starts to work at full power, and when the set temperature is reached, the gas supply force decreases.
Type of hob
Type of hob The type of hob of the cooker.
Depending on the type of energy used, hobs are divided into gas (gas burners), electric (cast iron electric burners and glass ceramics) and combined (they have both gas and electric burners).
You should pay attention to the gas hob only if your house has a mains gas supply. Otherwise, it makes no sense to purchase such a stove; an electric hob will suit you. It has a number of advantages: it is much safer (of course, if the electrical wiring is in order), it does not consume oxygen, it is easier to wash it due to the lack of gratings. At the same time, there is a very tangible drawback: such a surface heats up for a rather long time (the exception is induction cookers). In addition, electrical hobs make high demands on the cookware: its bottom must be even, and the diameter of the cookware itself must match the diameter of the burner.
Combined devices can operate on both gas and electricity. They are more difficult to repair and significantly more expensive, but the high price is fully offset by their functionality. If you have main gas in your kitchen and you are confident in the quality of your electrical wiring, then you can safely take this model. This option is especially relevant for those houses where there are interruptions in gas or electricity supply.
Grill type
Type of built-in grill.
Gas stoves are usually equipped with a gas or electric grill, electric - infrared (heater - halogen lamp) or electric (heater - spiral) grill.
Gourmets believe that dishes cooked on a "live" fire, i.e. gas tastes better. However, the advantage of an electric grill is obvious - its operation can be adjusted more precisely. Infrared is not so popular yet. Manufacturers claim that this type of grill is more economical and, in addition, helps to preserve more vitamins and taste in food.
A stove with an electric oven cannot have a gas grill ( see "Type of oven").
Additional oven type
Additional oven type ( see "Two ovens", "Type of oven").
Oven type
Stove oven type.
Ovens are gas and electric.
Cookers with gas and combination hob can have both gas and electric ovens. Cookers with electric burners are equipped only with electric ovens. Electric ovens have more functions and heating modes than gas ovens. Some cookers don't have an oven at all. As a rule, these are simple desktop models that are not intended for intensive use. Usually they are purchased for summer cottages or rental housing.
Timer type
Cooker timer type.
In some models, the timer itself automatically turns off the stove (off timer), in others it beeps (audio timer). In some models, the timer sound can be turned off ( see "Turning off the beeper").
Control type
Plate control type.
There are models with mechanical and electronic control on the market.
Most modern stoves have a mechanical type of control. The power and operating time are set using the rotary switches.
Less common are models with an electronic type of control, which is implemented in the form of conventional or touch buttons ( see "Switches"). Such models may have a display ( see "Display"), which displays the temperature, the selected program and the time remaining until the end of the program. Despite their great functionality, electronically controlled models also have disadvantages. They require the user to focus, and to turn them on, more manipulations are performed. In addition, cookers with electronic control type, as a rule, more expensive than models with mechanical control.
Electric ignition type
The way to turn on the electric ignition ( see "Electric ignition").
Electric ignition can be automatic or mechanical.
With automatic - ignition occurs when the switch is turned, which opens the gas supply to the burner. With mechanical electric ignition, after turning the burner switch, pressing a special button located on the burner control panel is required.
fryer
Built-in deep fryer.
Can be used for frying meat and vegetables in large amounts of oil. Usually built-in fryers are equipped with professional or semi-professional models.
Functionality of the oven
Type of oven depending on functionality.
There are classic (static) ovens and multifunctional ones.
A classic oven can have from 1 to 4 heating modes: top, bottom, top/bottom and grill. These modes are quite enough for the daily preparation of a wide variety of dishes.
The multifunctional oven has more than four heating modes. Typically, these ovens have many different combinations of operation, and also have convection (with the exception of gas ovens).
Slab color
The color scheme of the plate body.
The stove is always in sight, and therefore it is desirable that it is harmoniously combined with the kitchen set. Currently, the traditional white models have been replaced by a wide variety of options. Thanks to a wide range of colors, you can choose a stove in the same style with the interior of the kitchen.
Watch
Built-in clock.
Of course, a clock in the stove is far from the most important parameter, but for many it will seem like a convenient solution. After all, you can find out the time only by glancing at the stove, and it is always in sight.
Number of gas burners(from 1 to 8)
The total number of gas burners.
The most common option is 4 gas burners. Combined cookers ( see "Type of hob"), as a rule, have 3 gas burners (rarely 2).
Number of halogen burners (1)
The number of halogen burners located on the electric stove.
The halogen burner has great power, instantly heats up and cools down quickly. It provides maximum heat immediately after switching on, and thus the boiling time is greatly reduced. Heating is provided by a high-temperature coil combined with a halogen lamp - a quartz gas-filled tube. The lamp glows with a bright red light, highlighting a large number of heat, which is evenly distributed over the entire bottom of the dish with minimal energy loss. Since the halogen burner gains full power almost immediately after switching on, better way boil water quickly, make french fries or deep fry meat is not to be found. In terms of heating speed, such a burner is comparable to a gas burner. Unfortunately, stoves with such burners are rare and have a high cost.
Number of dual circuit burners(from 1 to 4)
The number of double-circuit burners in electric stoves.
A double-circuit burner is a burner with a variable heating zone, which consists of two concentric circles with different diameters. When using a dual-circuit burner, you can choose to turn on a larger or smaller diameter heating surface, suitable for a large frying pan or a small saucepan. The area of the burner is changed by lightly pressing the touch button or by simply turning the knob.
Number of induction hotplates(from 1 to 6)
Number of electric burners with induction heating.
The action of the induction burner is based on the formation of vortex fields in the induction coil. Induction hobs provide very fast boiling and great precision in heating control, they have high power. During the cooking process, the bottom of the dishes is heated directly, and the burners themselves remain cold throughout the entire time, which makes them absolutely safe. It should be noted that in the absence of dishes on the surface, the burner will not heat up (so you can not be afraid of the included burner, on which you forgot to put the pan). Another plus of these burners is the absence of inertia when the heating power decreases / increases (the reaction speed is not inferior to gas burners). The condition for using this type of burners is the presence of dishes made of cast iron or enameled steel, because glass or ceramics on such a stove will not heat up at all, and brass, stainless steel or aluminum will be very weak. Unfortunately, the prices for stoves with induction hobs are quite high.
Number of burners Double crown(from 1 to 2)
The number of burners "Double Crown" located on the gas stove.
"Double crown" - a gas burner, which, unlike the standard burner, has two rows of flame. The double gas burner has more power than a standard gas burner, which allows you to cook food faster. On such burners, the bottom of the dishes warms up more evenly, and the water boils very quickly.
Number of burners Triple Crown(from 1 to 2)
The number of "Triple Crown" burners located on the gas stove.
"Triple Crown" - a gas burner, which, unlike the standard burner and the "Double Crown" burner, has three rows of flames. Cooking becomes even faster, and the heating of the dishes is even.
Number of quick heat burners(from 1 to 5)
Number of express burners.
Such burners differ from the rest in greater power and shorter heating time. They are preferred for dishes that require rapid heating and high temperature processing (as well as for boiling). Available for both electric and gas stoves.
Number of three-circuit burners(from 1 to 2)
The number of three-circuit burners.
Such burners have a variable heating zone, which is three concentric circles. When using them, you can optionally turn on the heating surface of a larger or smaller diameter, depending on the cookware used. This allows you to reduce energy costs.
Number of electric burners(from 1 to 6)
The total number of electric burners.
The most common option is 4 electric burners. In combined stoves, there is usually 1 electric burner (less often 2).
Width(from 18.0 to 193.0 cm)
Cooker width.
According to the width of the plate, it can be conditionally divided into standard (60 cm) and narrow (50 cm). But there are plates with a width of 90 cm or more (as a rule, such models have 5-6 burners).
Electric ignition
The presence of electric ignition in the gas stove.
Electric ignition - a device for igniting the flame of a gas stove using an electric spark. It can be automatic, when the ignition occurs when the switch is turned, and mechanical, when a special button must be pressed to ignite (see "Type of electric ignition"). This feature is much more convenient to use than matches or a piezo lighter. Auto ignition is also useful from a safety point of view in the absence of a gas control system (see "Gas control of burners").
Dish drawer
Has a built-in drawer for utensils.
Usually it is located at the bottom of the plate. Such a box is available for most stoves.
Multi-circuit burners- gas burners with a double or triple ring of flame, each of which is ignited separately.
Geramat is a refractory ceramic material manufactured by Schott Glass for gas stoves. A sheet of this transparent material, very reminiscent of glass, separates the burner flame from the cookware (“gas under glass”).
Gas Control is a gas stove safety system that automatically ignites the burner when it goes out.
Auxiliary burner- It is a gas burner with a diameter of 40-55 mm and a power of up to 1000 watts. They are the most underpowered on the hob. Conventional burner - It is a gas burner with a diameter of 60-70 mm and a power of up to 2000 watts.
Ultra speed burner- This type of burner is a gas burner with a diameter of 90-100 mm with increased power (3500 W). Ideal for cooking dishes that require deep and fast cooking. On such a burner you can cook dishes in the largest pans with a noticeable time saving.
There are also burners with the so-called "Double Crown" - they have 2 rows of flame and even with a small diameter they have high power. In addition to an attractive design, modern gas panels are distinguished by a variety and practicality of surfaces. Today, a choice of enamelled coatings, stainless steel, glass ceramics, aluminum is offered.
Gas-burner- this is a device for mixing oxygen with gaseous fuel in order to supply the mixture to the outlet and burn it with the formation of a stable torch. In a gas burner, gaseous fuel supplied under pressure is mixed in a mixing device with air (air oxygen) and the resulting mixture is ignited at the outlet of the mixing device with the formation of a stable constant flame.
Gas-burners have a wide range of benefits. The design of the gas burner is very simple. Its start-up takes a fraction of a second and such a burner works almost flawlessly. Gas burners are used for heating boilers or industrial applications.
Today, there are two main types of gas burners, their separation is carried out depending on the method used to form a combustible mixture (consisting of fuel and air). There are atmospheric (injector) and pressurized (ventilation) devices. In most cases, the first type is part of the boiler and is included in its price, while the second type is most often purchased separately. A pressurized gas burner as a combustion tool is more efficient, since air is supplied to them by a special fan (built into the burner).
The purposes of gas burners are:
– supply of gas and air to the combustion front;
- mixture formation;
– stabilization of the ignition front;
– ensuring the required intensity of combustion.
Types of gas burners:
Diffusion burner - burner in which fuel and air
burns are mixed.
Injection burner - gas burner with gas premixing with air, in which one of the media necessary for combustion is sucked into the combustion chamber of another medium (synonymous with ejection burner)
Hollow premix burner – a burner in which the gas is mixed with the full volume of air in front of the outlets.
Burner not with hollow premix– a burner in which the gas is not completely mixed with air in front of the outlets. Atmospheric gas burner– injection gas burner with partial pre-mixing of gas with air, using the secondary air of the environment surrounding the torch.
Special burner– burner, the principle of operation and design of which determines the type of thermal unit or features of the technological process.
Recuperative burner– burner equipped with a heat exchanger for heating gas or air
Regenerative burner- a burner equipped with a regenerator for heating gas or air.
Automatic burner– a burner equipped with automatic devices: remote ignition, flame control, fuel and air pressure control, shut-off valves and means of control, regulation and signaling.
urbine burner– gas burner, in which the energy of the outgoing gas jets is used to drive the built-in fan that blows air into the burner.
Pilot burner– auxiliary burner used to ignite the main burner.
The most applicable today are the classification of burners according to the method of air supply, which are divided into:
- blastless - air enters the furnace due to rarefaction in it;
- injection - air is sucked in due to the energy of the gas jet;
- blast - air is supplied to the burner or furnace using a fan.
Gas burners are used at various gas pressures: low - up to 5000 Pa, medium - from 5000 Pa to 0.3 MPa and high - more than 0.3 MPa. Most often, burners operating at medium and low gas pressure are used.
Of great importance is the thermal power of a gas burner, which can be maximum, minimum and nominal.
At long work burners, where a larger amount of gas is consumed without breaking off the flame, the maximum heat output is achieved.
The minimum thermal power occurs with stable operation of the burner and the lowest gas flow without flashback.
When the burner operates at the nominal gas flow rate, which ensures maximum efficiency at the highest combustion efficiency, the nominal heat output is achieved.
It is allowed to exceed the maximum thermal power over the nominal one by no more than 20%. If the nominal heat output of the burner according to the passport is 10,000 kJ/h, the maximum should be 12,000 kJ/h.
Another important feature of gas burners is the range of thermal power regulation.
Today, a large number of burners are used various designs. The burner is selected according to certain requirements, which include: stability with changes in thermal power, reliability in operation, compactness, ease of maintenance, ensuring the completeness of gas combustion.
The main parameters and characteristics of the used gas burners are determined by the requirements:
- thermal power, calculated as the product of the hourly gas consumption, m 3 / h, and its lower calorific value, J / m 3, and which is the main characteristic of the burner;
– parameters of the combusted gas (lower calorific value, density, Wobbe number);
- rated thermal power equal to the maximum achievable power during long-term operation of the burner with a minimum excess air coefficient a and provided that the chemical underburning does not exceed the values \u200b\u200bspecified for this type of burner;
- nominal pressure of gas and air corresponding to the nominal heat output of the burner at atmospheric pressure in the combustion chamber;
– nominal relative flame length, equal to the distance along the flame axis from the outlet section (nozzle) of the burner at nominal heat output to the point where the carbon dioxide content at α = 1 is equal to 95% of its maximum value;
- coefficient of limiting regulation of thermal power, equal to the ratio of the maximum thermal power to the minimum;
- the coefficient of the working regulation of the burner in terms of thermal power, equal to the ratio of the rated thermal power to the minimum;
- pressure (vacuum) in the combustion chamber at the rated power of the burner;
– thermotechnical (luminosity, emissivity) and aerodynamic characteristics of the flame;
- specific metal and material consumption and specific energy consumption, referred to the rated thermal power;
- level sound pressure generated by the operating burner at rated heat output.
burner requirements
Based on the operating experience and analysis of the design of burners, it is possible to formulate the basic requirements for their design.
The design of the burner should be as simple as possible: no moving parts, no devices that change the cross section for the passage of gas and air, and no parts of complex shape located near the burner nose. Complex devices do not justify themselves during operation and quickly fail under the influence of high temperatures in the working space of the furnace.
Cross-sections for the exit of gas, air and gas-air mixture should be worked out in the process of creating a burner. During operation, all these sections must be unchanged.
The amount of gas and air supplied to the burner should be measured by throttle devices on the supply pipelines.
The cross sections for the passage of gas and air in the burner and the configuration of the internal cavities should be chosen in such a way that the resistance to the movement of gas and air inside the burner would be minimal.
The pressure of gas and air should mainly provide the required speeds in the outlet sections of the burner. It is desirable that the air supply to the burner be adjustable. Unorganized air supply as a result of rarefaction in the working space or by partial injection of air with gas may be allowed only in special cases.
Burner designs.
The main elements of a gas burner: a mixer and a burner nozzle with a stabilizing device. Depending on the purpose and operating conditions of the gas burner, its elements have a different design.
AT diffusion burners gas, gas and air are supplied to the combustion chamber. The mixture of gas and air occurs in the combustion chamber. Most diffusion gas burners are mounted on the walls of the furnace or furnace. In boilers, the so-called. hearth gas burners, which are located inside the furnace, in its lower part. A hearth gas burner consists of one or more gas distribution pipes, in which holes are drilled. The pipe with holes is installed on the grate or the hearth of the furnace in a slotted channel lined with refractory bricks. The required amount of air enters through the refractory slotted channel. With such a device, the combustion of gas streams emerging from the holes in the pipe begins in the refractory channel and ends in the furnace volume. Hearth burners create little resistance to the passage of gas, so they can work without forced draft.
Diffusion gas burners are characterized by a more uniform temperature along the length of the flame.
However, these gas burners require an increased excess air ratio (compared to injection burners), and also create lower thermal stresses in the furnace volume and worse conditions for gas afterburning in the tail part of the torch, which can lead to incomplete gas combustion.
Diffusion burners gas is used in industrial furnaces and boilers, where a uniform temperature is required along the length of the torch. In some processes, gas diffusion burners are indispensable. For example, in glass-making, open-hearth and other furnaces, when the combustion air is heated to temperatures exceeding the ignition temperature of the combustible gas with air. Diffusion gas burners are also successfully used in some hot water boilers.
AT injection burners Combustion air is sucked in (injected) due to the energy of the gas jet and their mutual mixing occurs inside the burner body. Sometimes, in gas injection burners, the suction of the required amount of combustible gas, the pressure of which is close to atmospheric pressure, is carried out by the energy of the air stream. In full mixing burners (all the air necessary for combustion is mixed with gas) operating on medium pressure gas, a short flame is formed, and combustion is completed in a minimum furnace volume. In partial-mix gas injection burners, only a part (40 ÷ 60%) of the air required for combustion (the so-called primary air) enters, which is mixed with the gas. The rest of the air (the so-called secondary air) enters the flame from the atmosphere due to the injecting action of gas-air jets and rarefaction in the furnaces. Unlike medium-pressure gas injection burners, low-pressure burners form a homogeneous gas-air mixture with a gas content greater than the upper ignition limit; these gas burners are stable in operation and have a wide range of heat load.
For stable combustion of the gas-air mixture in injection burners of gas medium and high pressure stabilizers are used: additional igniting torches around the main flow (burners with an annular stabilizer), ceramic tunnels inside which the combustion of the gas-air mixture occurs, and plate stabilizers that create a swirl in the flow path.
In furnaces of considerable size, gas injection burners are assembled into blocks of 2 or more burners.
Injection gas burners of infrared radiation (the so-called flameless burners), in which the main amount of heat obtained during combustion is transferred by radiation, are widely used. the gas burns on the radiating surface in a thin layer, without a visible torch. The radiating surface is ceramic nozzles or metal meshes. These burners are used for heating premises with a high air exchange rate (sports halls, retail premises, greenhouses, etc.), for drying painted surfaces (fabrics, paper, etc.), heating frozen soil and bulk materials, and in industrial furnaces. For uniform heating of large surfaces (furnaces of oil refineries and other industrial furnaces), so-called. panel injection radiant burners. In these burners, the gas-air mixture from the mixer enters a common box, and then the mixture is distributed through the tubes into separate tunnels, in which it is burned. Panel burners have small dimensions and a wide adjustment range, they are insensitive to back pressure in the combustion chamber.
The use of gas turbine burners, in which air is supplied by an axial fan driven by a gas turbine, is increasing. These burners were proposed at the beginning of the 20th century (Eikart turbo-burner). Under the action of the reactive force of the outflowing gas, the turbine, shaft and fan are driven in the direction opposite to the outflow of gas. The performance of the burner is controlled by the pressure of the incoming gas. Gas turbine burners can be used in boiler furnaces. High-pressure turbine gas burners with self-supply of air through recuperators and air economizers are promising: high-capacity gas-oil burners operating on heated and cold air.
Burners are subject to the following requirements:
1. The main types of burners must be mass-produced in factories according to specifications. If the burners are manufactured to an individual design, then they must be tested during commissioning to determine the main characteristics;
2. Burners must ensure the passage of a given amount of gas and the completeness of its combustion with a minimum air flow rate α, with the exception of burners for special purposes (for example, for furnaces in which a reducing environment is maintained);
3. When ensuring the specified technological regime, the burners must ensure the minimum amount of harmful emissions into the atmosphere;
4. The noise level generated by the burner should not exceed 85 dB when measured with a sound level meter at a distance of 1 m from the burner and at a height of 1.5 m from the floor;
5. Burners must operate stably without separation and flashover of the flame within the calculated range of thermal power regulation;
6. For burners with preliminary complete mixing of gas with air, the rate of outflow of the gas-air mixture must exceed the speed of flame propagation;
7. To reduce the consumption of electricity for own needs when using burners with forced air supply, the resistance of the air path should be minimal;
8. To reduce operating costs, the design of the burner and stabilizing devices should be fairly easy to maintain, convenient for revision and repair;
9. If it is necessary to save the reserve fuel, the burners must ensure a quick transfer of the unit from one fuel to another without violating the technological regime;
10. Combined oil-gas burners should provide approximately the same quality of combustion of both types of fuel - gas and liquid (fuel oil).
Diffusion burners
In diffusion burners, the air necessary for gas combustion comes from the surrounding space to the flame front due to diffusion.
These burners are commonly used in household appliances. They can also be used when increasing gas flow, if it is necessary to spread the flame over a large surface. In all cases, gas is supplied to the burner without admixture of primary air and mixed with it outside the burner. Therefore, these burners are sometimes referred to as external mixing burners.
The most simple diffusion burners (Fig. 7.1) are a pipe with drilled holes. The distance between the holes is chosen taking into account the speed of flame propagation from one hole to another. These burners have small thermal outputs and are used for burning natural and low-calorie gases under small water heaters.
Rice. 7.1. Diffusion burners

Fig.7.2. Bottom diffusion burner:
1 - air regulator; 2 - burner; 3 - viewing window; 4 - centering glass; 5 - horizontal tunnel; 6 - laying out of bricks; 7 - grate
Industrial burners of the diffusion type include hearth slot burners (Fig. 7.2). Usually they are a pipe with a diameter of up to 50 mm, in which holes with a diameter of up to 4 mm are drilled in two rows. The channel is a slot in the bottom of the boiler, hence the name of the burners - hearth slot.
From the burner 2, the gas enters the furnace, where air enters from under the grate 7. Gas jets are directed at an angle to the air flow and are evenly distributed over its cross section. The process of mixing gas with air is carried out in a special slot made of refractory bricks. Thanks to this device, the process of mixing gas with air is enhanced and stable ignition of the gas-air mixture is ensured.
The grate is laid with refractory bricks and several slots are left in which pipes with drilled holes for gas outlet are placed. Air under the grate is supplied by a fan or as a result of rarefaction in the furnace. The refractory walls of the slot are flame stabilizers, prevent flame separation and at the same time increase the process of heat transfer in the furnace.
injection burners.
Injection burners are called, in which the formation of a gas-air mixture occurs due to the energy of the gas jet. The main element of an injection burner is an injector that sucks air from the surrounding space into the burners.
Depending on the amount of injected air, the burners can be fully pre-mixed with air or with incomplete air injection.
Burners with partial air injection. Only part of the air necessary for combustion enters the combustion front, the rest of the air comes from the surrounding space. These burners operate on low gas pressure. They are called low pressure injection burners.
The main parts of injection burners (Fig. 7.3) are the primary air regulator, nozzle, mixer and manifold.
Primary air regulator 7 is a rotating disk or washer and regulates the amount of primary air entering the burner. Nozzle 1 serves to convert the potential energy of gas pressure into kinetic energy, i.e. to give the gas stream such a speed that provides the suction of the necessary air. The burner mixer consists of three parts: injector, confuser and diffuser. Injector 2 creates vacuum and air suction. The narrowest part of the mixer is confuser 3, which equalizes the jet of the gas-air mixture. In the diffuser 4, the final mixing of the gas-air mixture takes place and its pressure increases due to a decrease in speed.
From the diffuser, the gas-air mixture enters the collector 5, which distributes the gas-air mixture through the holes 6. The shape of the collector and the location of the holes depend on the type of burners and their purpose.
Low pressure injection burners have a range of positive qualities, thanks to which they are widely used in household gas appliances, as well as in gas appliances for enterprises Catering and other domestic gas consumers. Burners are also used in cast iron heating boilers.

Rice. 7.3. Injection atmospheric gas burners
a– low pressure; b- a burner for a cast-iron boiler; 1 - nozzle. 2 - injector, 3 - confuser, 4 - diffuser, 5 - collector. 6 - holes, 7 - primary air regulator
The main advantages of low-pressure injection burners are: simple design, stable operation of burners when loads change; reliability and ease of maintenance; noiselessness of work; the possibility of complete combustion of gas and work at low gas pressures; lack of pressurized air supply.
An important characteristic of incompletely mixed injection burners is injection ratio is the ratio of the volume of injected air to the volume of air required for complete combustion of the gas. So, if complete combustion of 1 m 3 of gas requires 10 m 3 of air, and the primary air is 4 m 3, then the injection ratio is 4:10 = 0.4.
The characteristic of the burners is also injection ratio is the ratio of primary air to gas consumption by the burner. In this case, when 4 m3 of air is injected per 1 m 3 of combusted gas, the injection ratio is 4.
The advantage of injection burners: the property of their self-regulation, i.e. maintaining a constant proportion between the amount of gas supplied to the burner and the amount of air injected at a constant gas pressure.
Mixing burners. Burners with forced air supply.
Forced air burners are widely used in various heating devices for utilities and industrial enterprises.
According to the principle of operation, these burners are divided into burners with preliminary mixing of gas (Fig. 7.4) and fuel and burners without preliminary preparation of the gas-air mixture. Both types of burners can operate on natural, coke, blast furnace, mixed and other low and medium pressure combustible gases. Working regulation range - 0.1 ÷ 5000 m 3 /h.
Air is supplied to the burners by centrifugal or axial fans of low and medium pressure. Fans can be installed on each burner or one fan per group of burners. In this case, as a rule, all the primary air is supplied by fans, while the secondary air practically does not affect the quality of combustion and is determined only by air infiltration into the combustion chamber through leaks in the furnace fittings and hatches.
The advantages of burners with forced air supply are: the possibility of using in combustion chambers with different back pressure, a significant range of regulation of thermal power and gas-to-air ratio, relatively small size of the flame, low noise during operation, simple design, the possibility of preheating gas or air and the use of burners large unit power.
Low pressure burners are used at a gas flow rate of 50 ÷ 100 m 3 / h, at a flow rate of 100 ÷ 5000 it is advisable to use medium pressure burners.
The air pressure, depending on the design of the burner and the required thermal power, is assumed to be 0.5 ÷ 5 kPa.
For better mixing of the fuel-air mixture, gas is supplied to most burners in small jets at different angles to the flow of primary blast air. In order to intensify mixture formation, the air flow is given a turbulent motion with the help of specially installed swirl blades, tangential guides, etc.
The most common burners with forced internal mixing air supply include burners with a gas flow rate of up to 5000 m3/h or more. They can provide a predetermined quality of preparation of the fuel-air mixture before it is fed into the combustion chamber.
Depending on the design of the burner, the processes of mixing fuel and air can be different: the first is the preparation of the fuel-air mixture directly in the mixing chamber of the burner, when the finished gas-air mixture enters the furnace, the second is when the mixing process begins in the burner and ends in the combustion chamber. In all cases, the speed of the outflow of the gas-air mixture is different 16...60 m/s. The intensification of the mixture formation of gas and air is achieved by jet gas supply, the use of adjustable blades, tangential air supply, etc. With jet gas supply, burners with a central gas supply (from the center of the burner to the periphery) and with a peripheral one are used.
The maximum air pressure at the burner inlet is 5 kPa. It can work with backpressure and underpressure in the combustion chamber. In these burners, in contrast to external mixing burners, the flame is less luminous and relatively small size. Ceramic tunnels are most often used as stabilizers. However, all of the methods discussed above can be used.
The GNP-type burner with forced air supply and central gas supply, designed by specialists from the Teploproekt Institute, is intended for use in furnace devices with significant thermal stresses. In these burners, the air flow is swirled with the help of blades. The burner kit includes two nozzles: a type A nozzle used for short-flare gas combustion with 4÷6 gas outlets directed perpendicular or at an angle of 45° to the air flow, and a type B nozzle used to obtain an elongated torch and having one central opening parallel to the air flow. In the latter case, the preliminary mixing of gas and air is much worse, which leads to an elongation of the torch.
Stabilization of the torch is ensured by the use of a refractory tunnel made of class A fireclay bricks. The burners can operate on cold and heated air. The coefficient of excess air is 1.05. Burners of this type are used in steam boilers, baking industry.
The two-wire gas-oil burner GMG is designed for burning natural gas or low-sulphur liquid fuels such as diesel, domestic, marine fuel oils F5, F12, etc. Joint combustion of gas and liquid fuel is allowed.
The gas nozzle of the burner has two rows of holes directed at an angle of 90° to each other. The holes on the side surface of the nozzle allow gas to be supplied to the swirling flow of secondary blast air, the holes on the end surface - to the swirling flow of primary air.
The process of formation of a gas-air mixture in burners with forced air supply begins directly in the burner itself, and ends already in the furnace. During combustion, the gas burns with a short and non-luminous flame. The air required for gas combustion is forced into the burner by means of a fan. Gas and air are supplied through separate pipes.
This type of burners is also called two-wire or mixing burners. The most commonly used burners are low-pressure gas and air. Also, some designs of burners are used at medium pressure.
Burners are installed in boiler furnaces, in heating and drying ovens, etc.
The principle of operation of the burner with forced air supply:
Gas enters nozzle 1 at a pressure of up to 1,200 Pa and leaves it through eight holes 4.5 mm in diameter. These holes must be located at an angle of 30° to the axis of the burner. Special blades, which set the rotational movement of the air flow, are located in the body 2 of the burner. During operation, the gas in the form of small streams enters the swirling air flow, which helps good mixing. The burner ends with a ceramic tunnel 4 with an ignition hole 5.

Rice. 7.4. Forced air burner:
1 - nozzle; 2 - body; 3 - front plate; 4 - ceramic tunnel.
Forced air burners have a number of advantages:
-high performance;
– a wide range of performance regulation;
– Possibility of working in heated air.
In the existing various designs of burners, the intensification of the process of formation of a gas-air mixture is achieved in the following ways:
– division of gas and air flows into small flows, in which mixture formation takes place;
– gas supply in the form of small jets at an angle to the air flow;
– by swirling the air flow with various devices built into the burners.
Combined burners.
Combined are burners that operate simultaneously or separately on gas and fuel oil or on gas and coal dust.
They are used in case of interruptions in the gas supply, when it is urgent to find another type of fuel, when the gas fuel does not provide the required temperature regime of the furnace; gas is supplied to the present only at a certain time (at night) to equalize the daily unevenness of gas consumption.
The most widely used oil-gas burners with forced air supply. The burner consists of gas, air and liquid parts. The gas part is a hollow ring with a gas supply fitting and eight gas spray tubes.
The liquid part of the burner consists of an oil head and an inner tube ending in nozzle 1 (Fig. 7.5).
The supply of fuel oil to the burner is regulated by a valve. The air part of the burner consists of a body, swirler 3, air damper 5, with which you can adjust the air supply. The swirler serves for better mixing of the fuel oil jet with air. Air pressure 2÷3 kPa, gas pressure up to 50 kPa, and fuel oil pressure up to 0.1 MPa.

Rice. 7.5. Combined oil-gas burner:
1 - fuel oil nozzle, 2 - air chamber, 3 - swirler, 4 - gas outlet pipes, 5 - air control damper.
The use of combined burners gives a higher effect than the simultaneous use of gas burners and oil burners or gas pulverized coal burners.
Combined burners are necessary for the reliable and uninterrupted operation of gas-using equipment and installations of large industrial enterprises, power plants and other consumers for which a break in operation is unacceptable.
Consider the principle of operation of the combined dust and gas burner designed by Mosenergo (Fig. 7.6)
When working on coal dust, a mixture of primary air with coal dust is supplied to the furnace through the annular channel 3 of the central pipe, and secondary air enters the furnace through the volute 1.
Fuel oil serves as a reserve fuel, in this case an oil burner is installed in the central pipe. When the burner is converted to gas fuel, the oil burner is replaced by an annular channel through which gas fuel is supplied.
A pipe with a cast-iron tip 2 is installed in the central part of the channel. The tip 2 has oblique slots through which gas escapes and intersects with the swirling air flow exiting the volute 1. In improved designs of burners, instead of slots, 115 holes with a diameter of 7 mm are provided in the tip. As a result, the gas outlet velocity almost doubles (150 m/s).

Rice. 7.6. Combined dust and gas burner with central gas supply.
1 - a snail for swirling the air flow, 2 - a tip of gas supply pipes,
3 - an annular channel for supplying a mixture of primary air with coal dust.
The new burner designs use a peripheral gas supply, in which gas jets, which have a higher speed than air jets, cross a swirling air stream moving at a speed of 30 m/s at a right angle. This interaction of gas and air flows ensures rapid and complete mixing, as a result of which the gas-air mixture burns with minimal losses.
7.3. Automation of gas combustion processes.
The properties of gas fuel and modern gas burner designs create favorable conditions for automation of gas combustion processes. Automatic control of the combustion process increases the reliability and safety of gas-using units and ensures their operation in accordance with the most optimal mode.
Today, partial or complex automation systems are used in gas-using installations.
Integrated gas automation consists of the following main systems:
– automatic control;
– security automation;
– emergency signaling;
– teletechnical control.
The regulation and control of the combustion process is determined by the operation of gas appliances and units in a given mode and ensuring the optimal mode of gas combustion. To do this, the regulation of the combustion process is intended for automatic control of household, municipal and industrial gas appliances and units. Thus, a constant temperature of the water in the tank is maintained for storage water heaters, a constant steam pressure for steam boilers.
The gas supply to the burners of gas-using installations is stopped by safety automatics in the event of:
- extinction of the torch in the furnace;
- lowering the air pressure in front of the burners;
- increase in steam pressure in the boiler;
– increase in water temperature in the boiler;
- lowering the vacuum in the furnace.
Disabling these settings is accompanied by corresponding sound and light signals. No less important is the control of the gas content of the room in which all gas appliances and units are located. For these purposes, electromagnetic valves are installed that stop the gas supply in cases where the MPC in the ambient air CH 4 and CO 2 is exceeded.
It is possible to achieve the optimal mode in the conditions of the technological process with the help of thermal control devices
The operating conditions of gas-using equipment determine the degree of its automation.
Remote control of gas-using installations is achieved by using control and signaling devices.
Burner calculations.
In gas-oil furnaces equipped with modern burners with automatic control of the combustion process, it has become possible to burn natural gases and fuel oil with small excesses of air with practically no or low chemical combustion incompleteness (less than 0.5%). Therefore, it is recommended to maintain the process of combustion of these fuels with an excess air ratio after the superheater not higher than 1.03 ÷ 1.05.
The principle of operation of a gas boiler is based on heating the circulating liquid passing through the heat exchanger. Heat is generated in the combustion chamber as a result of the operation of the gas burner of the heating device. It is from the quality setting, and then the operation of the burner, that the productive capacity of the boiler, its efficiency depends. Consider the main aspects of choosing and setting up a gas boiler burner in more detail.
How to choose?
What you need to pay attention to when choosing a burner device for the boiler:
- productive capacity
- noise level during operation (applies to supercharged models)
- type of heating equipment for which the burner is purchased
- type of fuel
- pros and cons of this device
- to foresee possible failures in the operation of the local gas supply line.
Considering these factors, it is possible to choose the most suitable burner for the boiler so that it works as efficiently as possible without burdening with frequent preventive maintenance.
Heating equipment combustion chamber
Gas boilers differ primarily in the design of the combustion chamber. It is of two types:
- open;
- closed.
open The chamber is a fairly simple combustion device. It looks like this: above the burner there is a heat exchanger in the form of a coil of thin copper tubes. Due to the open design, the air necessary for the combustion reaction is supplied to the place of ignition of the gas from the environment.
As a rule, there is enough air from the room (provided that good ventilation is organized). But there are wall-mounted models with air intake from the outside, for which a special hole is mounted in the wall. Open combustion chambers require a chimney.
It is most often installed for models of floor gas boilers, and was also used to complete an old-style boiler (in this case, the ignition was performed by an ignition burner).
Schemes of the device of the combustion chamber
Closed the combustion chamber differs in the design of the heating block. The heat exchanger is located above the burner. The body of the block is closed, the combustion air is blown by a fan installed in the chamber. A coolant is passed through the double walls of the chamber, heating it, increasing the efficiency of the boiler. The gas is burned almost completely, the combustion products are discharged by a coaxial pipe under air pressure.
Types of burners
According to their design, functional differences, burners are divided into:
By appointment:
- for high power industrial equipment
- for household equipment.
By type of fuel used:
- devices for natural gas;
- devices for liquefied gas;
- universal devices.
By adjusting the flame:
- single-stage - able to work on / off;
- two-stage (as a variety - models with smooth modulation) - operate at full power, when the desired temperature is reached, the flame is reduced by half;
- modulating - boilers with a modulating burner are distinguished by a smooth adjustment of the flame strength.
According to the principle of work:

Boiler gas burner device
Atmospheric and fan burners differ in their structure. This is due in a different way supply of oxygen to the chamber during fuel combustion.
Atmospheric burner device.
Air enters the combustion chamber directly from the room. Nozzles are located inside the burner channel. Gas is fed into the nozzles, mixing with air, which also has access here. At a short distance from the nozzles, there are outlet slots through which the finished fuel mixture is supplied. An area is created between nozzles and outlets reduced pressure, which contributes to the constant injection of air for mixing.
The ignition burner is constantly working in the combustion chamber to ignite the main device.
Fan burner device.
The device block consists of:
- engine;
- fan;
- automatic control unit;
- reducer;
- air pressure switch;
- fuel mass mixer.
Air is forced from the outside by a fan, fed into the combustion chamber to form a fuel substance. The ratio of air and gas can be adjusted with a damper and a fan.
burner flame
One of the indicators of the correct operation of the burner is the color of the flame. For gas equipment characterized by an even bluish flame without impurities of other colors. The presence of inclusions of yellow, red indicates that the burner is not working well, this reduces the efficiency of heating equipment.

First of all, this applies to injection burners, but sometimes it is also typical for fan burners. The flame simply lacks oxygen. Also, along with the air, dust and other small debris can get in, which will clog the device, reducing the efficiency of the boiler. All this directly affects the flame. If it hums, the burner is loud, the fire has changed color - you need to adjust correct work devices.
When is a burner flame adjustment required?
Atmospheric gas burner for heating equipment often fails. It is equipped with models of both wall-mounted and floor-standing boilers. The injection burner of outdoor equipment reduces its efficiency for various reasons:
- Burner power too high. It happens when a high-power burner is purchased for small heating equipment. At the same time, there is not enough space for combustion, the air flow for such a power is weak, which leads to the transition of the flame from blue to yellow, sooting of the combustion chamber, chimney.
- If the chimney is poorly cleaned, the draft of the boiler deteriorates. At the same time, the spent combustion products are poorly removed, the air flow is small. This worsens combustion, the flame turns yellow.
- The defect of the burner itself does not make it possible to correctly adjust complete combustion fuel.
- Due to pressure fluctuations in the gas supply system, well-regulated equipment can emit large amounts of unused gas into the chimney. Partially, it settles with soot, soot. A large layer of soot reduces traction, increases fuel consumption.
- Starting heating equipment after repair.
- The presence of extraneous noise during the operation of the boiler, gas burner.
- Change of type of fuel.
Hardware setup
floor standing gas boilers with atmospheric burner can be adjusted by yourself. Pressurized systems are regulated by an automatic control unit and do not require additional settings.
Scheme of actions when setting up single-stage equipment:
- Install the device on the boiler.
- Connect to the gas pipe.
- Check for absolute tightness.
- Remove the burner housing.
- Using a manometer, measure the gas pressure at the inlet.
- Connect to electricity. Make sure that the jumpers, phases are connected correctly.
- Install a gas analyzer in the chimney.
- Start device.
- Use a manometer to read the pressure at the outlet of the burner block. The pressure readings must correspond to the parameters indicated in the data sheet.
- Adjust the air flow with an air damper.
- The readings of the gas analyzer must also comply with all standards for the installation of gas equipment.
Setting up gas equipment should be carried out by specialists. Most simple boilers open type can be configured independently if you have certain skills, knowledge of the burner block device. The efficiency of the boiler, its level of efficiency, fuel consumption depend on the quality of the burner. It is superficially possible to determine that the equipment is malfunctioning by the changed burner flame.
Gas burner GGU-40 (power 36 kW) with automatic control and safety Honeywell VK4105G
Automation provides automatic ignition of the burner, maintaining the set temperature in the room up to +120 C
Gas consumption: — 4 m3/h (mains gas), — 3.3 kg/h (SUG).
General instructions
This Operation Manual (OM) describes the model of the Spektr gas burner GGU-40.
The OM contains information about the design, product parameters, device and operation, as well as the rules for safe operation, Maintenance and storage of the product, possible malfunctions.
Please read this Operation Manual carefully before starting work. The manufacturer does not accept claims in case of violation of the rules for preparing for operation, operation and maintenance of the product.
In connection with permanent job to improve the product, increasing its reliability and improving quality, changes may be made to the design that are not reflected in this manual.
In the normal position, the main gas valve (1) is closed by the force of the spring (2) and can only be opened when the gas pressure is sufficient to counteract the force of the spring. This very important built-in reliable mechanism ensures that the valve closes automatically in the event of a gas or power failure.
The main part of the system is a servomotor, consisting of a pressure relief valve (5) built into the regulator diaphragm, which is installed on top and regulates the operation of the main valve.
When the safety valve coil and auxiliary valve coil are energized, the gas flow passes through the orifice and open valve (5) into the servo system and regulator
This gas presses on the diaphragm (6) of the main valve, causing it to rise up and open the main valve. As soon as the main valve opens, the outlet pressure created by the regulator is taken up by the diaphragm through the channel feedback.
As soon as the pressure force exceeds the pre-set value, the regulator valve will open, resulting in a decrease in operating pressure. This will also reduce the force acting on the main valve spring, which will lead to proportional closing of the main valve. Thus, the valve allows the outlet pressure (burner pressure) to be maintained at a preset level.
Thus, the outlet pressure is constantly maintained at a certain level by comparing its value with a pre-set value and the corresponding valve adjustment. This means that a constant outlet pressure is maintained regardless of fluctuations in the inlet pressure.
When the valve is turned off, a small amount of working gas contained in the regulator and the diaphragm chamber above the main valve is vented to the main outlet compartment.
The reference pressure feedback system allows for further stabilization of the outlet pressure, providing compensation for the difference in air pressure in the valve and chamber.
If no pressure adjustment is needed, the regulator spring can be blocked by turning the adjusting screw all the way in or until the pressure regulator is turned off. In this case, the full pressure of the working gas opens the main valve as far as the pressure difference allows.
Intended use
2.1. Operating restrictions
2.1.1. The gas burner device can be installed in low-power hot water heating boilers and in household stoves.
2.1.2. The room in which the gas burner is operated must comply with the requirements of the "Safety Rules for Gas Distribution and Gas Consumption Systems".
2.1.3. Work on the installation of a gas burner must be carried out by employees of the gas facilities service in accordance with the requirements of the "Safety Rules for Gas Distribution and Gas Consumption Systems".
2.1.4. After the installation of the gas burner, the automatic control and safety must be checked for operation in all respects and adjusted.
2.2 Installing the gas burner
Installation of the gas burner device must be carried out in the following sequence:
2.2.1. Fix the HGU to the furnace wall with bolts, Figure-5, having previously applied a heat-resistant sealing element to the inner surface between the HGU and the furnace wall.
2.2.2. Install the draft sensor pos.3
2.2.3. Connect the draft sensor to the valve controller
2.2.4 Install the bulb at a height of 1.5 - 2 m and fasten it to the wall. If the GGU is installed in a sauna stove, the thermal bulb must be installed in the steam room as far as possible from the stove.
ATTENTION: In the bath, install the control unit in the dressing room.
It is forbidden to install the control unit in a sink or steam room.
2.3 Using the product
ATTENTION: DURING THE IGNITION AND OPERATION OF THE GAS BURNER,
THE ASH PAN MUST BE OPEN.
BEFORE STARTING THE BURNER INTO OPERATION, IT IS NECESSARY:
. check the presence of draft in the chimney and the absence of the smell of gas in the room;
. ventilate the room in which it is installed gas apparatus, and its firebox for 5-10 minutes, while the gas valves in front of the burner must be closed;
To turn on the GGU, you must:
. open the ash pan;
. set the thermostat knob to position "0";
. turn on the power (220V);
. open the gas valve on the gas pipeline;
. Slowly turn the thermostat knob clockwise and set the required temperature, the burner lights up at full power.
. visually verify that the GGU is running.
. to turn off, set the thermostat knob to position "0";
. close the gas valve on the pipeline
. after turning off the burner, to prevent the stove from cooling down due to draft, it is recommended to close the ash pan
2.4 Setting the maximum gas value Valve adjustment. Fig.6 Pa - gas pressure at the inlet to the valve, Pb - gas pressure at the outlet, Pmax - screw for adjusting the maximum gas value
Setting max. pressure (P.max):
. Connect the positive pressure point of the pressure gauge to the pressure point of the gas valve (Pb).
. Remove the cap from the gas valve and use a screwdriver to set the desired pressure value (Pmax).
. Check that the dynamic pressure at the measured port (Pa) is correct and screw the plug back into place.
2.5 Possible malfunctions
Fault Probable cause Remedy
GGU does not start No contact in the electrical circuit
draft sensor Clean the contact connection with fine emery cloth.
The draft sensor is out of order Replace the draft sensor
There is no contact in the electrical circuit of the thermostat Check the contacts, remove the cover of the electrical contact block, apply voltage to the coil directly, bypassing the thermostat.
ATTENTION!!!
THERMOREGULATOR COIL POWER SUPPLY 220V
Emergency lock
controller Rebooting the controller by shutting down
and power on the valve
Safety Requirements
3.1. Persons who are familiar with the device and operating rules of the gas burner and have been instructed in safe methods of working with gas are allowed to service.
3.2. To avoid accidents and failure of the gas burner, IT IS FORBIDDEN:
. turn on the burner for children and persons who have not been instructed in operation;
. operate a gas burner with faulty control and safety automatics;
. use fire to detect gas leaks (use a soapy emulsion for this purpose);
. turn on the burner in the absence of draft in the chimney;
. when turning on the burner, bring the face closer to the inspection hole by less than 0.5 m;
. the owner to repair the burner, as well as to make any changes to the design.
3.3. When the burner is not working, the GAS VALVES MUST BE CLOSED.
3.4. If you smell gas in the room, immediately turn off the gas to the burner, open windows and doors, call the emergency gas service by phone 04, remove people from the room. Prior to her arrival and until the gas leak is eliminated, do not perform work related to fire and sparking (do not turn on electric lighting, do not use gas and electrical appliances, do not light a fire, etc.).
3.5. In the event of a fire, immediately notify the fire department at tel: 01.
Maintenance
4.1. It is the responsibility of the owner to oversee the operation of the burner and to keep it clean and in good condition.
4.2. Preventive maintenance and repairs are carried out by gas workers in accordance with the "Instructions for the maintenance of in-house gas equipment".
Transport and storage
5.1. The gas burner must be stored in a horizontal position in one tier in a closed room, which guarantees protection from atmospheric precipitation and other harmful effects, in the manufacturer's container.
5.2. The gas burner device is transported by any means of transport, provided that it is protected from mechanical damage and direct moisture ingress.