How to determine by the leaf what is missing from a lemon or tangerine? Distinctive features of lemon leaves. Useful properties and methods of application How to distinguish a tangerine tree from an orange
Usually citrus seeds, along with the peel, we throw in the trash. Most of us are sure that only "savages" will grow out of them, which, with any care, will not bloom and never bear fruit, but in best case- in 20-25 years. Is it really?
Science and life // Illustrations
A lemon tree can be decorated with white fragrant flowers and fruits at the same time - both ripe golden and green. If the ripened fruit is not cut from the branch, then its color will turn green again. Such a lemon will turn yellow in 8-10 months.
Any dishes for seedlings are suitable, including a ceramic cup, as long as there is drainage and a hole in the bottom for water to drain.
For the appearance of side shoots, sometimes it is enough to bend the stem of the plant in the form of a wheel or bend the top.
Moroccan mandarin grown from seed. The plant is 1.5 years old. The seedling was selected on the basis of the proximity of the buds, later such a plant will bush even without shaping.
To speed up the fruiting of a growing plant, the branches are given a horizontal position. Make sure that the crown does not thicken too much; for this, do not allow branches to grow inside it.
Most buds and fragrant flowers appear on citrus fruits in March - May. In the photo: orange blossom. To ensure the ripening of one fruit, the plant must have 15-20 elastic, dense, dark green leaves.
With additional lighting in the autumn-winter months, the fruits of oranges ripen sweet.
Different types citrus fruits are easily distinguishable by a number of features, including the shape of leaf petioles, which are equipped with "lionfish" developed to varying degrees.
After 8-9 months, rather large fruits grow on a tangerine tree from small ovaries.
Under natural conditions - in the countries of Southeast Asia and in the subtropics of Italy, Spain - any citrus trees grown from seeds begin to bear fruit already in the 5-7th year. Therefore, in some states of India, many of them are usually propagated by seeds, and by grafting - only when it is important to fully preserve all the varietal characteristics of the plant.
However, the natural conditions of the fertile subtropics and those on our windowsill are not at all the same. In the first case, they are ideal for the development of citrus fruits, and in the second, they are incomparably tougher.
HOW TO ACCELERATE FRUITTING
All citrus trees grown from seeds are original in their own way, especially during flowering, when they are completely covered with white fragrant flowers, although each species is specific and has its own characteristics: oranges have the most beautiful crown with dark leaves, tangerines have bright appetizing fruits , grapefruits have very large fruits, however, the tree itself is often bulky and is more suitable for winter gardens and offices. The most practical for growing are lemons, which all year round delight with fruits, usually noticeably larger, brighter and more fragrant than purchased ones.
Citrus seedlings are able to give the first fruits already in the 4-5th year using certain techniques. But it all starts with the selection of seeds and their sowing.
The largest seeds are selected from any fruit and immediately sown in small pots or cups, always with a drainage hole in the bottom. It is more expedient to pre-treat the seeds with one of the preparations from the group of biological natural stimulants. For example, at night I dip the seeds in a solution of Sakhalin sodium humate (not darker than beer) - later this has a positive effect on the development of the root system, and then for another 8-12 hours - in water, to which I add zircon and epin-extra, one drop of the drug in a glass of water, this accelerates the development of seedlings, and most importantly, it helps them to endure insufficient lighting and dry air in the room.
It is advisable to sow a dozen or two plants at once, which will be required in the future to select the best, potentially early-growing ones. The seeds are placed in loose fertile soil to a depth of 1-2 cm, and when the seedlings grow up, at the age of 3-5 months, they are carefully transplanted, rather they are transferred, completely preserving the earthen clod, into a larger container and a handful of biohumus (compost, processed earthworms), which contributes to the accelerated development of plants.
Growing seedlings are selected according to the following outward signs:
Initially stocky crown (this is evidenced by the minimum distance between the buds on the stems); such plants, even without shaping, tend to bush in the future;
The minimum number of short needles (or complete absence such) and thin shoots;
The maximum number of leaves that rarely fall.
Inevitably, quickly exposed plants with few leaves and thin stretching shoots are rejected.
It is very important to prevent the single-stem development of the seedling in the form of a rod. Already in the first months of life, it is necessary to cause its lateral branching. To do this, pinch the tender top of the growing shoot each time with a fingernail or tweezers during the next “wave” of growth (citruses do not grow constantly, but in periods, “waves” - no more than 4-5 times a year, with interruptions one to three months). If after that only the top without side shoots grows, then it is removed again.
In the future, the grown side shoots with two or three leaves are pinched (do this as early as possible), then the branches will grow as short as possible. And subsequently they follow the same principle, trying to give the tree bushiness and proportionality of the crown. From time to time, the plant pots turn slightly - but not abruptly - no more than a quarter of a turn.
It is equally important to ensure that separate vertically growing branches (“tops”) do not appear inside the emerging crown. When branches appear, until flexibility is lost, they are tilted and tied with a ribbon or twine to a stem or a pencil stuck into the soil.
As the trees grow, they also make sure that the crown does not thicken too much, for this they strive to prevent the growth of branches inside it.
And one more important technique that brings fruiting closer is ringing. It is carried out as follows. The stem or one or two skeletal branches at the very base are tightly pulled (“ringed”) with copper wire so that it is slightly pressed into the bark. At this place, an influx is formed very quickly and deformation occurs, causing the accumulation of such substances inside the plant organism that stimulate the formation of fruit buds. After six months or a year, in order to avoid excessive constriction of the branches and the threat of breakage, the ring is carefully removed, and the operation site is covered with garden pitch or bandaged with a strip of elastic polyethylene.
CITRUS HABITS
The flowering and fruiting of citrus plants will be even closer by the regular inclusion of an artificial “sun” above them in the form of special phytolamps or fluorescent lamps (daylight), humidification of room air with the help of electric humidifiers or fountains and regular - once or twice a year, in February and June , - transplanting plants into containers, which each time are 3 - 5 cm larger than before. A soil mixture is suitable, sifted through a fine-mesh sieve and consisting of equal parts of completely rotted foliage (in ready-made it is easy to collect it in a park or in a forest under old maples and lindens), soddy land (it is enough to shake out the sod layers cut in a meadow with a good herbage) and compost with manure humus. In extreme cases, you can use ordinary loose soil from the garden, adding 1/3-1/4 of the volume of horse manure to it.
But even with such regular transplants, nutrients in fresh soil are only enough for three to five months, while citrus trees need good nutrition from late February to September. In this case, complex fertilizers help out, including all the necessary substances with trace elements. And it is better not in the form of dry mixtures, but in a liquid form. Fertilize with a solution highly diluted with water (no more than 1-2 g of the drug per 1 liter), otherwise it is easy to “burn” the roots of citrus fruits.
It is good to alternate fertilizing with “mineral water” with watering ready-made, commercially available infusions and organic concentrates.
INSTEAD OF CONCLUSION
Most often, all efforts are rewarded, and after a few years, citrus trees grown from seeds bloom and give the first fruits. Moreover, plants grown from seeds turn out to be much more hardy and more adapted to room conditions than citrus fruits of any variety that can be purchased at the store: they do not require ideal lighting or optimal air humidity. In other words, with more or less good care feel in the room no worse than unpretentious geranium or ficus. And all because initially these fruit trees appeared in the house, which became their own.
Having grown fruit-bearing trees from seedlings, in the future it is possible to propagate the best, promising plants in another simple way - by rooting short cuttings cut from them in a mini-greenhouse - a pot with wet sand under glass jar. Seedlings grown from cuttings bear fruit already in the third year without losing their main advantage - unpretentiousness.
Literature
Dadykin VV Citrus garden at your window. - M.: AST-Press Book, 2006.
Dadykin V. V. // Science and Life, 2006, No. 12.
Dadykin V. V. // Science and Life, 2004, No. 12.
Flower grower - note
If a tap water contains a lot of lime, rotted needles collected from under old fir trees will help save the earth in a pot from alkalization. Add it when planting in the soil mixture (ratio 1:6), but even better cover the top layer of earth in a pot with such needles.
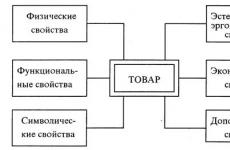
The lack of macro- and microelements is easy to determine by the appearance of citrus plants. With a nitrogen deficiency, growth decreases, the leaves turn yellow, especially the lower ones and at the base of the shoots. With a deficiency of phosphorus, the plant blooms weakly and many flowers fall off. With a deficiency of potassium, the edge of the leaf turns brown, becomes wrinkled and twists down. With iron deficiency, the leaves turn yellow and turn pale. With a deficiency of boron, the apical points of growth die off and the ovaries are deformed. With a deficiency of copper, sticky dark brown spots appear on the fruits.
To reduce water loss, cover the ground in a pot with a circle of thick polyethylene or plastic, after making a slot for the stem. But you can put a layer of sphagnum moss on top - it acts both as a sponge filled with water, and as an additional acidifier, and as a source of nitrogen.
Flowers and young, tender shoots of citrus fruits are a good addition to ordinary tea brewing, they give the drink a peculiar aroma and enrich it with vitamins.
Nothing slows down the development of any citrus fruits like an attack by hordes of pests - spider mites, false shields, aphids. Therefore, regularly, twice a month, wash the leaves under a strong stream of shower, and in the summer take the plant outside for treatment with proven means - a solution of FAS tablets (2 tablets per bucket of water), actars (5 g of the drug per bucket of water) or fitoverma (1 teaspoon spoon per 1 liter of water). Much more efficient, easier and safer for own health do not spray the plants from a spray bottle, but immerse their crown for one or two minutes in a bucket with a solution of the listed insecticides.
All small-fruited citrus fruits are high ornamental plants and are the best suited for landscaping winter gardens, living quarters and growing in bonsai culture. By the way, Buddhists in East Asia use this plant as a traditional decoration for the New Year (a symbol of happiness and prosperity).
Citron, zest, zest (Citrus medica) is the most thermophilic species of the genus citrus. As a rule, it is a small tree or shrub with very large oblong or turban-shaped yellow fruits (up to 20-40 cm long and 15-25 cm in diameter), with a rough, bumpy surface, yellow, fragrant. The peel is very thick (up to 5 cm), the slices are small, with sour or sweetish juice. One of its varieties finger citron (C. medica var. sacrodactylis) - called the "hand of the Buddha." There is practically no pulp in its fruits. Grown as an ornamental plant.
Pomeranian (Citrus aurantium) - a tree up to 10 m high, the fruit is almost round, with a thick orange peel with a rough surface, the flesh is very sour. A void forms inside a mature fruit, as a result of which it does not sink in water. Orange is often used as a rootstock for oranges and other citrus fruits.
In culture, a mutant form is known, called myrtle orange (C. aurantium var. myrtifolia). It perfectly adapts to room conditions, is used in bonsai culture because of its compact crown, small internodes (0.5-1 cm) and small dark green leaves (0.8 x 2 cm). The fruits are spherical, orange, 3-4 cm in diameter.
Orange (Citrus sinensis) is a tree up to 20 m high. In the 15th-16th centuries, it was a popular ornamental plant in European courts. It was for its cultivation in Europe that they began to build special glass rooms - greenhouses (from the French orangerie - an orange plantation). It was grown in winter gardens and as a kadochny culture.
real lime (Citrus aurantifolia) is a tree or shrub up to 4 m high. The peel of fruits in a ripe state is thin, green or green-yellow. The flesh is yellow-green, very sour, with a lemon aroma. The fruits ripen six months after flowering. Sensitive to cold. Feels good in room culture.
Mandarin (Citrus reticulata) is an evergreen tree up to 8 m high with a spreading crown. The fruits ripen 10 months after flowering. Can be grown in subtropical conservatories in the ground or as a container culture at home.
Pomelo, pompelmus, sheddock (Citrus grandis) - one of the largest citrus plants, fruits can be the size of a small watermelon, up to 30 cm in diameter and weighing more than 1 kg. It is very difficult to grow at home, as the plant takes up a lot of space and needs high humidity.
Grapefruit (Citrus paradisi) is an evergreen tree 12-15 m high. Rarely grown in room culture, for the same reasons.
But small-fruited citrus fruits are very popular in home floriculture. The most famous of them - kumquat oval (Fortunell amargarita) and its related species - kumquat japanese (Fortunella japonica) and Hong Kong (Fortunella hinsii). The diameter of their fruits, as a rule, does not exceed 3 cm.
Which citrus fruit do you prefer? First, it depends on the conditions you can create for them. It is clear that for big plants- oranges, grapefruits, pomelo and others - we need greenhouses with a subtropical climate. But even in them, these trees can be grown only for decorative purposes; it will still not be possible to get sweet ripe fruits. Another thing is lemons, limes and other small-fruited citrus fruits. They are quite suitable for room content. Just do not buy plants brought from the Black Sea coast of the Caucasus, as they are intended for cultivation in open field. Indoors, these plants winter time drop leaves, buds, ovaries and gradually die.
Top 10 Related Sites: Types and Forms of Citrus Fruits
Types and forms of citrus fruits at Supersadovnik.ru
Citron, zest, zedron ( Citrus medica) - the most thermophilic view from the genus citrus. As a rule, this is a small tree or shrub with very ...
citrus tree: definition kind on form sheet.
Grows from the bone citrus a tree (I don’t know which one exactly), already over a meter (didn’t cut it off - I’ll try in the spring). I'm waiting for flowers! How long can they not...
Classification citrus fruits- Fruits in our diet
Among citrus fruits fruit crops are found seedless (sterile) forms. Separate kinds exist only in culture, but in the wild ...
Kinds citrus, varieties citrus fruits| Catalog of natural …
Best types of citrus for beginners
Best types of citrus for beginners. Citrus... There is a variegated the form plants that do well indoors.
Citrus— Kindergarten.Ru
under the common name citrus fruits botanists and fruit growers unite several dozen species plants, some of which form cultivars...
Types and forms of citrus fruits» Women's online portal
15 Mar 2012 … All small-fruited citrus- highly ornamental plants and are the best suited for landscaping winter gardens, residential ...
Types of citrus fruits which you did not know about (13 photos) - Fishki.net
23 Apr 2012 … Very serious work done) 60 citrus species, ... or orange fruits similar in form for smaller lemons.
citrus - Citrus description species at FloralWorld.ru
16 Mar 2008 … widespread in all subtropical countries as the main rootstock for all citrus fruits. There are many forms plants, …
Citrus citrus| Lemon at home
May 4, 2014 … This also includes various kinds dwarf oranges, or ... citrus fruits amazing variety of plants forms and …
Proper care.
Save so you don't lose!
What are citrus plants afraid of, care mistakes, biological features citrus plants.
First of all, it is necessary to take into account the biological characteristics of citrus plants. In winter, they need relative rest. From October to February, the temperature in the room should be no more than 12 ° C
However, this time coincides with heating season, and high temperature leads to untimely growth and depletion of plants, which will further affect fruiting.
 The critical period is also early spring, when warm days are suddenly replaced by a sharp cold snap. At the same time, the growth that has begun slows down sharply, the leaves are deformed, and the buds and ovaries crumble. To avoid this, it is recommended to maintain the temperature in the room at 14-16°C.
The critical period is also early spring, when warm days are suddenly replaced by a sharp cold snap. At the same time, the growth that has begun slows down sharply, the leaves are deformed, and the buds and ovaries crumble. To avoid this, it is recommended to maintain the temperature in the room at 14-16°C.
 Sometimes in the summer, gardeners take plants to the balcony or even transport them to the country house, but it’s better not to do this, as citruses react painfully to any changes and very slowly adapt to new conditions. Overdrying and excessive moistening of an earthy coma is also a very common mistake. In the first case, the active roots die off, the leaves curl and fall off along with the flowers and fruits. With excessive watering, the roots rot, the leaves turn yellow.
Sometimes in the summer, gardeners take plants to the balcony or even transport them to the country house, but it’s better not to do this, as citruses react painfully to any changes and very slowly adapt to new conditions. Overdrying and excessive moistening of an earthy coma is also a very common mistake. In the first case, the active roots die off, the leaves curl and fall off along with the flowers and fruits. With excessive watering, the roots rot, the leaves turn yellow.
 It is best to pour water into the pan - then the substrate is evenly saturated with moisture and is not washed out nutrients. The most moisture-loving among citrus fruits is lemon, the most drought-resistant is orange. Often the plants are watered very warm water(40 ° C), which causes the death of the roots. You can't go to extremes either. When watering cold water the roots rot, and the plants also die. The water temperature should be 2-3°C, and during fruiting 5-10°C above room temperature.
It is best to pour water into the pan - then the substrate is evenly saturated with moisture and is not washed out nutrients. The most moisture-loving among citrus fruits is lemon, the most drought-resistant is orange. Often the plants are watered very warm water(40 ° C), which causes the death of the roots. You can't go to extremes either. When watering cold water the roots rot, and the plants also die. The water temperature should be 2-3°C, and during fruiting 5-10°C above room temperature.
 Remember that the roots of citrus fruits are located in the upper layer of the soil, so you need to loosen it carefully, and water it often, but in small doses.
Remember that the roots of citrus fruits are located in the upper layer of the soil, so you need to loosen it carefully, and water it often, but in small doses.
For successful cultivation, the light regime is also very important. Strong shading leads to the formation of large dark green leaves and the exhaustion of plants. Direct sunlight causes a pale color of leaves, burns of fruits and ovaries and their abscission. The most shade-tolerant lemon, the orange is photophilous and heat-resistant.
Citrus fruits love diffused sunlight, it is best to place them on a window facing the southeast or southwest. And remember: the higher the temperature in the room, the more intense the lighting should be. Dry room air causes great suffering to citruses - the tips of the leaves dry up, the buds, ovaries and fruits fall off. To avoid this, regularly wash and spray the plants. In the event that the pot is near the battery, then a container of water is placed on it, which, as it evaporates, will saturate the air with moisture.
Home citrus plants, soil composition, nutrition, top dressing, fertilizers.
Citrus fruits, especially lemons, are very demanding in terms of nutrition. It is no coincidence that in the plant kingdom they are called gluttons. Plants are fed all year round, except for the period from October to February, when they are given only a weak solution of potassium permanganate to disinfect the soil. The rest of the time, feeding is carried out, alternating organic fertilizers with mineral fertilizers, once every 7-10 days. This increases the sugar content of the fruit and reduces their bitterness. Recommended fertilizer mixtures: foskamide, Darina, ideal, agrovit - cor.
Citruses are highly adaptable to soil conditions. They just cannot stand very acidic soils and the presence of peat. Usually they make up a mixture of soddy and leafy soil, humus, sand (2: 1: 1: 1. Citrus fruits should not be placed in the same room with strongly smelling plants, as they do not like other people's smells. They do not like smokers either: in a sign of protest may even drop the leaves.
Responsibility is the transplant. The most common mistakes are: transplanting plants with flowers and fruits, which causes them to shed, as well as the destruction of an earthy coma, severe pruning of the roots. Both deep and shallow planting can be the reason for the lack of fruit. The root neck should be slightly above the soil level.
Home citrus plants, winter diseases, how to form a crown.
Citrus fruits cause the most problems to their owners in winter, when they shed their leaves. There can be many reasons for this phenomenon: light starvation, a combination of insufficient illumination with high temperature and low air humidity; the difference in the temperature of the aerial part and the root system of the plant, when the pot is blown with cold air from the window, and the crown is in favorable room conditions; lack or excess of nutrition. And other problems.
Some novice citrus growers have no idea about the correct formation of the crown. And this is the main reason for the lack of fruiting and the loss of decorativeness.
Without human intervention, the plant will not be able to form a crown in a short time. Thanks to pruning, shoots of the 4th and 5th branching orders develop faster, on which fruits are formed.
In mandarin, the crown is prone to thickening, so frequent thinning is necessary. The orange tree is rapidly reaching up, therefore, it is necessary to limit its growth. The lemon has very little branching, so the plant undergoes heavy pruning to get it to flower and bear fruit.
One adult plant in our apartment is capable of producing up to 30 fruits annually.
Domestic citrus plants, artificial pollination of flowers, fruiting, rejuvenation.
Artificial pollination of flowers. When pollinating flowers, pollen is applied with a soft brush to increase fruit set.
In the rooms you observe a large shedding of ovaries. To avoid this during fruit formation, water the plants more often and spray them with warm water. Do not forget about the rationing of fruits. The first flowers are removed on young plants necessarily. A three-year-old plant leaves only 2-3 fruits. In subsequent years, they proceed from this ratio: one fruit should be fed from 10-15 leaves, and, of course, the well-being of the plant itself is taken into account so that the first harvest does not turn out to be the last for it.
Only if the fruiting of a young and healthy tree is weak, then it can be strengthened. For example, pull the main branches with a tourniquet (this technique will cause the accumulation of plastic substances and the laying of flower buds); regularly feed the plant with superphosphate. You can grow a seedling and graft it into the crown of a fruit-bearing tree, or graft an eyeball from the top of the plant to its bottom.
If a citrus plant lives with you for a very long time and produces few fruits, it can be rejuvenated. For this everything large branches cut into 3-4 eyes, and their branching is cut into a ring. The rejuvenated plant is transplanted into nutrient soil, shortening the roots by one third. Here, perhaps, is all the wisdom of caring for citrus fruits.
If you sow citrus plants and do not sign each pot, as well as sow different seeds in one container, it will be difficult for an inexperienced eye to distinguish a lemon from a tangerine, an orange. Also similar to all citrus fruits, but not quite, kumquat and grapefruit.

There are several ways. Firstly, they offer to sniff and determine by smell, tearing off a piece of a leaf. A tangerine tree will smell like a tangerine, and a lemon sprout will smell like a lemon. If we continue to remain in the dark due to our inexperience, then there is a way to distinguish leaves by petioles. And they are actually different, because. there are no so-called "lionfish" on the petioles of a lemon, but orange, tangerine, grapefruit have them.

In the photo: a lemon leaf without lionfish on the petiole.
Petiole lionfish are the largest in grapefruit, slightly smaller in orange, and even smaller in tangerine.

Photo: Mandarin leaf with "lionfish" on the petiole.
This is how you can distinguish four types of citrus by leaf petioles. But nevertheless, in the future, the pot is recommended to sign, sticking a label, because these are the botanical rules. A peculiar leaf of a kumquat, more oblong and of many parallel veins, often located. Also, the kumquat often seems to be stunted, because it is sometimes considered a shrub, so its tree is smaller than others in height.
To be continued.
How to tell a lemon from an orange by the leaves. citrus leaves
Citrus plants are difficult to confuse with other plants due to features unique to this species, namely the spines in the axils of the leaves. Citron and orange have large thorns, lemons can be with or without thorns, but tangerines do not have thorns.
Petioles of leaves of citrus plants are equipped with extensions, "wings", by which experienced citrus growers determine the type of plant and its age. Also, the shape and size of the "wings" distinguish seedlings of citrus plants from each other:
- The lemon has no "wings";
- In mandarin - "wings" are barely noticeable;
- An orange has “wings” of medium size;
- In grapefruit - "wings" can be the size of a small leaf.
The color of the leaves of citrus plants depends on age: light green - young leaves; dark green - leaves older than 2 years.
The average lifespan of citrus leaves is 2.5-3 years. Depending on age, the role of the leaf in the life of the plant changes: young leaves are responsible for respiration, and old ones accumulate the nutrients needed for the growth of new branches, flowers and fruits. The loss of leaves is deadly for a lemon, as the nutrient supply is lost with the leaves.

Despite similar appearance and the popular belief that a lime is simply an unripe lemon, these fruits are very different from each other. Let's see what is more useful and what are the differences between these citrus fruits.
History of appearance and where they grow
Although many people think that a lime is an unripe lemon, they are completely different fruits. Both fruits are citrus fruits, but their homeland is different: the lemon appeared in China (it is believed that already in the 3rd century the Chinese grew lemon on their own, that is, it was not a wild plant), and lime - on the Malay Peninsula, not far from Indochina. It is also widely distributed in Mexico and other South American countries, Egypt and India. The lime is credited with more years, so it is more likely that the lemon came from the lime than vice versa.
Both the first fruit and the second love the tropical climate, but if the lemon is most often found in subtropical zones, then the lime lives in the tropics. That is, the probability of their being in the same area is as small as possible. Lime can be grown as cultivated plant and in the subtropics, but it will not bear fruit well in such conditions. In general, under appropriate conditions, it is able to bear fruit all year round, while lemon - once a year.
Lemons are less capricious, so they home growing is still popular today. Limes, on the other hand, grow at an altitude of more than a thousand kilometers above sea level, so it is not possible to grow them at home.
 Useful properties and its closest genetic relative lime have a lot of overlap. Many people confuse these two citrus fruits, some believe that lime is an unripe lemon. Although this is far from true. The debate continues about which fruit is healthier. Both citrus fruits contain ascorbic acid, belong to the same botanical genus and are used in cooking, this is where their similarities end. Let's see, looking at the photos, what are their main differences.
Useful properties and its closest genetic relative lime have a lot of overlap. Many people confuse these two citrus fruits, some believe that lime is an unripe lemon. Although this is far from true. The debate continues about which fruit is healthier. Both citrus fruits contain ascorbic acid, belong to the same botanical genus and are used in cooking, this is where their similarities end. Let's see, looking at the photos, what are their main differences.
What is the difference between lemon and lime
In addition to size and color, fruits have other distinctive features:
- The lemon is kept in cold store two months without loss of quality, and lime only two weeks.
- Lemon is sour, while lime is even more sour and has a bitter taste.
- The lemon is larger than the lime, although some varieties of the latter are not inferior in size to the lemon.

Lime and lemon are two different fruits
- The pulp of the lime has green color, and the flesh of a lemon is greenish or yellow.
- The fruiting of the lime is year-round, and the lemon will give birth once a year.
- Vodka is eaten with lemon, and tequila is not complete without lime.
- The homeland of lime is the tropics, and the lemon is an inhabitant of the subtropical belt.
- Lime has a more pronounced aroma.
Advice. When choosing citruses, pay attention to the weight, the heavier the fruit, the more juice it contains. Lime peel must be green, greenish color lemon indicates that the fruit is not ripe and will be very sour. The skin of the fruit should be elastic.
What unites them
The peel and seeds of citrus contain substances that prevent the development cancer cells and lower cholesterol. Both citrus fruits contain a high dose of vitamin C, so eating these fruits helps boost immunity.
Both citrus fruits carry a large number of vitamins
Vitamin P increases the elasticity of blood vessels. Also in the composition there are fruit acids, pectins, micro and macro elements, vitamins of group B. Essential oils give them flavor and have phytoncidal properties. However, it is impossible to say that they have the same effect on the body.
Healing properties of lemon
The pulp of the fruit contains citric acid, carotene, sugar, pectins and vitamins. In the 16th century, lemons began to be taken on long sea voyages as a remedy for scurvy. Later research proved that almost half of the daily dose of vitamin C is available in one lemon. Minerals are richly represented in lemon, not every juice has such an assortment of substances.
Lemons are used to prevent beriberi or vice versa hypervitaminosis. In the treatment of the gastrointestinal tract, scurvy, atherosclerosis, tonsillitis and gout. Indication for the use of lemon is a violation of mineral metabolism, arterial hypertension, urolithiasis. Lemon stimulates digestion and stimulates appetite. Substances contained in lemon help the body absorb Ca and Fe. Lemon has been reported to lower blood cholesterol levels. A glass of water with lemon juice, drunk in the morning on an empty stomach, helps to remove toxins from the body, and also helps to fight excess weight.

Lemon is widely used in cooking and cosmetics.
For cosmetic purposes, lemon is used as part of face masks, to remove freckles and age spots, to heal small cracks in the skin. Make hair balms, lotions and creams.
Useful properties of lime
Lime is used in a similar way to lemon. It is also a storehouse of vitamin C, but lime contains five times more of this vitamin than lemon. Limes contain folic acid, while lemons do not. Folic acid is involved in the development of the circulatory and immune systems, the use of lime is especially important during pregnancy, when the fetus is forming. Lime also helps with toxicosis.
Favorably affects excitability nervous system, has a calming effect, relieves fatigue and irritability. Fresh lime juice with a glass warm water on an empty stomach, helps burn excess fat.
Contraindications
Lemon and lime have restrictions in consumption:
- gastritis;
- pancreatitis;

It is worth being attentive to contraindications when eating citrus fruits.
- gastrointestinal ulcers;
- acute nephritis, colitis, enteritis;
- individual intolerance.
Advice. A cut lemon loses its properties very quickly. beneficial features as well as during heat treatment. It is recommended to use fresh citruses.
Application in cooking
Lemon juice is poured over fish (especially fatty species), seasoned with salads, served with barbecue. Lime and lemon are used in cocktails. Mojito with lime is very popular. Both the zest and the pulp are put into the baking. Candied fruits are made from the zest, added to teas in dried form.

Lemon and lime are used both for cooking main dishes and in desserts and drinks.
Lime works great with red pepper. In Asian cuisine, it is used everywhere. Lemon is seasoned with food before serving to preserve the citrus flavor, and lime is added at any stage.
To get the most juice out of a citrus, roll the fruit on the table, pressing hard on it. It will become softer and give off juice easily. Freeze the juice in the refrigerator, add it to water or mineral water and delight your body with a tasty and healthy drink.




Video So orange or lemon. How we are "bred".

Chinese lemongrass grows on loamy-sandy soil, which is well water-permeable and rich in minerals. Lemongrass does not tolerate waterlogged soil, grows slowly on heavy and clay soils. Liana of lemongrass up to 15 mm thick, if there is no suitable support, it will rise only 25 cm in height. Such plants grow slowly and lie. However, if the vine reaches the support, then the shoot develops quickly and grows according to the screw principle - clockwise. The wood of lemongrass is very strong, but flexible.
How lemongrass reproduces
In nature, plant reproduction occurs from basal shoots. But in the garden it can also be propagated by seeds (stratified) or cuttings, but only green ones, since lignified ones do not take root. Seed germination is low, but it can be increased by constantly changing the temperature regime.
How to germinate lemongrass seeds
500 g of seeds are taken, which are mixed with river sand (1: 5), and moistened so that when compressed and unclenched in a fist, the lump of sand slowly crumbles. The prepared mixture is placed in some old enamel saucepan with small holes. About 2.5 cm of fine river gravel is poured onto its bottom. The saucepan is covered with a covered nylon mesh wooden mug with holes. She is kept covered: the first 30 days near heating battery, the next 30 days at 2-5 ° in the cellar, then another 30 days at 13-15 °. Then, for only 48 hours, they visit it in the cold (you can bury it in the snow), and for the last 10 days the seeds are again kept at 8-10 °. By this time, the temperature of the soil outside should reach 8 °. The sand in the saucepan must be periodically loosened and moistened. After such stratification, seed germination will be approximately 85%. However, one should not forget that with too much moisture and a compacted mass, the seeds suffocate and therefore may lose their germination altogether.
Features of growing lemongrass from seeds.
How to distinguish citric acid from ascorbic acid. Where is citric acid used
A person uses citric acid in various areas of his life.
However, if we consider the need for human body- then
it is citric acid that is involved in the metabolic processes of our body, therefore, it is used as a means to improve energy metabolism (the so-called Krebs cycle) ...
But back to our acid. However, like sodium citrate itself, it is actively used by humans as a flavoring agent and preservative for the production of various drinks, including dry and fizzy drinks, confectionery, store-bought fruit juices, mayonnaise, canned fish and meat, processed cheeses, canned fruits and vegetables. .
Citric acid is also actively used in the oil and fat industry - it protects fats, vegetable oils, margarine, and animal fats from the likelihood of rancidity and bitterness. It is also very often added to the composition of various cosmetics- lotions, shampoos, balms, hair fixatives ... In all these products, it acts as a kind of acidity regulator ...
Well, as we can see, citric acid is a substance that is actively used in all spheres of human life.
And in fact, until you put 5-6 different varieties of lemon on one plate and do a real tasting, it’s quite difficult to imagine that they are divided into varieties.
Moreover, lemons are divided not only into botanical varieties, like apples or pears, but also into commercial varieties (depending on the condition of the fruits taken from one tree), such as tea leaves.
The first variety of lemons - primafiore (fruits from the first flowers) are small, dark green, very sour, but incredibly fragrant fruitlets, which are removed from the tree as soon as they reach the size of a small chicken egg. Primafiore lemons are rarely exported, they are mainly destined for the domestic market.
The second variety of lemons is called bianchetti, that is, white. These are lemons picked at the moment when they are no longer green, but not yet yellow. Bianchetti is the most sought-after lemon variety in Europe, we know them as "thin-skinned". Almost all fruits of lemons of different varieties in the bianchetti stage have an "average" lemon taste and aroma.
And finally, the third stage of lemon ripeness - bastardo - huge thick-skinned lemons, the peel of which splashes with oil, and the flesh has deep flavors, depending on the botanical variety. Those varieties of lemons that are served to the table in their natural form (and some are simply eaten as a fruit, such as a Cappuccino lemon) must fully ripen on the tree - only then will their varietal characteristics and advantages be fully manifested.

But The best way provide the family with delicious lemons - start a lemon tree at home.

One of the most common and commonly consumed fruits is the lemon. Recently, gardeners have been interested in the possibility of growing a lemon tree at home. It turned out that not only in the southern latitudes with a favorable hot climate, but also throughout the country, such a citrus tree can be grown. The main thing is to graft the lemon correctly.
What is it for?
Gardeners have learned to grow lemons in their gardens. In order for a seedling to grow from an ordinary lemon seed, it is enough to plant it in the ground, water it and wait for the seedlings. After a certain period of time, they will appear, however, there is no guarantee that the shoots will be able to grow into a tree that will bear fruit. You can achieve the desired result only if you properly graft a lemon onto a branch of another tree.
The very process of grafting to a tree is a combination of two branches or the transfer of a lemon bud to the main trunk of a dominant plant. With such an implantation of a part of one plant in the branches of another, their fusion occurs. All processes for the exchange of mineral substances, oxygen are carried out simultaneously both in the scion and in the rootstock. The grafted branch becomes part of the tree and receives all the necessary components from the donor root system for life and further development in a new place. The grafted lemon branch bears fruit at the same time as the plant chosen as the basis for the graft.
There are several ways to carry out this procedure.
Timing
Lemon should be grafted in the spring, and can be until the end of summer. Any plants in the period from April to August release a large amount of juice, which contributes to the establishment of a new cutting on the main branch of the stock. Depending on the method chosen for grafting a lemon, the timing of the fusion of shoots (grafts) with the main trunk also changes. It usually takes a month for a grafted plant to gain a foothold and become part of it.
Rules
You can plant a lemon at home if you choose the right stock. A rootstock is a plant that has many general characteristics with lemon. This is a tree on which a lemon cutting is grafted. It is desirable that it also be citrus plant or a tree belonging to the same family (root).
For rootstock use the lemon itself, bigaradiya (sour orange), sweet orange, tangerine, grapefruit. These plants have a strong root system. This feature allows the scions to supply the grafted plants with nutrients. In grafts of this group, calluses (a kind of corns) quickly grow at the sites of tree injuries where the grafting was carried out. Calluses protect the painful places of the injured tree and promote their rapid healing.
It is best to choose dwarf trees for rootstock. Trees grow very actively, which causes certain difficulties in care. Dwarf stock can be made independently.
Cut off the bark at a short distance from the roots of the tree in a circle. The removed bark is fixed in place of the cut with the reverse side. After it is tied to a tree. This procedure significantly slows down the movement of sap along the branches and, accordingly, the growth of the tree cannot be intensive. To maintain the slow growth of the tree, this action should be repeated once every few years. The main rule for the success of the whole event is the presence of a fruitful scion.
If you graft a lemon onto a tree that is fruitless or bears little fruit, the grafted cutting is very likely to fail.
In order for the incision to heal quickly and efficiently, it is wrapped with a film of polyethylene or other material.
Or a different kind of citrus?
This plant has many different varieties and varieties that can be distinguished by some external features: the height, shape and size of the fruit, the shape of the leaves, and some others.
An easy way to determine whether a lemon belongs to a particular variety is to look at the lemons.
The surest way to determine whether a lemon belongs to the Pavlovsky variety is to have a ripened fruit on your hands.
The fruits of Pavlovsky lemon are distinguished by their large size., the weight of large can reach 300-500 grams. Usually, their weight ranges from 120 to 150 grams. The shape of a lemon can be very different, the shape variety of fruits in Pavlovsky lemon is quite widely represented. They can be round, oval, round oval or elongated. The surface of the fruit is usually smooth and shiny, sometimes it can be slightly tuberculate.
Such lemons are highly valued for their delicate citrus aroma and excellent taste. Their skin is not thick, usually 4-5 mm, but sometimes even thinner. Therefore, fruits from the Pavlovsky lemon are often eaten directly with the skin.
Productivity of Pavlovsky lemon not the highest - 10-15 fruits per year. At optimal conditions content can bear fruit all year round.

Green fruit lemons varieties Pavlovsky
But what if there are no fruits on your lemon? Then it is necessary to determine the varietal belonging of the plant according to other characteristics. You need to look at the appearance of the plant. One way to determine if you have Pavlovsky or not - look at its crown and leaves.

You can judge the lemon variety by the leaf, but its shape may differ when the plant is grown in different conditions.
Bitter orange (bigaradia, orange)
Fresh fruits have a too bitter taste, which is why they cannot be consumed fresh, but are highly valued for making marmalade, seasonings, liqueurs. Leaves, flowers and fruits are the best source of bigaradium oil used in perfumery.
The orange originated from Southeast Asia. Unknown in the wild. It was brought to the Mediterranean by the Arabs in the 11th century, five centuries before the appearance of the sweet orange. Widely grown in tropical and subtropical countries, it is the main rootstock for citrus fruits. Orange trees are tall, leaf petioles are broad-winged, flowers are large, fragrant. The fruits are almost round, the peel is thick with a rough surface, fragrant, orange-red. The pulp is very sour and bitter, the seeds are numerous, polyembryonic. This orange has hybrids: citradium (bigaradia and trifoliata) - a powerful, cold-resistant stock.
Orange varieties include:
- Pomeranian - medicinal plant. The photo shows a mitroleaf orange (C. myrtifolia), a small bush with thick leaves growing on top of each other. Small flowers, white, odorless and self-pollinating. They produce yellow-red fruits. This species, due to its natural proportions, is excellent for bonsai.

- Bergamot is a small tree that has fruits with sour pulp.
kumquat care
Kinkan (kumquat, fortunella)
The genus consists of 4 species, of which only one - Hong Kong Fortunella - is found in the wild. These miniature citrus fruits are also called Japanese oranges. Kinkan blooms unlike other citrus fruits in autumn, the fruits ripen in February - March. It is a small shrub, reaching 50 - 60 cm in height in apartments. The flowers are small, white, collected in brushes, with a pleasant, delicate aroma. The fruits are bright orange, small - from 2 to 5 cm. They are delicious fresh, but especially jams and jams made from them.
Care is similar to other citrus fruits.
The plant is light and moisture-loving. He needs a sunny location, in summer it is advisable to take the plant out to open air. In winter, they are kept in a cool, bright room at a temperature of 4-6C. If it is impossible to reduce the temperature, then additional lighting is necessary for the normal development of the plant. Watering is plentiful in summer, moderate in winter, avoiding waterlogging or drying of the substrate, and only with warm water. As with other citrus fruits, watering with cold water causes leaf drop. It is necessary to regularly spray the plant, especially in dry air in the heat and with steam heating, often wipe the leaves.
For fruiting, regular top dressing, a temperature of about 20 ° C and the correct formation of the crown are necessary. All side shoots are pruned in spring, leaving no more than 3-4 young shoots on each side branch. Propagated by cuttings at a temperature of 25-28C, grafting and seeds. At vegetative reproduction already in the 2nd year, plants can be harvested
In room culture, most often grownkinkan japanese
(Fortunella Japonica, Marumi kumquat). It is a low-growing tree up to 1.5 m tall, often having a bushy shape. Shoots flattened, trihedral, with short spines. The leaves are dark green, shiny, up to 8 cm long, with essential oil glands.
The flowers are axillary, white, with a strong pleasant aroma.

It can bloom even at a tender age.
The fruits are round, the smallest among citrus fruits (up to 2.5 cm in diameter), brightly orange color with a thin peel, usually with 4-7 slices. The pulp is sour, the peel is sweet. This species is winter-hardy, therefore it grows well in open ground on the Black Sea coast of the Caucasus and in the Crimea.
At kinakana oval
(Fortunella Mrgarita, Nagami kumquat) shoots without thorns, smaller leaves, oval fruits, golden or orange.
The peel of the fruit is smooth, fragrant, sweetish-spicy. The pulp is juicy, with a sour taste. The fruits are edible, they are eaten fresh with the peel, and are also used to make candied fruits, jams, jellies, are used to decorate desserts, to improve the taste of fish and poultry dishes.
At kinkana fukushi
(Fortunella Obovata) fruits are larger (up to 5 cm in diameter) than other kinkans, oval or pear-shaped, orange in color. The peel of the fruit is smooth, fragrant, very sweet. The pulp is juicy, sweet and sour dessert taste. There are no seeds in the fruit.

Obovata blooms several times a year. At the same time, flowers, ovaries and ripe fruits can be seen on the branches.


Kinkan is often attracted to hybridization, its natural and artificial intergeneric and interspecific hybrids with lemon, mandarin and other citruses are known:
calamondin
(hybrid mandarin with kumquat)

variegated calamondin

limequat(lime and kumquat) 

orangequat
(orange and kumquat)

The appearance and taste of the fruits of hybrids differs from the original ones.
Hybrid care
In addition, there are hybrids:
- tangor (orange and tangerine), such as Satsuma tangerine, King orange,
- citrange (orange and trifoliata),
- citranjquat (orange and trifoliata) + kumquat,
- citrangell (orange and trifoliata) + desert lime,
- lemonade (lemon and orange),
- limolaime (lemon and lime),
- Limandarins (lemon and mandarin) these include Red and White lemons from China,
- citrandarine (tangerine and trifoliata),
- citradium (bigardia and trifoliata),
- tangelo (tangerine and grapefruit)

- maniola (tangerine and grapefruit) planted from a seed this year, while it is like this
You have heard many names, you have tasted many of them, and I am sure that many hybrids grow from seeds, they may already bear fruit.
lime care
Lime
Real lime, or Mexican lime - C. aurantifolia lime.
The lime is native to the Malay Peninsula. Lime occupies one of the last places in terms of resistance to low temperatures, damaged at minus 1-2 degrees C, well adapted to the conditions of a humid tropical climate, in which lemon does not bear fruit well, therefore, in the tropics, lime is the main "sour citrus".
Millions of lime trees are cultivated in India, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Myanmar, Brazil, Venezuela, West African countries. A small evergreen tree or shrub in nature with a height of 1.5 to 4.5 meters.
The crown is dense, the branches are covered with short spines up to 2 cm long with smooth oval leaves 6 cm long and 4 cm wide with small petioles and rounded lionfish. Inflorescences axillary with 1-7 flowers small white flowers up to 2 cm in diameter. Remontant flowering.

seed at the best varieties few from 0 to 4.
The fruit resembles a small lemon in shape and size, outwardly differing from it only in its dark green skin.
at full maturity very thin, the flesh is greenish, yellowish-green, juicy, very sour. Lime juice is used to make citric acid. The oil is used as a flavoring agent in the production of soft drinks. Concerning healing properties lime, among citrus fruits it truly is a “champion”. Lime is richer than others in vitamin C (6-8%) and contains B vitamins, potassium and zinc.
Propagated by layering. Many people think that lime cuttings will not root well, but this fact needs to be checked - I put several cuttings on rooting, if they take root, I will definitely let you know.
I report: lime cuttings take root almost 100%.

There are several types of lime, such as the Italian lime (C. limetta) or C. hystrix.
Mandarin care
Mandarin
Unlike lemon, it is the most frost-resistant of all types of citrus fruits: the critical temperature is 8-10 degrees. below zero (skeletal branches freeze), then, with its further decrease, the whole plant dies.
Mandarin is a small branched evergreen tree with leathery lanceolate leaves on petioles with small wings. The life span of each leaf is up to 4 years. The flowers are small, white, fragrant, collected in small inflorescences-brushes. The fruits are medium-sized, oval-flattened, sweet-sour with a bright orange peel. Unlike other citrus fruits, the peel is easily separated from the pulp.
A light-loving plant, but it needs to be shaded from the hot midday sun. The plant has three periods of growth during the year: in April-May, August-September and November-December. Mandarin blossoms in May, and the fruits ripen in late October. The plant bears fruit with good care annually, starting to bear fruit at 3-4 years of age.
Like all subtropical crops, mandarin needs a cool content in winter (8-12C), especially with a lack of light, since under short daylight conditions the plant forms thin, weak shoots that need to be removed.
Water the plant regularly throughout the year, but moderately when the topsoil dries slightly. Overwatering leads to the death of the plant, and the lack of moisture - to twisting and falling of the leaves. Mandarin does not like drafts, therefore, when taken out into the air in summer, it must be placed in a place protected from the wind. In addition, the plant needs a constant supply of fresh air, which must be taken into account when kept indoors, and spraying with water at room temperature.
Be sure to regularly feed the plant every 10-15 days from the beginning of February to November. With additional lighting, top dressing is not stopped even in winter, but with half-concentration fertilizer. Mandarin is propagated by air layering, grafting, sometimes cuttings and seeds. Cuttings are taken from shoots with a diameter of 4 mm, which have already completed growth. Thicker cuttings are very difficult to root, thinner ones give weak growth or die. The cuttings take root within a month, it is rather difficult, therefore they are preliminarily kept in a heteroauxin solution. The necessary conditions rooting - the substrate temperature is not lower than 21-22C, air temperature - 20C, humidity - 90%. It is best to graft mandarin in April-May on seedlings of orange, lemon or orange, which have reached a thickness of 8-10 mm.
The best varieties for an indoor garden:
Unshiu broadleaf
A tree up to 2 m tall without thorns, with a spreading crown and corrugated leaves.
High-yielding, fast-growing and shade-tolerant mandarin variety, which belongs to the Japanese group of varieties - Satsuma. It begins to bear fruit for 3-4 years, in June there is a massive discharge of the ovary. The fruits are round or pear-shaped, almost devoid of seeds of medium size (68 - 70 g) are distinguished by juiciness, high sugar content (7.6%), moderate acidity (1.07%), significant presence of vitamin C (30 mg), juice yield - 71.5%...
Kovano-Vase
A variety of dwarf tangerines (mountain tangerine) in nature up to 1.5 meters high, in an apartment up to 1 m. The leaves are small, lighter and thinner than those of the Unshiu tangerine. Flowers small, mostly solitary. The main flowering takes place in the spring, but throughout the year a small number of flowers can be seen on the tree. Begins to bear fruit in the 2nd year. From a tree up to 100 fruits, good taste, the size of the fruits of the Gamlin orange variety. The plant is photophilous. This group includes the following varieties of mandarins:
To be continued.. Article written Alex