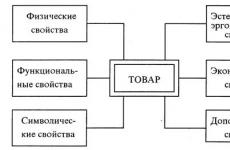
"Modern forms of organizing a lesson are the improvement of the methodology for constructing lessons, the desire to create optimal conditions for teaching, educating and developing students.". General forms of organization of educational activities of students Forms p
In science, the concept forms considered from both purely linguistic and philosophical positions. In the explanatory dictionary of S. I. Ozhegov, the concept of "form" is interpreted as a type, device, type, structure, construction of something, due to a certain content. In other words, the form- this is an external appearance, an external outline, a certain established order. The form of any object, process, phenomenon is determined by its content and, in turn, has the opposite effect on it. In the "Philosophical Encyclopedia" the concept of form is defined as the internal organization of content; the form "embraces the system of stable connections of the subject" and, thus, expresses the internal connection and the method of organization, interaction of the elements and processes of the phenomenon both among themselves and with external conditions. The form has a relative independence, which increases the more, the more history this form has.
With regard to learning, the form is a special design of the learning process, the nature of which is determined by the content of the learning process, methods, techniques, means, activities of students. This design is internal organization of content, which in real pedagogical activity the process of interaction, communication between a teacher and students when working on a certain educational material. This content is the basis for the development of the learning process, the way of its existence; it has its own movement and contains the possibilities of infinite improvement, which determines its leading role in increasing the effectiveness of training. In this way, form of education should be understood as a construction of segments, cycles of the learning process, realized in a combination of the teacher's control activity and controlled learning activities students to assimilate a certain content of educational material and master the methods of activity. Representing the external view, the external outline of segments - learning cycles, the form reflects the system of their stable connections and connections of components within each learning cycle and as a didactic category designates the external side of the organization of the educational process, which is related to the number of trainees, the time and place of training, as well as the order of its implementation.
Some researchers believe that in pedagogy there is a need to point out the difference between two terms that include the word "form": "form of learning" and "form of organization of learning." In the first case, this is the collective, frontal and individual work of students in a lesson or any training session; in the second case - some kind of lesson (lesson, lecture, seminars, practical and laboratory classes, debate, conference, test, subject circle, etc.). In philosophy under organization is understood as "ordering, establishing, bringing into the system some material or spiritual object, location, ratio of parts of an object." Moreover, it is precisely these “two meanings of the concept of organization that relate both to objects of nature and social activity and characterize the organization as the location and interconnection of elements of a whole (subjective part of the organization), their actions and interactions (functional part)” .
Based on this interpretation of the term "organization", it is rightly stated that form of learning organization involves "ordering, establishing, bringing into a system" the interaction of a teacher with students when working on a certain content of the material (I. M. Peredov). The organization of training aims to ensure the optimal functioning of the process of managing educational activities on the part of the teacher. Built on the optimal combination of process components as an integral dynamic system, it contributes to its effectiveness. The organization of training involves the design of specific forms that would provide conditions for effective learning. academic work students under the guidance of a teacher.
Here is one example of such an organization. The lesson begins with students reading a paragraph, a chapter of a textbook from the point of view of a task, while they write out questions that arise during reading, fix incomprehensible things. The teacher, in turn, collects these questions, classifies, notes their quality and depth, content, establishes their connection with the previous topic, other academic subjects, current problems of production, economics, culture, and life. After each student has become familiar with the new material at his own pace, students' questions are clarified and sorted out. The most prepared students answer them. The teacher, as necessary, clarifies, supplements the answers of the students, answers the most difficult questions, using the teaching methods and techniques known to him. Then practical exercises begin: exercises, problem solving, laboratory works. Here the teacher evaluates not only knowledge, but also the ability to apply it. At the same time, he can attract stronger students to help weak students, creating creative groups, expanding much-needed business communication. Based on the results of practical work, grades are given. Those who did not cope with the task work through the material of the topic being studied in reserve time (out of class, out of class) together with the teacher and strong students.
In this nature of the training session, the forms of organizing the educational activities of students, the forms of organizing training are very clearly visible. The given example of the organization of educational work means that the same form of education (for example, a lesson, a lecture) can have various modification and structure depending on the tasks and methods of educational work organized by the teacher.
The history of world pedagogical thought and teaching practice knows a wide variety of forms of organization of learning. Their emergence, development, improvement, gradual withering away of some of them are connected with the requirements and needs of a developing society, because each new historical stage in the development of society leaves its mark on the organization of education. As a result, pedagogical science has accumulated significant empirical material in this area. The question arose about the need to systematize the diversity of forms of organization of education, to isolate the most effective, corresponding to the spirit of the times, the historical era. In this regard, scientists identified such grounds for classifying the forms of organization of education as the number and composition of students, place of study, duration of study work. On these grounds, the forms of education are divided accordingly:
- - for individual
- - individual-group;
- - collective;
- - cool;
- - auditorium; extracurricular;
- - extracurricular.
Note that this classification is not strictly scientific and is by no means recognized by all scientists and teachers, however, this approach to the classification of forms of organization of education allows us to slightly streamline their diversity.
An epochal phenomenon not only in the history of the development of pedagogical thought, but also in the history of the development of society as a whole was the justification by Ya. A. Comenius lesson system of education, the main unit of training sessions in which the lesson was made. The advantages of such a system include:
- a) a clear organizational structure that ensures the orderliness of the entire educational process; ease of management;
- b) the possibility of children interacting with each other in the process of collective discussion of problems, collective search for solutions to problems;
- c) the constant emotional impact of the teacher's personality on students, their upbringing in the learning process;
- d) the cost-effectiveness of teaching, since the teacher works simultaneously with a fairly large group of students;
- e) creating conditions for introducing a competitive spirit into the educational activities of schoolchildren and at the same time ensuring systematic and consistent progress in their movement from ignorance to knowledge.
Noting these advantages, it is impossible not to see a number of significant shortcomings in the classroom system. Thus, the class-lesson system is focused mainly on the average student: it creates unbearable difficulties for the weak and delays the development of the abilities of stronger students; create difficulties for teachers in taking into account the individual characteristics of students in organizational and individual work with them, both in terms of content, and in terms of the pace and methods of teaching; does not provide organized communication between older and younger students, etc.
Along with the lesson, the system of general forms of organization of educational activities of students includes a whole range of forms of organization of the educational process, such as lectures, seminars, practical and laboratory classes, disputes, conferences, tests, exams, optional classes, consultations; forms of extracurricular, extracurricular work (subject circles, studios, scientific societies, olympiads, competitions), etc.
Lecture- this is an organic unity of the teaching method and organizational form, which consists in a systematic, consistent, monologue presentation by the teacher (teacher, lecturer) of educational material, which, as a rule, is of a pronounced theoretical nature.
Seminar- one of the main forms of organizing practical classes, the specificity of which is the collective discussion by students (students) of messages, reports, abstracts made by them independently under the guidance of a teacher. The purpose of the seminar is an in-depth study of a topic or section of a course.
Laboratory and practical classes- one of the forms of interaction between the teacher and students. It consists in conducting experiments by students on the instructions of the teacher with the use of instruments, the use of tools and other technical devices. In the process of laboratory and practical exercises, observations, analysis and comparison of observational data, formulation of conclusions take place. Mental operations are combined with physical actions, moral acts, since students, with the help of technical means influence the studied substances and materials, cause phenomena and processes of interest to them, which significantly increases the productivity of cognitive interest.
Optional- one of the types of differentiation of teaching by interests; an optional academic subject studied by students of higher and secondary educational institutions at their request to expand their general cultural and theoretical horizons or obtain an additional specialty.
Dispute- Collective discussion of topical problems that lie in the sphere of life of the participants and their social experience. The dispute enables its participants to apply their knowledge and experience in understanding and resolving the problem under discussion.
Note that within the framework of these forms of education, collective, group, individual, frontal work of students of both a differentiated and undifferentiated nature can be organized. When the same task is given to the whole class, the whole study group ( paperwork, laboratory or even practical task in the workshops), then this is an example undifferentiated individual work of a frontal nature. When a class, a study group as a whole, or each subgroup individually, collectively solves one problem, jointly masters a common topic, then there is collective, frontal or group work.
The most important feature of the above forms of organization of educational activities is the fact that in any of them the student learns to work: listen, discuss issues in team work; concentrate and organize their work, express their opinions, listen to others, refute their arguments or agree with them, argue their evidence and supplement others, make notes, compose reports, compile bibliography, work with sources of knowledge, organize their own workplace, plan your actions, keep within the allotted time, etc.
Cm.: Makhmutov M.I. Modern lesson. M., 1985. S. 49.
STATE BUDGET EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION
SECONDARY EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL №1 NAMED AFTER G.M.SHUBNIKOV
Report
"Features of the lesson in elementary school from the standpoint of the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard of the IEO"
Prepared
primary school teacher
Machina V.V.
Baikonur
The new social demands reflected in the Federal State Educational Standard define the goals of education as the general cultural, personal and cognitive development of students, which provides such a key competence of education as “to teach to learn”. The most important task of the education system is the formation of a set of universal educational activities that provide the competence to "teach to learn", and not just the development by students of specific subject knowledge and skills within individual disciplines.
In a broad sense, "universal learning activities" - self-development and self-improvement through the conscious and active appropriation of new social experience. In a narrower (actually psychological meaning) "universal learning activities" is a set of student actions that ensure his cultural identity, social competence, tolerance, the ability to independently acquire knowledge and skills, including the organization of this process.
The theoretical and methodological basis for designing the formation of UUD as a whole is system-activity and cultural-historical approaches (L.S. Vygotsky, A.N. Leontiev, D.B. Elkonin, P.Ya. Galperin, V.V. Davydov), integrating achievements of pedagogical science and practice (competence-based and Zunov paradigms of education). The method of teaching, in which the child does not receive ready-made knowledge, but obtains it himself in the process of his own educational and cognitive activity, is called the activity method. According to A.Disterweg, the activity method of teaching is universal. “Accordingly, he should act not only in primary schools, but in all schools, even higher educational institutions. This method is appropriate wherever knowledge is yet to be acquired, that is, for every student.”
How to build a lesson to implement the requirements of the Second Generation Standards? To build lessons within the framework of the GEF IEO, it is important to understand what the criteria for the effectiveness of a lesson should be.
Lesson objectives are set with trends in the transfer of function from teacher to student.
The teacher systematically teaches children to carry out a reflexive action (to assess their readiness, to detect ignorance, to find the causes of difficulties, etc.).
A variety of forms, methods and techniques of teaching are used, which increase the degree of student activity in the educational process.
The teacher owns the technology of dialogue, teaches students to put and address questions.
The teacher effectively (appropriate to the purpose of the lesson) combines reproductive and problem-based forms of education, teaches children to work according to the rule and creatively.
At the lesson, tasks and clear criteria for self-control and self-assessment are set (there is a special formation of control and evaluation activities among students).
The teacher achieves understanding of the educational material by all students, using special techniques for this.
The teacher seeks to evaluate the real progress of each student, encourages and supports minimal progress.
The teacher specifically plans the communicative tasks of the lesson.
The teacher accepts and encourages, expressed by the student, his own position, a different opinion, teaches the correct forms of their expression.
The style, the tone of relations, set in the lesson, creates an atmosphere of cooperation, co-creation, psychological comfort.
At the lesson, a deep personal influence "teacher - student" is carried out (through relationships, joint activities, etc.).
Consider the types of training sessions:
Classic traditional lesson (combined or mono-purpose).
Integrated
School lectures and seminars
Project lessons
Creative workshops
Autonomous teaching
The objectives of the classic lesson are:
Diagnostic (whether the goal is achieved or not) and operationality (indications of its achievement)
General goals: teaching, developing and educating are detailed by micro goals, i.e. tasks
Goal setting: children should say in their own words so that at the end of the lesson they summarize
Commensurate (70% - according to the abstract, 30-35% - the teacher can change)
The ability to change, modernize - this is the professionalism of a teacher, this is acceptable.
The objectives of the lesson are divided into:
A goal focused on the development of the personality of the child
Subject goals
Let us dwell on the goals focused on the development of the personality of the child:
Development of a personal-semantic attitude to the subject (actualize the personal meaning ..., help to realize the social, practical and personal significance of the educational material)
Development of value relations to the surrounding reality (to promote awareness of the values of the subject being studied, to help realize the value of joint activities)
Goals related to the development of intellectual culture (to create substantive and organizational conditions for the development of the ability to analyze, compare, highlight the main thing, classify a cognitive object)
Development of a research culture (to promote the development of the ability to use scientific methods of cognition (observation, hypothesis, experiment); create conditions for the development of skills to formulate problems, propose ways to solve them
Development of a culture of self-management by educational activities (to ensure the development of the ability to set a goal and plan one’s activities, to promote the development of skills to exercise self-control, self-assessment and self-correction of educational activities)
Development of information culture (create conditions for the development of the ability to structure information, develop the ability to make simple and complex plans)
The development of a communicative culture (to promote the development of communication skills in children, to ensure the development of dialogic and monologue speech)
Development of a reflective culture (to promote awareness of the reflexive algorithm "I-we-cause"
How did I feel in class?
How were we able to solve the case?
What was good, what was bad?
Have we achieved results?
Reflection is the ability to step back and take any of the positions in communication.
Now let's focus on the subject goals:
Organize the activities of students in the study and consolidation of facts, concepts, laws, regulations
To organize the activities of students in the independent application of knowledge in a variety of situations
Provide testing and assessment of knowledge and practices
Organize activities to correct knowledge and methods of action
I propose a reference table for designing a training session
| Educational objectives of KM | Possible Methods and methods of implementation |
| Organizational stage |
|
| Greeting, check of readiness, organization of attention | Report of the attendant, fixation of those absent, poetic mood, etc. |
| Checking homework |
|
| Establish the correctness, completeness and awareness of homework, identify and eliminate the problems found during the check | Tests, additional questions, continue the answer ..., multi-level independent work |
| Preparing students for work at the main stage |
|
| Provide motivation, actualization of subjective experience | Communication of the topic and purpose (in the form of a problematic task, in the form of a heuristic question, through showing the final results, using a technological map of mental activity - a cluster. At the beginning of the lesson, a riddle is given, the answer to which will be opened when working on new material |
| Stage of assimilation of new knowledge and methods of action |
|
| Provide perception, comprehension and primary memorization of the studied material To promote the assimilation of methods, means that led to a certain choice | Working with definition Using everyday analogies Presentation of the main material simultaneously in verbal and sign-symbolic forms, presentation of the studied material in comparative and classification tables, story, lecture, message, modular training, use of a computer textbook, problem-based learning, collective learning, building a structural-logical scheme, genetic teaching method |
| Primary check of understanding of the studied |
|
| To establish the correctness and awareness of the material studied, to identify gaps, to correct gaps in understanding the material | Reference text, preparation by students of their questions, their examples on new material |
| The stage of consolidating new knowledge and methods of action |
|
| To ensure, in the course of consolidation, an increase in the level of comprehension of the studied material, the depth of understanding | Using reciprocal tasks, question-answer communication, inventing your own tasks |
| Application of knowledge and methods of action |
|
| Ensure the assimilation of knowledge and methods of action at the level of their application in various situations | Multi-level independent work, business game, learning situations, group work, discussion |
| Generalization and systematization |
|
| To ensure the formation of an integral system of leading knowledge of students, to ensure the establishment of intra-subject and inter-subject communications | Building a “tree” of a “topic”, building a “topic building”. Building a block formula: minuend-subtracted=difference. Learning situations, “topic intersection” |
| Control and self-control of knowledge and methods of action |
|
| Identification of the quality and level of assimilation of knowledge and methods of action | Multi-level independent and test papers, tests, tasks for highlighting essential features (depth) of the task, for designing several ways to solve the same problem (flexibility), tasks with redundant, conflicting data (ability for evaluative actions) |
| Correction of knowledge and methods of action |
|
| Carrying out correction of identified gaps in knowledge and methods of action | The use of exercises divided into small stages and links Application of detailed instructions with regular monitoring. Tests, tasks with gaps, structural logic diagrams with gaps |
| Homework Information |
|
| Ensure students understand the purpose, content and methods of doing homework | Three levels of homework: Standard Minimum elevated Creative |
| Summing up the lesson |
|
| Give a qualitative assessment of the work of the class and individual students | Message from the teacher, summing up by the students themselves |
| Reflection |
|
| Initiate students' reflection on their psycho-emotional state, motivation of their activities and interaction with the teacher and classmates | Telegram, SMS, unfinished sentence, coordinates |
LLC Training Center
"PROFESSIONAL"
Abstract by discipline:
"PEDAGOGY"
On this topic:
"Forms of organization of educational activities"
Executor:
Ivanshina Tatyana Alexandrovna
Moscow 2018.
Content
Introduction………. ………………………………………………………………..2.
1. Forms of organization of educational activities in the system of additional education………………………………………………………………………….4
1.1 training session - the main element of educational activities in additional education…………………………………………………...5
1.2 basic requirements for the construction of a modern training session ... ..6
1.3 main stages of the training session …………………………………………6
1 4 classification of occupations in additional education ……………...6 1.5 classification of occupations in additional education by labor intensity.
2. Traditional and non-traditional forms of organizing children's activities in
educational process in the system of additional education……………7-13
3. Conclusion……………………………………………………………………… 13
4. References……………………………………………………………………………14
“Comprehensive development, spiritual wealth cannot be achieved by force. True wealth is formed when a person himself is drawn to knowledge, to science, to art.
L.V. Zankov
1. Introduction
In the history of world educational practice, there have been various forms of organization of education, the emergence and development of which has always been determined by the needs and interests of the state.
Forms of organization are an outward expressioncoordinated activities of the teacher and students, carried out in a certain order and mode.They determine how to organize training in real conditions and are characterized by the number of participants in the interaction, the place, time and procedure for its implementation..
.
Despite the fact that the first rudiments of the system of individual education and upbringing were formed back in the primitive communal society, it developed with the advent of writing, it finally took shape officially in the Middle Ages. In connection with the increase in the number of students, they began to select children of approximately the same age into groups, therefore, there was a need for a more perfect organizational design of the pedagogical process.The most widespread both in our country and abroad was the class-lesson system of education, which arose in the 17th century. and has been developing for more than three centuries. Its contours were outlined by the German teacher I. Sturm, and developed theoretical basis and embodied in practical technology Ya.A. Comenius. Its features were put forward: a strictly regulated mode of educational work, a permanent place and duration of classes, a stable composition of students of this age, a stable schedule of the same level of preparedness.
Further development the teachings of Ya. A. Comenius came in the works of K. D. Ushinsky. He deeply scientifically substantiated all the advantages of the class-lesson system, created the theory of the lesson, developed the typology of lessons and the stages of the lesson. Form of organizationlearning activitiesis an independent didactic category that retains the main feature - to be an internal organization of any content.
The profound transformations taking place in the field of youth training require a sharp increase in the efficiency of the pedagogical process in all types of educational institutions.
As you know, education is now considered as universal way preservation and development of culture. Necessary maximum use of the entire arsenal of possibilities of the educational and pedagogical process, it is required to create and implement pedagogical technologies focused not only on increasing the level of knowledge, but also on developing professional self-determination, that is, activity-semantic unity.
Under such conditions, the pedagogical process in an educational institution should increasingly focus on the creative development of the individual. All this involves the use of a variety of forms and methods of teaching. As many scientists emphasize, it is in the pedagogical form that the set educational goals are realized.
Pedagogical science has accumulated a significant fund of knowledge necessary for the further improvement of organizational forms of training and education.
Additional education of children in modern Russia occupies a special position. It is associated with important tasks for the state of productive use of their free time by children, acquisition of cultural identity by the younger generation, early identification and development of capable children in various fields - culture, art, sports, scientific and technical creativity, etc.
The variety of content of additional education corresponds tovariety of organizational formsbased on communication, dialogue between the teacher and pupils, the development of their creative abilities.In additional education, these forms also carry an educational load and can be used as active ways for children to master educational programs.
All of the above made it possible to choose the topic of the essay: "Forms of organization of educational activities."object t is the learning process.Subject - forms of organization of educational activities.
The purpose of this work is to consider and systematize the usevarious formsorganizationseducationalchildren's activities,based on communication, dialogue between the teacher and students, the development of their creative abilities in the system of additional education. In the course of the work, the following tasks should be completed: - to study the psychological and pedagogical literature on the topic “Forms of organization of educational activities”; - systematize the usevarious formsorganizationseducationalactivities of children in the system of additional education.
1. Forms of organization of educational activities of children in the system of additional education.
The educational process organized in the system of additional education must meet the following requirements:
--
have a developmental character, i.e. should be aimed at developing children's natural inclinations and interests;
--
be varied in form(group and individual, theoretical and practical, performing and creative classes) and in content;
-
- be based on a variety of additional educational programs- modified, copyright, adapted, all of them must undergo a psychological and pedagogical examination before being included in the educational process and psychological and pedagogical monitoring during their implementation, so as not to harm the physical and mental health of students;
--
be based on developing methods of teaching children.
For a teacher of additional education, it is no longer enough to know only the subject area that he teaches, he must havepsychological and pedagogical knowledge;
--
use diagnostics of interests and motivation of childrenin order to provide such a variety of activities and forms of their implementation, which would allow different children with different interests and problems to find something to their liking;
--
be based on the social order of society;--reflect regional characteristics and traditions.
Lesson- this is an organizational form of education in which the teacher, for a set time, directs the cognitive activity of a permanent group of students, taking into account their characteristics, using the means and methods of work for the successful mastery of the basics of the subject, education and development of cognitive abilities and spiritual strength of students.
The form of education is the organized interaction of the teacher and students in the course of obtaining knowledge. Allocate forms of training: frontal, group, individual.
With frontal learning, the teacher manages the educational and cognitive activities of the entire class working on a single task.
Atgroupforms of educationeducator manageseducational and cognitive activities of groups of students in the class.
In the process of individual trainingthe teacher teaches each student separately when there is a directcontact with the student; the opportunity to understand the student, to come to the aid,Correct mistakes.
Classes in the system of additional education require a creative approach both on the part of the teacher and on the part of his students. Therefore, the content, means and forms are more unusual, which gives the lesson the necessary acceleration for the development of the individual. True, each time is different. It all depends on what position the teacher takes. However, students in such a lesson develop more successfully. For a teacher, a well-structured lesson is an opportunity for self-realization, a creative approach to work, and the implementation of one's own ideas.
1.1 training session - the main element of the educational process in additional education, but today its form of organization is changing significantly.
The main thing is not the communication of knowledge, but the identification of the experience of children, their inclusion in cooperation, in an active search for knowledge. Turn a study sessionin An interesting, exciting and educational route for children helps:
Organization of the work of children at an accessible level for them, at the limit of their capabilities and at an acceptable pace;
Clear, step-by-step explanation high level training material or practical operation training;
Setting not on memorizing educational information, but on the meaning and practical significance of the knowledge gained;
Mandatory control, which can be carried out in the course of explaining a new topic, after studying it and as a final check;
Implementation of an individual approach at each training session (finding out the goals and possibilities, the creative potential of each child based on knowledge of abilities, needs and inclinations).
Technology system The modern lesson has great variability, but at the same time it is subordinated to the main task - to educate the child's faith in his own strength and the desire for independent activity.
The forms of conducting training sessions are selected by the teacher, taking into account:
age psychological features students;
goals and objectives of the educational program;
subject matter and other factors.
1.2 Basic requirements for the construction of a modern training session:
creation and support of a high level of cognitive interest and activity of children;
expedient use of class time;
application of various methods and means of training;
a high positive level of interpersonal relations between the teacher and children;
practical significance of the acquired knowledge and skills.
1.3 The main stages of the training session.
Organization of the beginning of the lesson, setting educational, educational, developmental tasks, communication of the topic and lesson plan.-Checking the knowledge and skills that children have, their readiness to learn new things.- Acquaintance with new knowledge and skills.-Exercises for mastering and consolidating knowledge, abilities, skills on the model, as well as their application in similar situations, the use of creative exercises.- Summing up the results of the lesson, formulating conclusions.1.4 Classification of occupations in additional education
Information-cognitive type : mini-lecture, conversation, demonstration, exercises, experience, model making.
creative type : creating your own creative product.
Motivational - stimulating type : didactic game, exhibition, concert, competition, club day, competition.
Correction-controlling type : educational testing, mutual certification, protection, offset, test.
1.5 Classification of classes in additional education by labor intensity.
The most labor intensive : final games, KVN, concerts, competitions, excursions, exhibitions, club meetings.
Relatively labor intensive - classes similar to a school lesson, training, practical exercises, participation in concerts, exhibitions, parent meetings with children's performances, individual work, work with an ensemble, analysis of a performance (hike).
Less labor intensive - gatherings, tea parties, exercises, independent work, workshops, participation in creative activities at the invitation of other UDOD.
Traditional and non-traditional forms in the educational process
traditional forms organization of children's activities in the educational process.
For many years, teachers have been using traditional forms of classes in additional education.
The first traditional form is the lecture. The oral presentation of a particular topic develops the creative thinking activity of students. Often the lesson is also conducted in the form of a seminar. This form of training is group. At the lesson, students discuss pre-prepared reports or abstracts.
Such traditional forms of organizing classes in additional education develop analytical thinking, demonstrate the result of independent work and improve public speaking skills. Often, to study this or that material, teachers go on excursions with students. This method of studying information is a group trip or hike. Its purpose is to visit a particular attraction. Thanks to this method and visual representation, sensory perception is enriched. Consider the main types of classes.
- Lecture - an oral presentation of a topic that develops the creative thinking activity of students. When conducting a lecture, it must be taken into account that most students are not able to listen intently for a long time, therefore, during the lesson, it is important to solve the problems of enhancing mental, cognitive, and practical activities. For this purpose, the teacher is recommended to use the following methods:
The teacher during the lecture makes 10 significant mistakes, students who find mistakes will be rewarded;
Every 5 minutes during the lecture, students are given short oral or written express tasks;
Students are given sheets of summary the text of the lecture, where basic concepts, dates, names, principles, etc. are missing; during the lecture, students must insert the missing information;
The teacher invites students to write theses during the lecture;
The teacher leaves a few minutes at the end of the lecture, announcing this in advance, and conducts a quiz on the main concepts raised during the lecture;
- Seminar - the form of group lessons in the form of a discussion of prepared messages and reports under the guidance of a teacher forms analytical thinking, reflects the intensity of independent work, and develops public speaking skills.
- Discussion - comprehensive public discussion, consideration of a controversial issue, a complex problem; expands knowledge through the exchange of information, develops the skills of critical judgment and defending one's point of view.
Students are offered topics for discussion, or they themselves propose them. The teacher during the discussion plays the role of an organizer of the discussion and a consultant, as a rule, he does not express his point of view until final stage discussions so as not to influence the course and outcome of the discussion ahead of time. To intensify the discussion, several students before it are given the task to select specific factual materials that can be read out during the discussion. A role assessment group is created from the students, which at the end of the lesson comes up with an analysis of the positions and an assessment of the role of the participants;
- Conference - meeting, meeting of representatives of various organizations to discuss and resolve any issues; instills the skills of open discussion of the results of their activities.
Lesson - press conference- this session usually completes the study of the topic and is carried out in two ways: - several students prepare for a press conference, the group asks them questions, a special jury gives points for each question and each answer; - students ask questions to the teacher, the jury gives points to students and the teacher for questions and answers;
Occupation - testing - carried out using a computer or in the usual way, each student receives cards with tasks with answer options (you must choose the correct answer);
- Excursion - a collective hike or trip for the purpose of inspection, acquaintance with any attraction; enriches sensory perception and visual representations.
- Tourist trip - movement of a group of people for a specific purpose; implements the goals of knowledge, education, health improvement, physical and sports development.
- Expedition - trip of a group with a special task: it solves a complex of diverse tasks for organizing effective practice in the process of obtaining a profile result outside the classroom conditions.Occupation-expedition- the meaning of conducting small cognitive expeditions is to achieve several goals in a short time: to create a real situation for the ethical, aesthetic, emotional and cognitive inclusion of students in the process of collective and individual interaction with living and man-made reality.
Project Protection - the lesson is preceded by a "brainstorming", during which the subject is considered possible projects, then the students, divided into microgroups, determine the problems to be solved in the design process (at the same time, at all stages of the independent work of the group, the teacher acts as a consultant or assistant), goals, direction and content of activities and research, the structure of the project. At the last stage, an open defense of the project takes place, the result of the defense is the awarding of developers of the best projects;
- Educational game
- an occupation that has certain rules and serves to learn new things, relax and enjoy; characterized by modeling life processes in a developing situation.
10-
Occupation - game - involving students in the game allows you to achieve the effect of emancipation, active search, the ability to analyze, make decisions, communicate. The teacher needs to take into account the basic principles of organizing game interaction:
The teacher should offer a flexible game system suitable for each student;
The child should have the right to choose and make independent decisions;
The game should be accessible to all participants, provide equal opportunities;
The game should give the pupil the opportunity to explore, understand, cognize the world around him;
Non-traditional forms organization of children's activities in the educational process in additional education.
Increasingly, in our practice of modern education, teachers use non-traditional lessons, the main purpose of which is to form students' positive motivation for learning, the development of their creative principles. A non-standard lesson is a lesson that has something original. Changes are possible in the goals, methods, teaching aids, and even in the very organization of the lesson.
. The final result depends on the chosen form of teaching. It should be noted that the teaching methodology is directly related to the relationship between the student and the teacher. As a rule, teachers who present the material in an interesting way and conduct the lesson in a non-standard manner inspire respect among students. They enjoy attending their classes and easily learn new information.
Most often, non-traditional forms of classes in additional education are based on games, competitions, trainings and role playing. It is believed that such teaching methods are more effective. Thanks to them, children easily learn the material and attend classes with pleasure.Non-traditional forms of training include:
Integrated classes based on interdisciplinary connections;
Classes-competitions: contests, tournaments, quizzes, etc.;
11-
Classes based on the methods of social practice: reportage, interview, invention, commentary, auction, rally, benefit performance, oral magazine, newspaper, etc.;
Classes based on non-traditional organization of educational material: presentation, confession, etc.;
Fantasy activities: fairy tale, surprise, adventure, etc.;
Imitation-based lessons social activities: court, investigation, etc. The above forms of organizing the activities of students in recent times are widely used both in the practice of the school and in the practice of additional education.
Specific forms of classes:
quiz lesson - the quiz is designed so that students show knowledge and understanding of terms, events, processes, norms, rules, etc.; questions can be distributed to students in advance or kept secret;
activity - competition (competition, tournament) - educational, cognitive competitions are based on the principles of competitiveness, interest, quick reaction; During the lesson, the group is divided into two teams that compete with each other. The judging panel gives points to the teams (theoretical knowledge, reaction, completeness and originality of answers, acquired practical skills and abilities are evaluated);
occupation - a fairy tale - children unite by 2-3 people, compose fairy tales on a given topic and then show them to the group; fairy tales can be prepared in advance, parents, teachers can take part in them, they can be accompanied by music, decoration.
- Presentation object, phenomenon, event, fact - description, disclosure of the role of the object, social purpose in human life, participation in social relations.
- sociodrama - role-playing game, predetermined by the position of the main characters; the situation of choice, on which the course of life and socio-psychological relations depend, awareness of oneself in the structure of social relations.
12-
- Project Protection - the ability to project changes in reality in the name of improving life, the correlation of personal interests with public ones, the proposal of new ideas for solving life problems.Protection methodThe project is quite important, with its help the child develops the ability to project changes in reality to improve life.
Thisthe lesson is preceded by a “brainstorming”, during which the topics of possible projects are considered, then the students, divided into microgroups, determine the problems to be solved in the design process (at the same time, at all stages of the independent work of the group, the teacher acts as a consultant or assistant), goals , the direction and content of activities and research, the structure of the project. At the last stage, an open defense of the project takes place, the result of the defense is the awarding of developers of the best projects;
- Round table - collective work to find the social meaning and personal meaning of the phenomenon of life - “Freedom and Duty”, etc.
tea drinking - has great power, creates a special psychological atmosphere, softens mutual relations, liberates.Tea drinking is a method that is also included in non-traditional forms of conducting classes in additional education. It is incredibly important if it is necessary to establish relationships in the team and rally it. Tea drinking creates a special psychological atmosphere. Thanks to this method, uncommunicative children can be liberated.
- "Toughie" - solving difficult issues in life together with the group, a confidential conversation based on good relationships.The method called "Die Hard" allows you to establish trusting relationships in the team. Its goal is to solve difficult life issues collectively.
.- Day of good surprises - an exercise in the ability to show signs of attention, to bring joy to people.
- Envelope of questions - free exchange of opinions on various topics in a friendly atmosphere.
- graduation ring - report of graduates of creative teams, analysis of the past, plans for the future; creating an atmosphere of friendship, mutual understanding; developing the ability to interact with people
13-
Philosophical table - collective work to find the social meaning and personal meaning of the phenomenon of life - "Freedom and Duty", "Man and Nature", etc.
There is a diverse arsenal of teaching methods, methods of motivation and stimulation of cognitive interest, control and correction.
Conclusion
Forms of organization educational activities children - a way pedagogical organization activities of children and the content of the educational program. In institutions for the education of children, activities are carried out in associations of different ages and same ages of interest, such as a club, studio, ensemble, group, section, circle, theater and others.
Conclusions: teacherit is important to remember that the goal of all classes is to raise and maintain students' interest in a particular direction, to increase the effectiveness of learning.
Various forms of learning activity are based on General characteristics. The common point is the structure of the lesson. It can repeat the usual move with its argument, communication of new knowledge, control of what has been learned, or it can be original, with a changed sequence of ordinary steps, with transformed ways of organizing, with a game basis.
Despite the variety of types of classes, they are all subject to certain requirements, the observance of which contributes to increasing the effectiveness of training:
Each lesson should have a theme, purpose, specific content, certain methods of organizing the educational process;
Each lesson should be teaching, developing and educating;
The lesson should be a combination of collective and individual forms of work;
The teacher must select the most appropriate teaching methods, taking into account the level of preparedness of students.
In the educational process, depending on the tasks to be solved, the teacher works with students frontally, in small groups, individually.
The system of forms of educational activity of students in the lesson is frontal, individual and group. All components of the learning process are also inherent in these forms. They differ from each other in the number of students and ways of organizing work.
frontal the form of organization of educational activity of students is called this type of activity in the lesson, when all students of the class, under the direct supervision of the teacher, perform a common task. At the same time, the teacher conducts work with the whole class at the same pace. In the process of telling, explaining, showing and under, he seeks to influence all those present at the same time. The ability to keep the class in sight, to see the work of each student, to steal the atmosphere of creative teamwork, to stimulate the activity of students are important conditions for the effectiveness of this form of organization of educational activities of students.
Most often it is used at the stage of primary assimilation of new material. With a problematic, informational and explanatory-illustrative presentation, which is accompanied by creative tasks of varying complexity, this form allows you to involve all students in active educational and cognitive activities.
A significant drawback of the frontal form of educational work is that it is, by its nature, focused on average students. For an abstract average student, the volume and level of complexity of the material, and the pace of work, are calculated. Students with low learning opportunities in such conditions are not able to acquire knowledge: they require more attention from the teacher, and more time to complete assignments. If, however, the pace is reduced, then it will negatively affect strong students; the latter are satisfied not by an increase in the number of tasks, but by their creative nature, the complication of content. Therefore, in order to maximize the effectiveness of the educational activity of students in the classroom, along with this form, other forms of organization of educational robotics are used.
. Individual form of organization of work of students provides for the independent performance by the student of the same tasks for the whole class without contact with other students, but at the same pace for all. According to the individual form of organization of work, the student performs the exercise, times. Binding
task, conducts experiments, writes an essay, abstract, report, etc. An individual task can be work with a textbook, reference book, dictionary, map, etc. Widely practiced is individual work in a grammatical study.
The individual form of work is used at all stages of the lesson, to solve various didactic tasks: the assimilation of new knowledge and their consolidation, the formation and consolidation of skills and abilities, to repeat the creation and generalization of the material covered. It prevails in the performance of homework, independent and control tasks in the classroom.
The advantages of this form of organization of educational work are that it allows each student to deepen and consolidate knowledge, develop the necessary skills, abilities, experience of cognitive creative activity, etc.
However, the individual form of organization has disadvantages: the student perceives, comprehends and assimilates the educational material in isolation, his efforts almost do not agree with the efforts of others, and the result of these efforts, his assessment concerns and interests only the student and the teacher. This shortcoming is compensated by the group form of activity of students.
The group form of learning activity emerged as an alternative to the existing traditional forms of learning. It is based on ideas. J-J. Rousseau. YGPestaloishchi,. J. Dewey on the free development and upbringing of the child. YG. GPestaloishchi believed that a skillful combination of individual and group learning activities increases the activity, amateur performance of students, creates conditions for mutual learning, which contributes to the successful mastery of s. Nunn, skills and habits of newcomers.
At the beginning of the 20th century, group learning as a specific form of its organization appeared in the region. Dalton Plan (USA). In the 1920s and 1930s, it was used in the Soviet school under the name "brigade-la plowing method" The word "brigade" emphasized teamwork in work, and "laboratory" - compatibility in completing educational tasks at vikonan's primary tasks.
According to the curricula approved. People's Commissariat in 1930, c. USSR, the liquidation of classes took place, their replacement by links and brigades, and the material of various subjects grouped around. Complex-projects. As a result of knowledge about nature (physics, chemistry, biology) and knowledge about society (social science, history, geography, literature, etc.), students had to learn in the process of implementing complex topics and projects (for example, "struggle for industrial financial plan", "struggle for collectivization village", etc.). The application of new forms of education quickly led to significant shortcomings: lack of c. UCHN gives her a sufficient amount of systematized knowledge, a decrease in the role of the teacher, waste of time. These shortcomings were identified in the resolution. Central Committee. VKP (b) "On curricula and mode in primary and secondary school" (1931), where the team-laboratory method and the project method were condemned, and the project method was condemned.
For many years, no forms of learning, alternative lessons, have been used or developed. And rational grains, which included group forms, were forgotten
V. Western. Europe and. In the United States, group forms of educational activity of students were actively developed and improved. French teachers made a significant contribution to the development of the theory of group learning activities. K. K. Garcia,. S. Frenet,. R. Gal,. RKuzine, Polish -. Vokon,. R. Petrikovsky,. ChKupisevich. Group forms have become widespread in the practice of the American school, where they are used in teaching various subjects. Research carried out. National Training Center (USA, Maryland) in the 80s of the XX century, show that due to group training, the percentage of assimilation of the material increases sharply, since there is no effect not only on the minds of students, but also on their feelings, will (actions, practice, practice).
Only in the 1960s, in connection with the study of the problem of cognitive activity and independence of students in Soviet didactics, did the interest in group forms of education reappear (MODagashov, BPEsipov, IMCheredo ravdov).
The reorientation of the learning process to the student's personality has significantly intensified research into group forms of schoolchildren's learning activities. A significant contribution to the development of the general principles of group learning was made by prake. VKDyachenko. VVKotova. HYLIIMETSA,. Yushalovanogo,. ISF. Nor,. OJ. Savchenko,. OGYaroshenko and Druoshenko and others.
. Group form of organization of educational activities of students provides for the creation of small groups within the same class. There are the following forms of group interaction:
1. Paired form of study - two students do some work together. The form is used to achieve any didactic goal: mastering, consolidating, testing knowledge, etc.
Working in pairs gives students time to think, exchange ideas with a partner, and only then verbalize their thoughts in front of the class. It promotes the development of speaking, communication, critical thinking, onuwata persuasion and discussion skills.
2Cooperative-group learning activities - it is a form of organizing learning in small groups of students united by a common educational goal. According to this organization of teaching, the teacher directs the work of each student indirectly through the tasks with which he directs the activity of the group. Fulfilling part of the common goal for the whole class, the group presents and defends the completed task in the process of collective discussion. The main results of such a discussion become over the bath of the whole class and are recorded by all those present at the lessons.
3. Differentiated-group the form provides for the organization of the work of student groups with various educational opportunities. The task is differentiated by the level of complexity or by their number
4Lankova form provides for the organization of educational activities in permanent small student groups managed by leaders. Students work on a single task
5. Individual-group form provides for the distribution of educational work among group members, when each member of the group performs part of a common task. The result of the implementation is first discussed and evaluated in the group, and then submitted for consideration by the entire class and the teacher.
Groups can be stable or temporary, homogeneous or heterogeneous.
The number of students in a group depends on the total number of students in the class, the nature and amount of knowledge developed, the availability necessary materials, the time allotted to complete the work. A group of 3-5 people is considered optimal, since in the case of a smaller number of students it is difficult to comprehensively consider the problem, and in the case of a larger one, it is difficult to determine what work each student has done.
Grouping can be carried out by the teacher (mostly on a voluntary basis, according to the results of the lottery) or by the students themselves of their choice
Groups can be homogeneous (homogeneous), i.e. grouped according to certain characteristics, for example, by the level of educational opportunities, or heterogeneous (diverse). In heterogeneous groups, when strong, average and weak students enter one group, creative thinking is better stimulated, an intensive exchange of ideas takes place. To do this, enough time is provided for expressing different views, discussing the problem in detail, and considering the issue from different perspectives. Bokyiv.
The teacher directs the work of each student indirectly, through the tasks that he proposes to the group, and which regulate the activities of students
The relationship between the teacher and the students takes on the character of cooperation, because the teacher directly interferes in the work of the groups only if the students have questions and they themselves turn to the teacher for help.
The solution of specific educational problems is carried out thanks to the joint efforts of the members of the group. At the same time, learning activity does not isolate students from each other, does not limit their communication, mutual assistance and cooperation, but, on the contrary, creates opportunities for combining efforts to act in a coordinated and coordinated manner, to be jointly responsible for the results of completing a learning task, while tasks in a group are performed in such a way that allows you to take into account and evaluate the individual contribution of each member of the group.
Contacts and exchange of opinions in the group significantly activate the activity of all students - members of the group, stimulate the development of thinking, contribute to the development and improvement of their speech, replenishment of knowledge, and expansion of individual experience.
In the group learning activities of students, the ability to learn, plan, model, exercise self-control, mutual control, reflection, etc. is successfully formed. It plays an important role in the implementation of the educational function of learning. Mutual understanding, mutual assistance, collectivity, responsibility, independence, the ability to prove and defend one's point of view, cultures and dialogue are brought up in group educational activities.
The table shows the possibilities of choosing the form of group learning activities at different stages of the lesson:
Forms of group learning activities at different stages of the lesson
Table 7
The success of working in groups depends on the teacher's ability to complete groups, organize work in them, distribute their attention so that each group and each of its participants feel the teacher's interest in their success, in normal and fruitful interpersonal relationships.
The main form of education in elementary school today is still the traditional lesson. This is explained by the fact that most of the teachers are teachers who have worked at the school for decades, which means that they adhere to the traditional classical teaching methods. In any case, it is not easy for a person to readjust. So the teacher needs time and conditions to learn how to work in a new way.
Feature of federal state educational standards general education- their activity character, which puts the main task of developing the personality of the student. Modern education refuses the traditional presentation of learning outcomes in the form of knowledge, skills and abilities; GEF formulations indicate real activities.
The task set requires a transition to a new system-activity educational paradigm, which, in turn, is associated with fundamental changes in the activities of a teacher who implements the Federal State Educational Standard. Teaching technologies are also changing, the introduction of information and communication technologies opens up significant opportunities for expanding the educational framework for each subject in the educational institution.
What main points should a teacher take into account when preparing for a modern lesson in accordance with the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard?
The methodological basis of the Federal State Educational Standard is a system-activity approach, which is aimed at the development of the individual, the formation of civic identity. The system-activity approach makes it possible to single out the main results of education and upbringing in the context of key tasks and universal learning activities that students should master. The development of the student's personality in the education system is ensured, first of all, through the formation of universal educational activities, which are the basis of the educational and upbringing process. Mastering universal learning activities by students creates the possibility of independent successful assimilation of new knowledge, skills and competencies, including the organization of assimilation, that is, the ability to learn. This possibility is ensured by the fact that universal learning actions are generalized actions that generate a broad orientation of students in various subject areas of knowledge and motivation for learning. In order for students' knowledge to be the result of their own searches, it is necessary to organize these searches, manage, develop their cognitive activity. Standing in front of the teacher serious problem- how to optimally include each child in mental activity in the classroom, as the personality develops in the process of activity. The use in the lesson of various combinations of individual, group, collective, pair work ensures the inclusion of each student in the educational process. It contributes to the gradual formation of not only subject knowledge and skills, but also the development of the student's communication skills, teamwork skills. Therefore, we can talk about the possibility of each student of the school to master educational standard in the subject, to obtain high-quality learning outcomes.
The organization of the educational process can become more efficient, better quality, if the following organizational forms are combined when designing a training session:
frontal work, where problematization occurs and the necessary minimum of educational material is presented
work in constant pairs (groups) - training, repetition, consolidation of the material presented in the previous frontal work
work in pairs (groups) of shift composition - deep development of individual moments of the material on the topic under study
individual work - independent completing assignments on the topic of the lesson
What is each of the listed forms of organization of educational work of students in the lesson? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each of them? How to combine these forms of work of students in the specific pedagogical activity of the teacher?
Frontal shape organization of educational activity of students is called this type of activity of the teacher and students in the lesson, when all students simultaneously perform the same work common to all, discuss, compare and summarize the results of it with the whole class. The teacher works with the whole class at the same time, communicates with students directly in the course of his story, explanation, demonstration, involvement of students in the discussion of the issues under consideration, etc. This contributes to the establishment of especially trusting relationships and communication between the teacher and students, as well as students among themselves, instills a sense of collectivism in children, allows students to be taught to reason and find errors in the reasoning of their classmates, form stable cognitive interests, and intensify their activity. From the teacher, of course, a great ability is required to find a feasible work of thought for all students, to design in advance, and then create learning situations that meet the objectives of the lesson; the ability and patience to listen to everyone who wants to speak out, tactfully support and at the same time make the necessary corrections during the discussion. Due to their real capabilities, students, of course, can at the same time make generalizations and conclusions, reason during the lesson at different levels of depth. This teacher should take into account and question them according to their abilities. This approach of the teacher during the frontal work in the lesson allows students to actively listen and share their opinions, knowledge with others, listen carefully to other people's opinions, compare them with their own, find errors in someone else's opinion, reveal its incompleteness. As for the teacher, using the frontal form of organizing the work of students in the classroom, he gets the opportunity to freely influence the entire class team, present educational material to the whole class, and achieve a certain rhythm in the activities of students based on their individual characteristics. All these are the undoubted advantages of the frontal form of organizing the educational work of students in the classroom. That is why, in the conditions of mass education, this form of organization of students' educational work is indispensable and the most common in the work of a modern school. The frontal form of educational work, as noted by scientists-teachers - Cheredov I.M., Zotov Yu.B. and others, has a number of significant drawbacks. Students with low learning abilities work slowly, learn the material worse, they need more attention from the teacher, more time to complete tasks, more different exercises than students with high learning abilities. Strong students, on the other hand, do not need to increase the number of tasks, but to complicate their content, tasks of a search, creative type, work on which contributes to the development of schoolchildren and the assimilation of knowledge at a higher level
Individual form organization of student work in the classroom. This form of organization assumes that each student receives a task for independent completion, specially selected for him in accordance with his training and learning opportunities. Such tasks can be work with a textbook, other educational and scientific literature, various sources (reference books, dictionaries, encyclopedias, anthologies, etc.); solving problems, examples, writing summaries, essays, abstracts, reports; conducting all kinds of observations, etc. individual work it is advisable to carry out at all stages of the lesson, when solving various didactic problems; for the assimilation of new knowledge and their consolidation, for the formation and consolidation of skills and abilities, for generalization and repetition of the past, for control, for mastering the research method, etc. For poorly performing students, it is necessary to draw up such a system of tasks that would contain: sample solutions and tasks to be solved based on the study of the sample; various algorithmic prescriptions that allow the student to solve a certain problem step by step - various theoretical information that explains the theory, phenomenon, process, mechanism of processes, etc., allowing you to answer a number of questions, as well as all kinds of requirements to compare, compare, classify, generalize and etc. Such an organization of the educational work of students in the classroom enables each student, by virtue of his abilities, abilities, composure, to gradually but steadily deepen and consolidate the acquired and acquired knowledge, develop the necessary skills, skills, experience of cognitive activity, form his own needs for self-education. This is the advantage of the individual form of organization of educational work of students, this is its strengths. But this form of organization also contains a serious drawback. Contributing to the education of students' independence, organization, perseverance in achieving the goal, the individualized form of educational work somewhat limits their communication with each other, the desire to transfer their knowledge to others, and participate in collective achievements. These shortcomings can be compensated for in practical work teachers with a combination of an individual form of organizing students' educational work with such forms of collective work as frontal and group work.
group form of organization of educational work of students. The main features of the group work of students in the lesson are: the class in this lesson is divided into groups to solve specific learning problems; each group receives a specific task (either the same or differentiated) and performs it together under the direct supervision of the group leader or teacher; tasks in the group are performed in such a way that allows to take into account and evaluate the individual contribution of each member of the group; the composition of the group is not permanent, it is selected taking into account that the learning opportunities of each member of the group can be realized with maximum efficiency for the team. The size of the groups is different. It ranges from 3-6 people. The composition of the group is not permanent. It varies depending on the content and nature of the work to be done. In group work, learning is transformed from the individual activity of each student into joint work. The student is forced to learn to negotiate, sacrificing his personal interests, constructively and quickly resolve conflicts. Gradually, the student gets used to feeling the class community as part of his world, he is interested in maintaining friendly relationships. Group work is especially effective when discussing problematic tasks, since only with a joint discussion can a solution be found. Group work requires the student to consider more factors. He must adapt to the pace of work of other members of the group, must correctly understand them, clearly formulate his thoughts and desires, correlate them with the tasks chosen by the group. All this contributes to the process of self-regulation. When summing up, everyone can compare their work with the work of group mates, see the notebooks of their comrades, listen to the rationale for the decision and analysis of errors. Thus, the background for the formation of self-esteem of each student is expanding. Since there is a joint search in the group, erroneous answers do not frighten the guys, but make them look for a new solution. Confusion with the wrong decision is not observed. The guys should learn to understand that learning is not the assimilation of ready-made knowledge and conclusions, but a process of cognition, which includes wrong decisions. Advantages group organization student work in the classroom are obvious. The results of the joint work of students are very tangible both in accustoming them to collective methods of work, and in the formation of positive moral qualities of the individual. But this does not mean that this form of organization of educational work is ideal. The group form also has a number of disadvantages. Among them, the most significant are: difficulties in recruiting groups and organizing work in them; students in groups are not always able to independently understand complex educational material and choose the most economical way to study it. As a result, weak students have difficulty mastering the material, while strong students need more difficult, original assignments and tasks. Only in combination with other forms of teaching students in the classroom - frontal and individual - the group form of organizing the work of students brings the expected positive results. It cannot be universalized and opposed to other forms.
Each of the considered forms of organization of education solves its own specific educational tasks. They complement each other. The preparedness of students and their individual characteristics, the qualifications of the teacher - all this affects the choice of one form or another of organizing students' activities. The combination of various forms is multivariate. It is carried out either sequentially, when one form follows another, or in parallel, when the combination proceeds simultaneously and the forms of work enter one another. As experience and many experiments conducted by various teachers show, a combination of forms of organizing activities should be applied, going from a combination of simple ones to more complex ones, taking into account the age of students, the specifics of the subject. For determining the best option the organization of activities needs to know how a particular form affects the effectiveness of educational activities of various groups of students. “Such a combination of forms of educational work, in which the shortcomings of some are neutralized and higher performance of others is ensured with minimal cost time is optimal. (Cheredov I.M. "Method of planning school forms of organization of education"). The choice of form depends on many factors, but to a greater extent on the stage in the learning process. Teachers who deal with this issue have identified some patterns and developed recommendations for choosing the optimal combination of student work forms in the lesson.
Each form has its own disadvantages and advantages, therefore, when planning a lesson, the teacher must select a combination of forms in such a way as to strengthen the strengths and neutralize weak sides every form.
The methodological goal of each lesson is to create conditions for the manifestation of cognitive activity. Creation of pedagogical situations of communication, allowing each student to show initiative, independence, creating an environment for the natural self-expression of the student. The pace of personal development is individual, therefore it is important to bring the personality of each student into the development mode.