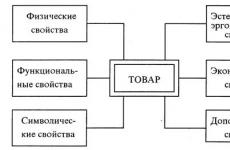
Types and properties of heat-insulating materials. We choose a heater for the walls of the house outside: price, types and overview of manufacturers Types of modern heaters
Good thermal insulation will not be superfluous at any temperature. If you perform it efficiently and choose the right insulation, in the cold season there will be more heat in the house, and in the summer heat - coolness. Knowing what is the heater, can be easily selected best option for interior or exterior decoration.
 Variety of types of heat insulators
Variety of types of heat insulators
There are several criteria for dividing heat insulators into certain groups. The classification is based on the purpose, form and composition of materials.
Varieties of insulation in shape
When choosing a material according to this criterion, you need to consider what surface it will be mounted on. For exterior walls, slab or block heat insulators are more suitable. Inside the house it is better to insulate with fibrous or rolled materials.
Table 1. Types of heat-insulating materials by shape:
| The form | Name | Peculiarities |
|---|---|---|
Bulk  | Expanded clay, polystyrene, crushed cork | granular material. Used to fill cavities |
Loose and fibrous  | Ecowool, glass wool | Installation is carried out by blowing into prepared contours or applied by spraying |
Slab  | Foamed concrete, chipboard | Sheets of a fixed size and a certain shape |
Rolled  | Basalt wool, polyurethane | Flexible, thinner than slabs |
Block  | foam concrete | Simultaneously perform the function of insulation and supporting structure |
To choose the right insulation, you need to be well versed in its varieties. Then it will last longer and will perform its functions to the fullest.
Types of insulation by composition
This classification is based on what raw materials the product is made from. Natural-based heaters are more suitable for interior decoration, and artificial materials are used for external thermal insulation or for rooms with high humidity.
Table 2. Classification by composition:
Each type of material has its own set of characteristics. According to it, they determine how suitable it is for warming a particular object.
Types of insulation according to the principle of action
Thermal insulation is of two types - reflective and preventive. The first variety reduces heat consumption by lowering the level of infrared light.
Reflective insulation instead of retaining heat does not allow infrared radiation to freely pass through the walls of the house. They do not transmit heat, but reflect. Most often, aluminum foil is used for this purpose. The surface of this material may reflect 90-97% the warmth that comes into contact with it.
Aluminum foil is laid in several layers. The last layer is covered with polyethylene. Such a heater does not take up much space, but at the same time it retains a comfortable microclimate in the house for a long time and at the same time performs the function of a vapor barrier.
 Reflective type of insulation - aluminum foil
Reflective type of insulation - aluminum foil
The second type involves the use of a heater with low thermal conductivity. For its manufacture, different groups of materials are used - organic and inorganic. Such heat insulators act according to a certain mechanism. Their role is to slow down the passage of heat - so that it does not go outside for as long as possible.
What are wall insulation
To choose a heat insulator for walls, you first need to understand its types and their technical characteristics.
“The main property of a heater is the degree of thermal conductivity. This is an indicator of the amount of heat that this material is able to pass.
For interior decoration materials of organic origin are used. They are made using natural raw materials - waste from the woodworking industry or agricultural products. Additional components are plastic and cement. Each species has its own characteristics.
Arbolit
For its manufacture, crushed sawdust, wood shavings and reed stalks are used. Cement with calcium chloride and alumina is used as a binding component.
 Wood concrete insulation
Wood concrete insulation
Arbolite properties:
- environmental friendliness - 90% consists of organic substances;
- almost not affected by mold and fungus;
- provides good sound insulation and air exchange;
- low heat conductivity - no more than 0.12 W / (m * K);
- easily withstands frost, fireproof.
The material is excellent for processing. It can be sawn into pieces, screwed into it with screws or hammered nails. From this it does not crumble and does not break.
particle board
90% consists of crushed chips. The remaining 10% are formaldehyde resins and antiseptics. The material is also impregnated with flame retardants - substances that increase its fire resistance.
Chipboard characteristics:
- homogeneous structure;
- environmental friendliness;
- resistance to temperature extremes;
- humidity - within 5-10%;
- ease of installation.
“To choose high-quality plates, you need to focus on your sense of smell. If the product does not smell, then it is completely safe for health. Chipboard with a high content of synthetic resins has a pronounced smell of chemistry.
 particle board
particle board
The plates have weak edges. So that they do not crumble, the sheets must be adjusted to each other with maximum density. They also do not withstand a large bending load, so they can sag.
Foamed polyethylene
Has a porous structure. Consists of polyethylene and hydrocarbon-based foam component.
 Foamed polyethylene
Foamed polyethylene
It has the following set of features:
- provides good vapor barrier;
- almost does not absorb moisture;
- not affected by chemicals and decay;
- withstands temperatures from -40 to +100 degrees;
- serves as a reliable sound insulator.
Foamed polyethylene is produced in rolls.
Fiberboard
The basis for the material is wood shavings. Magnesite or cement is added to it as a binding component. Sold in slabs.
 Fiberboard
Fiberboard
The features of this heater include:
- fire safety;
- ability to absorb noise;
- low thermal conductivity - up to 0.1 W / (m * K);
- increased resistance to aggressive chemical environment.
Suitable for wall insulation in rooms with abundant humidity - for a pool or bathroom.
Price for fiberboard
Fiberboard
Honeycomb insulation
It contains cells in the form of a hexagon. By appearance they look like honeycombs. The raw material for the material is cellulose, fiberglass or special fabrics. On top of the honeycomb are covered with a thin layer of film. Epoxy or phenolic resin is used to bind the fibers. The outer side of the heat insulator is a sheet of plastic.
 corrugated fabric insulation
corrugated fabric insulation
Distinctive properties of insulation:
- absorbs noise;
- retains heat for a long time;
- fireproof;
- strongly absorbs moisture.
"The strength of the corrugated fabric is low, so it is not used as an independent heat insulator - only together with asbestos and aluminum in the form of a three-layer panel."
Ecowool
The basis for it is paper and cardboard waste. If you lay ecowool with a continuous coating, there will be no seams on the surface of the walls.
 Ecowool
Ecowool
Material features include:
- high sound insulation;
- health safety;
- quickly absorbs moisture;
- retains heat for a long time.
But over time, the thermal insulation coefficient decreases, because the material loses up to 20% of its initial volume.
Cork wallpaper
At the same time, it can act as a heater and finishing material. The raw material for it is the bark of the cork tree. It is first crushed and then pressed. Cork wallpaper can be left in natural form or varnish.
 Cork insulation
Cork insulation
They differ in the following characteristics:
- environmental friendliness;
- long service life;
- fire resistance;
- excellent soundproofing.
The material also has antistatic and antimicrobial properties. Cork wallpaper creates an optimal microclimate in any room.
 Stone wool. Advantages.
Stone wool. Advantages.
What are facade heaters
 Facade insulation
Facade insulation
“The right choice of insulation and its quality installation provides uniform heating in the room due to the free circulation of heated air. The outer layer of the heat insulator retains heat longer, which makes it possible for the walls to be dry. This prevents them from premature destruction.
External thermal insulation has other advantages. It provides:
- protection of the facade from the aggressive effects of the external environment;
- additional sound insulation;
- unhindered "breathing" of the walls.
Various types of materials are used as insulation.
"Warm" plaster
As the basis for the preparation of this mixture is used cement mortar, but instead of sand, the following components are added to it:
- crushed pumice;
- perlite sand;
- expanded clay crumbs;
- expanded polystyrene in granules.
 "Warm" plaster on the facade of the building
"Warm" plaster on the facade of the building
This composition provides good vapor permeability and sound insulation. "Warm" plaster does not absorb moisture and refers to non-combustible materials. It protects the house from the invasion of bacteria. Through a thick layer of plaster, mold with microbes cannot penetrate inside.
But under the influence high temperatures, wind or rain, the degree of thermal insulation is gradually reduced.
Thermal panels
At the same time they perform the function of insulation and finishing material. They are not cheap, which is explained by the presence of a complex of positive qualities.
 Thermal panels
Thermal panels
Thermal panels have the following characteristics:
- extensive color palette;
- variety of textures;
- durability;
- health safety;
- aesthetic appeal;
- little weight.
At the same time, the material is easy to mount. Additionally, it provides protection against fungi and microbes.
Prices for thermal panels
Thermal panels
polyurethane foam
Consists of polyester and emulsifiers. Differs in foamy-cellular structure. It is applied by spraying, therefore it is suitable for walls of complex configuration.
 polyurethane foam insulation
polyurethane foam insulation
This insulation easily withstands temperature changes. It is completely fireproof.
Material Features:
- keeps warm for a long time;
- almost does not pass steam and moisture;
- high resistance to fungi and mold;
- not subject to corrosion;
- absorbs noise well.
It is also chemical resistant. Does not deform when in contact with acid, gasoline or alcohol. Polyurethane foam is an unattractive material for pests and insects. The average service life is from 50 years, but under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, it gradually collapses.
Styrofoam
A material with a porous structure, produced by foaming. Consists of small granules, tightly adjacent to each other. The higher its density, the stronger the material.
 Styrofoam insulation
Styrofoam insulation
Foam characteristics:
- moisture resistance;
- long service life - from 60 years;
- resistance to extreme temperatures;
- resistant to bacteria and fungus.
This is the cheapest of all types of heaters. On top of the foam, it is recommended to apply a layer of facade plaster, otherwise it will be subject to deformation.
Styrofoam prices
Styrofoam
Video - How to choose the thickness of the foam for insulation
Basalt insulation
It consists of basalt fiber, which is produced on the basis of natural minerals.
 Basalt heat insulator
Basalt heat insulator
Differs in the following set of qualities:
- increased porosity - up to 70%;
- low thermal conductivity;
- resistance to temperature extremes and chemical attack;
- high vapor permeability - the material remains dry in any weather;
- light weight;
- great strength.
Basalt insulation is considered completely safe for health.
foam concrete
Refers to block-type heat insulators. Its strength is the same as that of ordinary concrete. The difference is only in the structure - in foam concrete it is porous. To make it, a foaming component is added to the concrete composition.
 foam concrete
foam concrete
Material Specifications:
- does not give in to rotting, is not covered with mold;
- life time - from 25 years old;
- light weight;
- environmental friendliness;
- low thermal conductivity;
- protects the building from dampness by creating an optimal microclimate in it.
Foam concrete can be easily cut or screwed into it with self-tapping screws, which simplifies the process of its installation.
Foam glass
It is a glass panel treated with a special compound. In the process of processing, the glass changes its structure - it becomes fine-meshed. Due to this, its thermal insulation characteristics increase:
- strength;
- resistance to chemicals;
- low combustibility.
Foam glass also serves as a decorative finish.
 Foam glass insulation
Foam glass insulation
"Optimal time for facade works- from the end of spring to the beginning of autumn, when the average air temperature is + 5-25 degrees. Thermal insulation of facades is undesirable in extreme cold or heat - this reduces its quality and service life.
Heaters for a wooden house
Wood is considered a special type of material. Walls made of it should be well ventilated and less in contact with moisture. Therefore, not all types of heat insulators are suitable for wooden buildings. Mineral wool or penoizol is most suitable for this purpose.
"Polyfoam for insulation wooden house cannot be used. It will prevent the tree from "breathing" normally. As a result, condensation forms on the walls, which will lead to the appearance of fungus and mold, the wood will begin to rot.”
Mineral wool
It has a fibrous structure, is made from molten glass with the addition of rock. Is different good set characteristics:
- easily withstands high temperatures;
- unaffected by chemicals;
- low thermal conductivity;
- excellent sound insulation;
- elasticity, ease of installation;
- environmental friendliness;
- service life within 30-80 years.
Available in rolls or slabs. Roll insulation is more often used for large buildings, and slabs for small houses. Does not require additional fixation.
 Mineral wool
Mineral wool
“When working with it, it is imperative to use protective clothing and a mask.”
Rodents do not eat this material, but if you do not cover it with trim from above, they can settle in it. Mineral wool can be used to insulate houses made of wooden beam and frame technology.
Prices for mineral wool
Penoizol
The texture resembles ordinary foam, but the mechanism of action is similar to that of mounting foam. The material is applied to a special frame. During the day it dries up and becomes hard.
 Penoizol
Penoizol
Penoizol features:
- average level of vapor permeability;
- completely fireproof - it can extinguish itself in case of fire;
- not afraid of moisture;
- during installation, it fills the existing voids.
To work with this material, you will need special tools.
What are the dimensions of the heater
 Insulation dimensions are an important criterion
Insulation dimensions are an important criterion
What is the heater
The main criterion for choosing the size of a heat insulator is its thickness. Length and width do not play a big role. They are taken into account only when calculating the required amount of materials. The dimensions of the insulation depend on its belonging to a particular type.
Table 3. Insulation dimensions:
| Name | Thickness | Length | Width |
|---|---|---|---|
| Styrofoam | 20-100 mm | 500-2000 mm | 1000 mm |
| Penoplex | 20-100 mm | 1200-2400 mm | 600 mm |
| Mineral wool | 46-214 mm | 1176 mm | 566-614 mm |
| Izolon | 3.5-20mm | from 10 m | 600-1200 mm |
| Arbolit | 250 mm | 500 mm | 200-400 mm |
| Chipboard | 10-22 mm | 1830-2800 mm | 20170-2620 mm |
| Fiberboard | 30-150 mm | 2400-3000 mm | 600-1200 mm |
When buying materials, you need to pay attention to the area of the roll or plate. Usually it is indicated on the packaging. To calculate how much insulation you need, you need to do the following:
- Calculate the perimeter of the building - add the length and width. Multiply this amount by 2.
- Measure the height and multiply this value by the perimeter of the house.
- The resulting value is divided by the area of one roll or plate.
- Multiply this number by 0.15.
 House insulation
House insulation
To reduce heating costs and keep heat in the house for a long time, you need to choose a high-quality heat insulator. If you need to insulate the house from the outside, it is better to use inorganic materials - they are less exposed to the external environment.
Video - How to insulate the facade of a house without experience, with your own hands
For interior decoration, heaters from natural materials. Knowing specifications of each type, you can easily choose the best option for a heat insulator for your home.
Nowadays, choosing the right insulation for your home is a rather difficult task. There are a huge number of types of heaters. But all this diversity faces one task - to ensure the maximum preservation of heat inside the room in winter, and in the summer, on the contrary, to prevent penetration as much as possible. warm air from the street.
Variety of heaters
The insulation must ensure the constancy of the microclimate inside the room at any time of the year. It must be said right away that in nature there is not yet a single ideal insulation that would be suitable for both external and internal insulation, was effective in any climate and at the same time cost mere pennies.
Each heater has its pros and cons. Therefore, the choice of a particular type is always determined by a number of initial conditions. And perhaps the most important condition in this case is the financial capabilities of a particular person. Someone can afford expensive cork panels or polyurethane foam coating, while someone is forced to be content with free sawdust from the nearest sawmill. The reality is that, despite the abundance of modern insulation materials, sometimes old, time-tested methods of insulation work no worse, and in some cases much more efficiently than their modern expensive counterparts.
physical characteristics
All heaters have certain physical properties, by which it is possible to determine in advance how effective this or that type is and how much its use is justified under given conditions. Knowing these indicators greatly simplifies the task of choosing a specific material from the variety that modern retail. It is important to know what properties heaters have, namely:

Classification of heat insulators
There are a lot of classifications depending on which specific property in this case is the main one when choosing one or another heat insulator. For example, they can be classified according to their density, thermal conductivity, material of manufacture, application method, heat saving method, flammability, etc.
The classification according to the heat saving mechanism is the most comprehensive, as it covers almost all types of heat insulators. Effective heat saving is carried out through the use of a heat insulator with low thermal conductivity or a thermal insulator capable of reflecting infrared radiation back into the room.
- Thermal insulators of the preventing type of organic or inorganic origin.
- Reflective thermal insulators.
organic heaters
- chemical inertness.
- Environmental Safety.
- Good fire resistance.
- Relative cheapness.
- Good mechanical strength.
- High moisture resistance.
Often they are used as intermediate layers in multilayer structures, for example, in sandwich panels. The main representatives of these heaters are:
Arbolit or wood concrete
 Wood chips are used as a binder cement mixture and special additives that neutralize the sugars in the wood and thereby make the composition more durable. This type of insulation can be used not only as a heat insulator, but, given its good strength characteristics, it can be used as an independent structural material with very good thermal insulation properties.
Wood chips are used as a binder cement mixture and special additives that neutralize the sugars in the wood and thereby make the composition more durable. This type of insulation can be used not only as a heat insulator, but, given its good strength characteristics, it can be used as an independent structural material with very good thermal insulation properties.
This type of heat insulator is environmentally friendly, as it does not contain potentially harmful substances.
Expanded polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Heat-insulating foam obtained by porousization of polyvinyl chloride resins. It has low flammability. Belongs to the group of slow-burning and hardly flammable materials. Environmentally very controversial material, since the combined chlorine in its composition can be released in the form of hydrogen chloride if corrosion occurs metal surfaces that are in contact with this heat insulator.
Chipboards (chipboard)
95% consist of wood chips, the remaining 5% percent are adhesive resins and water repellents. For greater resistance to environmental influences, chipboard boards are treated with antiseptics. Thermal conductivity is slightly lower than that of wood concrete. One variety is fibreboard (MDF), which is less durable than chipboard.
polyurethane foam
 This environmentally friendly thermal insulator is the reaction product of two highly toxic substances: a diisocyanate and a polyol. A feature of this insulation is that it is prepared directly at the construction site and immediately applied to the surface to be treated. The material is environmentally absolutely safe and, given the method of application by spraying, is able to penetrate into all hard-to-reach places.
This environmentally friendly thermal insulator is the reaction product of two highly toxic substances: a diisocyanate and a polyol. A feature of this insulation is that it is prepared directly at the construction site and immediately applied to the surface to be treated. The material is environmentally absolutely safe and, given the method of application by spraying, is able to penetrate into all hard-to-reach places.
In the West, this highly efficient insulation has been successfully used for several decades. It has just appeared on the market in our country and is not yet known to everyone. Of the negative qualities, perhaps, only one can be distinguished: its high price.
Fiberboard
According to its characteristics, it is very similar to wood concrete, since the heat-insulating basis of this insulation is the so-called wood wool, which is narrow strips of wood shavings. Cement is used as a binder. Special additives from liquid glass and calcium chloride make it unable to burn with an open flame. Depending on the brand of cement, fibrolite is divided into heat-insulating (F-300) and heat-insulating-constructive (F-500).
 The second name is ecowool. 80% consists of shredded newsprint, 20% - non-volatile flame extinguishing agents. As the latter, boric acid and borax are used. Thanks to these additives, the insulation can withstand open fire well. It has very good thermal insulation properties. The main disadvantage is that after several years of operation, ecowool becomes caked, loses up to 20% of its volume and partially loses its heat-saving properties.
The second name is ecowool. 80% consists of shredded newsprint, 20% - non-volatile flame extinguishing agents. As the latter, boric acid and borax are used. Thanks to these additives, the insulation can withstand open fire well. It has very good thermal insulation properties. The main disadvantage is that after several years of operation, ecowool becomes caked, loses up to 20% of its volume and partially loses its heat-saving properties.
Cork heat insulator
It is used mainly in the form of cork panels for internal insulation of floors and walls. The cork oak bark serves as a heat-insulating base. The same bark contains natural glue suberin, which eliminates the use of artificial adhesives. From the point of view of ecology, it is the safest insulation, resistant to decay, not eaten by insects. The best insulation for floors and walls. The only downside is the high price.
Inorganic heaters
Various mineral components are used as a heat insulator. For example, glass, slag, rocks, asbestos, etc. After special processing, these components acquire pronounced heat-saving properties. The main properties of such heaters are:
- High fire resistance.
- Environmental Safety.
- Long service life without loss of thermal insulation properties.
- chemical inertness.
Mineral wool
In addition to excellent thermal insulation properties, it has a pronounced resistance to high temperatures and chemicals. There are three varieties depending on the initial products of production:
- Glass wool.
- Slag.
- Stone wool.
- Basalt wool.
 Glass wool is a material consisting of fibers 15–50 mm long and 5–20 microns wide. For the production of fibers, waste from the glass industry is used.
Glass wool is a material consisting of fibers 15–50 mm long and 5–20 microns wide. For the production of fibers, waste from the glass industry is used.
In other words, in the case of glass wool, we are dealing with glass needles of microscopic thickness. This causes one of the most unpleasant properties this material: in case of contact with the body, persistent skin itching occurs, contact with the eyes threatens serious problems with vision, and getting into the lungs causes inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system. At the same time, glass wool has very good thermal insulation properties, is chemically absolutely inert, and has high strength characteristics.
Slag wool is produced from blast-furnace slag. It has fibers of medium size: length 10-16 mm, width 4-12 microns. Like glass wool, it is quite scratchy and irritating to the skin. It has a very high hygroscopicity, absorbs water well, which makes it unsuitable for external insulation. In addition, in a room with high humidity, it can exhibit increased corrosion aggression in relation to metals due to the residual slag acids contained.
 Stone wool is obtained from rocks by heating the latter to 1500 degrees and subsequent stretching in the form of thin fibers. In terms of its heat-saving properties, it is approximately the same as the other two, but, unlike glass wool or slag wool, it has one significant advantage: stone wool fibers do not splinter, so it is much safer to work with it.
Stone wool is obtained from rocks by heating the latter to 1500 degrees and subsequent stretching in the form of thin fibers. In terms of its heat-saving properties, it is approximately the same as the other two, but, unlike glass wool or slag wool, it has one significant advantage: stone wool fibers do not splinter, so it is much safer to work with it.
Basalt wool does not contain any other components in its composition, except for basalt. This makes it the most environmentally friendly of all four types of mineral wool.
reflective type
 Relatively new reflex heat insulators of a fundamentally different type of action. The basis is the ability of these materials to slow down thermal convection. The absorbed heat is then re-radiated into the surrounding space with the help of infrared radiation. Reflective heat insulators are capable of retaining up to 97% of thermal energy due to their reflective surface. Heat insulators of this type include the following:
Relatively new reflex heat insulators of a fundamentally different type of action. The basis is the ability of these materials to slow down thermal convection. The absorbed heat is then re-radiated into the surrounding space with the help of infrared radiation. Reflective heat insulators are capable of retaining up to 97% of thermal energy due to their reflective surface. Heat insulators of this type include the following:
- Penofol.
- Armophon.
- Porilex.
- Ecofol.
These are very effective heaters, for example, 4 mm thick foam foam corresponds to 10 cm thick mineral wool in terms of heat-saving properties. The types of wall heaters are primarily determined by this list, since reflective heat insulators are most effective for interior walls and ceilings.
Wide range of heaters for wooden houses, they can insulate the house outside, and some even inside the house. Which types are suitable for frame house? Which is the best, consider their characteristics in this article! Correctly carried out will not be superfluous in any climatic conditions.
When it is done correctly, then under its “protection” it will not only be warmer in the house in winter, but also noticeably cooler in summer.
Installation of insulation will create a comfortable microclimate in a room for any purpose - in a residential building, office or production workshop.
In addition, saving heat is an obvious financial savings. It is completely unreasonable to heat the street, despite the fact that the technologies used today provide an opportunity to start saving energy resources at an early stage. construction works. Most of all, those parts of the building that are more adjacent to the external environment need the use of heaters -, and.
The material produced in this way has excellent properties, besides it is not combustible, and therefore does not pose a fire hazard. But a huge part of the wonderful qualities of a heater can be irretrievably lost when it gets wet. This should be taken into account.
Cotton wool stone
 stone wool
stone wool This is a fibrous material that goes on sale in the form of rolls and portioned plates, and has an extremely low thermal conductivity.
The highest quality product is made from rocks called gabbro-basalt. This non-combustible material is used with equal success in the construction of private facilities and the construction of various production facilities. A wide range of use is also explained by the possibility of its use at extremely high t, reaching a rate of one thousand degrees.
The insulation's complete immunity to fire is complemented by its excellent moisture resistance. This is a hydrophobic material, the peculiarity of which is that it does not absorb water, but repels it.
This ensures that the insulation remains dry even after a long period of time. This, in turn, will allow her to maintain her high working qualities. The unique properties of basalt wool make it possible to use it even in boiler rooms, baths and saunas, where both high humidity and high temperature are combined. Strength in this case is not directly dependent on the density of the material.
This is a fairly soft material, while having a sufficient margin of safety. Its structural stability is due to the special arrangement of the individual constituent fibers - chaotic and vertical. The material has high anti-corrosion properties.
It can quite peacefully coexist with concrete and metal, without the occurrence different kind chemical reactions. High biological stability provides him with immunity to various biological pests: damage by insects and rodents, the occurrence of fungal diseases,
 The basalt insulation passed the combustion test, but the organic heaters burned out
The basalt insulation passed the combustion test, but the organic heaters burned out Basalt rock is the main raw material for the production of this type of wool.. Treatment with formaldehyde resins gives the material a sufficient level of strength, and the materials used modern technologies guarantee the complete elimination of harmful phenols even at the stage of material production.
The final product that reaches the consumer is a harmless and environmentally friendly material with high insulating qualities.
It is actively used for warming floors of residential and industrial premises, for thermal insulation of roofs and facades, including as an external insulation.
It has found wide application in rooms with extreme levels of humidity and temperature. The best basalt insulation, stone wool made from rocks is a guarantee of high quality for a long time.
Glass wool
 The missing 7% is accounted for by specially added flame retardants. Insulation fibers contain lignin, which becomes sticky with increasing humidity. All elements included in the insulation are non-toxic, absolutely non-volatile and harmless to health. Cellulose insulation is not amenable to combustion, rotting processes, has excellent soundproofing and heat-insulating performance.
The missing 7% is accounted for by specially added flame retardants. Insulation fibers contain lignin, which becomes sticky with increasing humidity. All elements included in the insulation are non-toxic, absolutely non-volatile and harmless to health. Cellulose insulation is not amenable to combustion, rotting processes, has excellent soundproofing and heat-insulating performance.
It can retain approximately 20% humidity while maintaining its working qualities. The material releases moisture to the outside and dries quickly, retaining all its performance. The disadvantage of ecowool can be considered the difficulty of its manual application to the surface, as well as the impossibility of arranging a "floating floor" due to its inherent softness.
Penoizol
Another name for the material is carbamide foam. it modern material with high sound and heat insulating characteristics, which is a cheap insulation. It is a cellular organic foam with particularly low density and low thermal conductivity. The material has a high resistance to fire, resistance to microorganisms, low price. It is easy to handle and has an air content of up to 90%.
 Insulation of the attic with penoizol
Insulation of the attic with penoizol The tests carried out demonstrated the capabilities of the material. It turned out that the time of its operation, as the middle layer of the structure of the frame structure, is actually not limited by anything. Tests of its fire resistance showed that the material can be safely classified as slow-burning.
This is the only heat-insulating material of polymer nature used, which is not at all adapted to self-combustion. Its fire resistance index refers it to the G2 flammability subgroup.
Even if the highest temperature occurs during a fire, when the metal begins to melt, the carbide foam will only evaporate, and without releasing toxic or harmful substances.
Isocom
This is a special foil material (on both sides or only on one). It is a fabric made of polyethylene foam, covered on the outside with a highly polished aluminum foil. This is a multi-layered vapor, sound and heat insulating material that combines completely different qualities.

With a minimum thickness of the insulating layer, it provides excellent properties of reflection of the heat flow, successfully combined with the highest (almost maximum) thermal resistance. Properly installed material is characterized by exceptionally effective thermal insulation of the building along its entire contour.
It is a harmless, environmentally friendly material that does not pose a threat to the ozone layer. It does not contain glass or other fibers that are unsafe for human and animal health.
Without changing its exceptional properties, it serves for about 50 years, without deforming or being damaged during all this time.
Installation is quite simple and very convenient: it does not require special equipment. Excellent protection against steam and moisture. Used almost everywhere.
Thermal insulation of house structures in different quantities is needed for all temperature conditions from the equator to northern latitudes. To date, there are so many materials that retain heat in the premises that when choosing among them, you can get confused and choose not what you need. Next, we will consider the most popular and effective types of heaters, compare their characteristics and determine the scope of each of them.
Classifications
Thermal insulation materials can be divided into groups according to different criteria. For example, in terms of composition:
- Organic heaters made on the basis of natural components (fibreboard, cork);
- Synthetic materials created by chemical reactions (all polyethylene, polyurethane materials);
- Mineral wool.
Types of insulation for the home can also be divided by resistance to external precipitation and other influences. This will determine the scope of the material:
- For internal applying;
- For external thermal insulation.
It should be noted that only materials that do not absorb water in any way are suitable for outdoor use. Their fibers must repel moisture, and the pores in the insulation must be closed. These include all types of polyurethane foams, polyethylene foam, foam plastic.
Types of insulation for walls inside should, first of all, let steam through so that it does not linger in the room. Otherwise, moisture accumulates in the rooms, condensation forms, and pockets of mold colonies spread. The material must be safe for others (odorless, toxic fumes, if possible with a high ignition threshold). The group will include:
- Mineral wool;
- Heaters based on cement and organic components;
- Ecowool;
- Cork.
There are much more types of insulation for walls from the inside than for external walls, because some plates that can be used to sheathe the facade are also suitable for internal insulation.
There are other, narrower classifications, for example, division by pore type:
- With closed pores (PPU, polystyrene);
- With open pores (cork, foam block).
Now we will consider each type of heat-insulating material and determine its main parameters for ease of choice.
Polymer heat-insulating materials
Synthetic thermal insulators are a large family of components for keeping your home warm.
polyurethane foam

PPU has not yet received widespread use, since surface finishing with this material is a relatively expensive process. And yet, PPU is considered one of the most effective heat insulators for several reasons:
- Light weight, only 40…60 kg/m3;
- Low degree of thermal conductivity no more than 0.025 W / m * C;
- Easy installation - spraying;
- No cold bridges with proper surface coverage;
- Low vapor permeability;
- Cheap raw materials.
The disadvantages include:
- The need for special spray equipment;
- The high cost of the work itself.
To reduce the cost of finishing, you can rent an installation machine and make a heat-insulating coating yourself, but with inept handling, the quality of work cannot be guaranteed.
When spraying, PPU is applied in a certain layer (depending on the calculated thickness), and after polymerization and solidification it turns into a porous coating that is not afraid of moisture and rodents.
PPU can be used to insulate walls, ceilings of rooms and attics.
Extruded polystyrene foam

This is a material similar in properties to conventional polyurethane foam in the form of decorated plates. It is easier to work with it - you just need to lay the blocks over the area of the insulated coating and you do not need to dry anything. Extruded polystyrene foam is sometimes called foam rubber.
PPU boards almost do not differ from their “relative” in terms of characteristics:
- Thermal conductivity is only 0.3 W / (m * C);
- Density up to 45 kg/m3;
- Vapor permeability is even lower - only 0.015 mg / (m * h * Pa).
Material advantages:
- Low price compared to the total cost of PPU;
- Simple installation, which can be done by hand;
- The lightness of the material.
Flaws:
- There are bridges of cold;
- Sealing of joints between plates is required;
- Insufficient material safety data. Like PPU, expanded polystyrene is tested for safety only in the factory.
This type of insulation for walls outside and inside fits equally well.
Styrofoam

A relative of the group of foamed thermal insulation materials made of synthetic polyester. One of the most accessible materials that contribute to the preservation of heat in the house. Represents the balls compressed among themselves with emptiness thanks to which heated air does not get outside of the room.
Advantages of foam:
- Sufficient efficiency - thermal conductivity is only 0.05 W / m * C;
- The mass can vary between 40-125 kg depending on the composition and density of the material;
- Low price on slabs;
- Easy installation.
Flaws:
- According to many sellers, foam plastic is a completely safe insulation that is not afraid of fire and does not flare up when sparks occur. This is a deep delusion: if you try to set fire to the stove in the middle, keeping it strictly on the horizon, then only the light from the candle will remain on the surface. If the ignition is started from the edge, the material will immediately begin to melt and smoke heavily. The emitted gas is very dangerous for human life.
- Lack of environmental friendliness: the foam does not breathe, there are no natural ingredients;
- Low vapor permeability contributes to the accumulation of moist air in the room. To solve the situation, it is necessary to install a ventilation system.
- A considerable degree of absorbency can fail in a frosty winter: water accumulates in the channels, where it can expand when it solidifies and turns into ice.
Styrofoam should be used for outdoor use, but it can work well indoors if needed.
Penoizol

Another name is carbamide foam. This is the same sprayed polymer material as PPU, but less expensive.
- Penoizol is able to absorb water up to 1/5 of its volume, but then it easily gives up liquid, while maintaining its shape. This allows the use of a heat insulator even in wet rooms.
- Penoizol serves up to 60 years without changing the initial characteristics.
- Low shrinkage up to 5% of the total volume.
Flaws:
- When using low-quality raw materials, you can get a result that is far from expected. For example, when drying, the foam will smell unpleasant or shrink significantly;
- Like PPU, penoizol requires special equipment for spraying.
The material is suitable for indoor use.
Mineral wool
Mineral wools are natural heaters which are received by processing of natural raw materials.
glass wool

It is based on recycled glass fibers, stretched to the state of thin threads. On sale you can find glass wool in slabs or rolls, they are the same in terms of characteristics.
Glass fiber is a safe material, moreover, it is also effective:
- The thermal conductivity of the plate is only 0.056 W / m * C;
- Density up to 100 kg/m3;
- But the vapor permeability failed - only 0.53 mg / (m * h * Pa). In other words, glass fiber easily takes on moisture, and then it is difficult to give it away.
What should be prepared in advance:
- Glass threads are fragile, so it is necessary to take the stove correctly and move it at least once from place to place;
- Shrinkage of the material occurs relatively quickly; after 10 years, the insulation becomes unusable and needs to be replaced.
Glass wool is suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, but with the condition of mandatory hydro and vapor barrier.
Mineral wool

Mineral wool is of two types:
- 1) Slag;
- 2) Stone.
Both types are produced from the remains of the stone industry. To bind the components, carbamide or phenol is used, which gives the plate a waterproof effect.
Average technical characteristics of mineral wool:
- Thermal conductivity - 0.047 ... 0.12 W / m * C;
- Density depending on origin 35…150kg/m3;
- The ability to pass steam is high - 0.51 mg / (m * h * Pa).
Like glass wool, stone wool can be used both indoors and outdoors. However, it is not recommended to sheathe living rooms with this material: blocks can emit phenol fumes.
Ecowool

This is a special type of insulation material based on cellulose and additives. Ecowool is sprayed like polyurethane foam. It lays down evenly on the surface of the wall or ceiling, after which it is necessary to allow the material to dry completely. Unfortunately, during drying, cellulose can settle down significantly, as a result of which it is necessary to carefully work out each joint, seam, correctly distribute the solution and apply it.
Advantages of ecowool:
- Low thermal conductivity up to 0.041 W / m * C;
- Excellent sound insulation: a layer up to 1.5 cm thick is able to absorb sounds up to 9 dB;
- There are no cold bridges at the joints of the supporting frame and the main parts of the building.
Flaws:
- The thermal efficiency parameter is constantly decreasing due to rapid shrinkage;
- Due to the above reason, after a few years, the upper section of the wall is exposed.
Ecowool is not suitable for insulation of facades from the outside.
Izolon

Combined material based on polyethylene foam, closed on both sides with aluminum foil. As you know, metal conducts heat well, but not in our case: the shiny layer reflects heat in the opposite direction. It turns out that the insulation will be effective only if proper styling shiny layer to the room.
Izolon is a completely safe material. They do not burn and do not support combustion, with a minimum sheet thickness, the effect of heat transfer is achieved, as is the case with conventional heaters, and does not require special installation skills.
As a rule, isolon is used indoors, including cast floors.
Fiberboard
Fiberboard is a combined material, which includes:
- wood shavings;
- A solution of cement and water;
- Liquid glass.
Insulation is produced in the form of plates, which are laid in the usual way.
The material absorbs little water, has a low coefficient of thermal conductivity.
Despite the fact that the fibrolite almost does not absorb water, the liquid that nevertheless got on the fibers evaporates for a long time, mold starts in the coating.
Fiberboard is used to assemble internal and external walls and partitions, to cover the roof, attic, floor, etc.
Cork

The cork tree is a unique representative of the flora, which provides a person with a heat-insulating material of natural origin. The removed bark is carefully prepared:
- 1) Grind in a special machine;
- 2) Add natural glue suberin;
- 3) Form plates and rolls of different thicknesses and densities.
The output is an excellent heat-insulating material for flooring, indoor walls. Cork is an exceptionally safe and environmentally friendly product that can be used to decorate children's rooms.
The appearance of the coating allows you to use it as a floor covering and insulation at the same time.
We systematize information
The types of heaters and their characteristics that we reviewed are presented in the table, where you can compare them and choose the option that suits you:
The modern market offers a huge variety of heaters of organic, mineral and synthetic origin. We examined the basic products that are most often used to preserve heat in residential and office premises.
What is a heater and how does it work? What is the thermal insulation for different types works? What is the difference between homogeneous types of insulation? Is it possible to add insulation to structural elements? Is there an alternative to conventional insulation methods? You will find answers to these and other questions in this article.
Heat loss was a stumbling block for builders in the old days. If they coped with the task of structural strength quickly (even in ancient Egypt they used an analogue of today's concrete), then the situation with heat retention was not so simple.
Lacking our current technologies, they were forced to build incredibly thick walls or intensively heat the premises from the inside. Approximately 150 years ago, a compromise was found - a durable construct of small thickness (100-300 mm) plus a heater. And if everything is more or less clear with the construct - brick, wood, concrete, then there are a great many heaters today. They will be discussed.
How does a heater work
The best and most affordable heat insulator is air. Strictly speaking, this is a rarefied gas, the molecules of which are relatively far from each other - many times further than those of denser materials (stone, water, wood). Due to this, the ability to receive (heat capacity) and transfer (thermal conductivity) heat from the air is very small.
This suggests an "elementary" solution - to insulate the surface with a sealed shell filled with atmospheric air. This method will not withstand even a theoretical test - the cold surface of a denser medium (shell) will create heat exchange between itself and the air in contact with it, air will begin to move in the shell, it will begin to mix and eventually the temperature will even out. Plus, there is condensation. And the sealed case of the capsule will be an excellent cold bridge.
What needs to be done to make the air work
The problem described above is solved by "immobilizing" the air. Breaking the volume of the chamber into separate cells, the researchers achieved ever higher results. In the end, they came to the conclusion that the gas is best retained in a loose environment and fibers. The principle of keeping the air still is absolutely natural. Nature uses it in the wool of animals, in the leaves of a tree thrown down for warming the roots, in a “dome” of spruce paws covered with snow.

In order to visually classify modern heaters, we will conditionally divide them into four groups: mineral wool (plates and mats), polymer, backfill and an alternative group.
Mineral wool boards and mats
The most common type of insulation today. Has excellent operational properties and manufacturability (ease of use).
How is mineral wool obtained?
Empirically, as a result of incandescence and blowing of rocks of the gabbro-basalt group and marls, mineral (stone) wool was obtained. When using raw materials with a high content of silicon, the cotton wool fibers partially vitrified and the so-called glass wool was obtained - inconvenient to work with and harmful to health. However, its thermal insulation properties were at the proper level. It was a transitional stage in the evolution of technology, which was subsequently improved. Until today, the principle of obtaining stone wool has not changed, but it has become safer and more convenient to work with (due to the combination of raw materials). All stone wool products are non-combustible and vary in density.
Interesting fact. Produced in a similar way cotton candy, only ordinary sugar is used instead of rock.
Mineral wool mats - fibers formed in the form of a mat 50 or 100 mm thick. Initially they were stitched. Designed for laying on horizontal surfaces with a slope of no more than 45 degrees.

Mineral wool slabs - fibers formed in the form of a slab with a thickness of 50 or 100 mm and dimensions of 500-600x1000-1200 mm. It differs from the mat in greater density, due to which the slab is more rigid and is not subject to vertical settlement and clumping.

Scope: any kind of "dry" insulation of residential and industrial buildings. Floors, walls, ceilings, roofing. Ideal insulation for frame houses.
Interesting fact. Why are most mineral wool boards 600 mm wide? This type of insulation came to us along with " Canadian technology» construction of frame houses. It provides for a distance between the wall studs and the floor joists of 600 mm - insulation is placed in this space without additional adjustment.
Advantages
- Fire resistance. By itself, cotton wool does not burn, but burns out, transferring heat. This requires a high temperature (from 600 ° C) and a constant supply of oxygen - the conditions for a very strong fire in the wind.
- Soundproofing. Goes as a "bonus" to thermal insulation in all materials.
- Light weight. Due to the sparseness of the fibers, as we have already found out, the main material in cotton wool is air.
- Possibility of further finishing (for slabs). The material of the plate is perfectly connected with cement adhesives, which allows them to be putty.
- Self-supporting boards. They can be fixed to the walls with dowels.
- Non-toxic. Everything that could evaporate - evaporated during production in a hot shop.
- Possibility of partial replacement of damaged sections.
Flaws
- It is afraid of moisture, requires steam and hydrobarriers. Even a small amount of water can permanently ruin the insulation area and it will have to be replaced.
- Draft, compressibility. It does not allow the use of mineral wool for insulation of screeds (pouring with concrete or mortar).

The range of prices for stone (basalt, mineral) wool insulation depending on the brand and manufacturer:
| Brand, manufacturer, volume, quadrature, number of plates in a package | Density, kg / m 3 | Sheet size, mm | Price 1 m 2, rub. | Price 1 m 3, rub. | Package price, rub. |
| mats | |||||
| Hitrock P-75 LIGHT, 0.24 m 3 / 4.8 m 2 / 8 pcs. Smolensk, Russia | 32-35 | 1000x600x50 | 66,6 | 1330 | 320 |
| TechnoNIKOL ROCKLIGHT 0.432 m 3 / 8.64 m 2 / 10 pcs., Russia | 30-37 | 1000x600x50 | 69,5 | 1390 | 600 |
| IZOBEL PL-75 0.24 m 3 / 4.8 m 2 / 8 pcs. Belgorod, Russia | 35-37 | 1000x600x50 | 73,0 | 1460 | 350 |
| ROCKWOOL LIGHT BATTS 0.3 m 3 / 3 m 2 / 5 pcs. Denmark (factories in Russia) | 35-37 | 1000x600x100 | 173 | 1730 | 520 |
| ISOROC ISOLIGHT-L, 0.24 m3 / 4.8 m2 / 8pcs. TZMM Tambov, Russia | 35-37 | 1000x600x50 | 87,5 | 1750 | 420 |
| TechnoNIKOL 40 0.48 m 3 / 4.8 (9.6) m 2 / roll, Russia | 11-13 | 4000x1200x50 (100) | 60 (118) | 1190 | 570 |
| Isover Classic-Twin-50 0.37 m 3 / 7.4 m 2 / roll France (factories in Russia) | 11-13 | 6150x1200x50 | 60,8 | 1220 | 450 |
| Ursa GeoM-11 F (foil) 1.08 m 3 / 10.8 m 2 / roll, Spain | 11-13 | 9000/1200/100 | 266 | 2660 | 2880 |
| Plates | |||||
| TechnoNIKOL Rocklight 0.432 m 3 / 8.64 (4.32) m 2 / 10 (5) pcs., Russia | 30-37 | 1200x600x50 (100) | 80 (160) | 1600 | 690 |
| ISOLIGHT-L-150 0.27 m 3 / 1.8 m 2 / 3 pcs., Russia | 40-42 | 1000x600x150 | 245 | 1630 | 440 |
| IZOVOL ST-50 0.3 m 3 / 6 m 2 / 5 pcs., Russia | 50-52 | 1000x600x50 | 95 | 1900 | 570 |
| ROCKWOOL ACOUSTIC BATTS 0.3 m 3 / 6 m 2 / 10 pcs., Denmark (factories in Russia) | 45-47 | 1000x600x50 | 105 | 2100 | 630 |
| URSA P-20- U 24 0.9 m 3 / 18 m 2 / 10 pcs., Spain | 40-42 | 1250x600x50 | 110 | 2220 | 2000 |
| Hitrock P-75 0.27 m 3 / 5.4 (2.7) m 2 / 10 (5) plates, Smolensk, Russia | 62-66 | 1000x600x50 (100) | 120,3 (240,7) | 2400 | 650 |
Polymer insulation
The two most popular types of polymer insulation are polystyrene foam or expanded polystyrene (PP) and its derivative, extruded polystyrene foam (EPPR). They are obtained by extrusion (squeezing raw materials through a hole of a given shape).
Polyfoam (expanded polystyrene) - foamed polyethylene in the form of a sheet with a thickness of 15-200 mm and dimensions of 1000-1200x500-1200 mm. Varies in density.

Advantages (compared to EPPR): low price
Disadvantages: looseness, even dense PP is not used for insulation of screeds.
The dependence of the price of polystyrene on the brand and purpose on the example of products from Knauf, Germany:
| Name | brand | Sheet size, mm | Packing volume, m 3 | Package price, rub. | Price 1 m 3, rub. |
| Knauf Therm Compact | 15 | 1000x600x50 | 0,3 | 660 | 2200 |
| Knauf Therm 15-T (for unloaded structures) | 15 | 1000x1200x50 | 1,2 | 1700 | 1400 |
| Knauf Therm 25 (for building insulation) | 25 | 1000x1200x50 | 1,2 | 2800 | 2330 |
| Knauf Therm Facade 25 (for plaster facades) | 25 | 1000x1200x50 | 1,2 | 3280 | 2730 |
| Knauf Therm 35 for building insulation | 35 | 1000x1200x50 | 1,2 | 4200 | 3500 |
| Knauf Therm Floor for floors and foundations | 35 | 1000x1200x50 | 1,2 | 4500 | 3750 |
| Knauf Therm F (5 in 1) for foundations, plinth, blind area, roofing on rafters | 35 | 1000x600x50 | 1,2 | 5200 | 4330 |
Extruded polystyrene foam is a gas-saturated polyethylene melt. It has the form of a sheet with a thickness of 30-70 mm and dimensions of 500-600x800-1400 mm. Varies in density and color.

Advantages (compared to PP):
- Significantly stronger than PP. Suitable for pouring concrete.
- It has an adapted tongue-and-groove system along the edges, which creates an overlap connection - it does not require filling joints.
- Less thermal conductivity.
- Combined purpose - can serve as an element of waterproofing.
Disadvantages: higher price.
Approximate prices for extruded polystyrene foam using the example of PENOPLEX products:
General characteristics for PP and EPPR
Advantages:
- Fire resistance. The material is foamed and saturated with carbon dioxide
- Light weight (10-15 kg/m3)
- Wide distribution. Simplified technology allows even a handicraft way to obtain material of acceptable quality.
- Not afraid of moisture
Flaws:
- Fusibility. The material is afraid of high temperatures (from 80 ° C)
- When melted, toxic
Scope: polystyrene foam and expanded polystyrene - an excellent insulation for frame houses, brick and concrete buildings, foundations. Acts as a waterproofing element.

Interesting fact. Styrofoam and extruded polystyrene foam with a thickness of 50 mm or more have a stable temperature of +5 °C. That is, in any frost, the temperature inside the sheet will be positive.
Backfill insulation
The most striking example of the history of the use of this type of thermal insulation is infill wooden panels for the construction of prefabricated low-rise buildings in the USSR. They were covered with sawdust, which at that time was an absolutely justified decision: literally everything household products from knife handles to window frames- made of wood. A huge amount of waste was disposed of with benefit. Other wastes (shingles, slabs, trimmings) were also thrown onto these shields, many of these houses are still inhabited.
Today, backfill insulation greatly loses in ease of use to wool and polyethylene slabs. However, it has one insurmountable advantage - it can be mixed with wall and floor material, thus introducing insulation into the structure. The most popular types are expanded clay, vermiculite and foam ball.
Expanded clay
An artificial stone obtained by firing clay.
Properties: granules 5-30 mm. Density 350-600 kg/m 3 . Not afraid of moisture, organics. Has a low bearing capacity. Does not require vapor barriers. Not combustible, does not sink in water.
Application: in a dry way - backfilling of sinuses, lag of a wooden floor and ceilings. Wet way- mixing with mortar, concrete (insulation screeds).

The price of the issue - expanded clay in bags M-450 fraction 10-20 (packing of 0.043 m 3 per bag) costs about 150-180 rubles per bag. There are about 25 bags in 1 m 3 and the price is 3750-4500 rubles, respectively.
Vermiculite
Natural stone (mineral), mined in quarries.
Properties: granules 1-5 mm. Density 350-750 kg/m 3 . Properties coincide with expanded clay. It is an adsorbent (absorbs odors).

Application: the same as expanded clay. When insulating walls and ceilings, it is first placed in a geotextile bag, the bags are laid in place.
Issue price - 1 m 3 of vermiculite costs about 5000 rubles.
Styrofoam ball
Frozen individually pores of expanded polystyrene. They are usually mixed with mortars and concrete during the installation of starting and load-bearing screeds. They are also added to raw materials in the production of small-piece concrete blocks for construction. Improves thermal insulation, while reducing the bearing capacity.

The price of the issue - the cost of 1 m 3 of the ball ranges from 1300-1600 rubles.
Alternative group (old)
In this group we will include all other materials that can be used as insulation, and simply list them. Basically it is a natural raw material. It should be noted that all these materials are absolutely environmentally friendly and harmless to humans.
Sawdust and straw: keep air from moving and heat transfer. They can be filled or laid between floor or ceiling joists. In a mixture with dry clay, they perform an additional vapor barrier function. To make building blocks, they are mixed with raw clay and shaped. A solution of clay with sawdust is used for plastering (coating) walls.
Reeds: dry reed cobs are laid in the manner of mats.
Moss: make up for local warming - plugging sinuses and crevices, caulking log cabins. Absolutely not subject to decay, but weathered. Exceptionally flammable.
Turf: placed directly on the roof. Requires waterproofing (usually clay).

Ash slag or "buzzer": by-product of roasting (fuel combustion waste). It has characteristics similar to expanded clay, but of much worse quality. It is poured dry and mixed with clay and cement mortars.
The asking price is free.
Alternative group (modern)
Here we will give one, but an advanced method of insulation - spraying polyurethane foam. The essence of the method boils down to the fact that the insulation is "manufactured" on the spot, immediately before being applied to the surface. With the help of a special machine, the raw material (polymer) is dissolved and mixed with air - liquid polyurethane is obtained. This method is actively gaining market positions as a convenient and high-quality insulation for frame houses and cottages, walls and roofs of any design. The process is completely identical to applying mounting foam with a gun.

The price of the issue is the cost of 1 m 2 (up to 100 m 2) of spraying hard polyurethane foam with a layer thickness of 50 mm - 650 rubles or less, depending on the volume. The same price will cost the application of light polyurethane foam 100 mm thick.