Entrepreneurial policy. Entrepreneurship motivation policy: goals, objectives, economic feasibility of development and application
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Similar Documents
The essence of small and medium business as an object of state regulation at the federal level. Analysis of the state of small business in Chelyabinsk region, the functions of the Ministry of Economic Relations in regulating its development.
term paper, added 03/10/2012
The policy of state support for entrepreneurship. Organization of state activities to support business. Economic mechanisms of business regulation. Problems of development of small businesses, development of a mechanism for their support.
term paper, added 07/20/2012
Stages of development of entrepreneurship. Essence and functions of entrepreneurship. Types of entrepreneurship. An objective basis for distinguishing types of entrepreneurship. Enterprise and its types. Creation and legal registration of a new enterprise.
term paper, added 04/11/2004
Legal characteristics of entrepreneurship and trade. Sources of legislation regulating this activity. Types of offenses in the field of business and trade, forms and methods of combating them, determining responsibility for them.
thesis, added 12/16/2011
Concept and characteristics entrepreneurial activity, its subjects and objects, forms and types of implementation. Rights and obligations, types of responsibility of business entities. Reflection of the legal norms of entrepreneurship in the legislation.
abstract, added 12/15/2010
The concept of entrepreneurship, types, the need for state support. Legal Framework development of entrepreneurship in Russia. Analysis of regional business support policy. Institutional framework for business development support.
term paper, added 01/10/2014
The concept of individual entrepreneurship and entrepreneurial activity. The procedure for state registration and licensing of an individual entrepreneur, his responsibility, the taxation system. Analysis of the development of small business.
term paper, added 10/07/2013
The success of the company is determined by the knowledge of the needs of the market and the fruitfulness of the entrepreneurial economic initiative of the managers and their staff.
Economic initiative- these are independent actions of the company's personnel aimed at obtaining a given result. The initiative, in turn, is a function of the target setting, determined by the firm itself or imposed on it from the outside, including by order of a higher economic body or the requirements of shareholders. To achieve this goal, the staff carries out a comprehensive analysis of the internal potential of the company and the state of the external environment in which it operates, and, First of all, the analysis
physical and moral depreciation and the structure of the production capacity of the company;
personnel and their qualifications;
the company's finances and leverage opportunities;
conjuncture of the market segments of interest to the company.
Based on the data obtained, the most appropriate direction of activity and the development strategy of the company are determined. Company priorities, short-term tasks and long-term goals of the company as a whole and its divisions are established. The tactics of behavior of specialists and managers is built, aimed at achieving the strategic goal of the company and the formation of its priorities.
Target – this is a specific end state or desired result that the firm (a group of people or an individual) seeks to achieve.
Priorities - these are the main values adopted by the company in its activities for the period of movement towards the goal, expressed in the form of an idea (for example, the creation and production of a new product) or tactics of behavior in order to conquer sales markets. Most often, priorities are expressed in specific indicators: quality characteristics goods, financial resources and their distribution. For example, top priorities might be:
maximum return on invested capital;
minimum costs for the production of specific products;
elimination of dependence on some external factors (deliveries of raw materials, materials, services, etc.);
high product quality as a guarantee of expansion (or retention) of sales markets.
Politics – these are forms and methods of tracking and maintaining priorities in order to achieve the main goals of the firm. On the basis of the established goals, priorities and developed policy of the enterprise, the main directions of activity of its structural divisions and officials responsible for obtaining the intended results, and their specific tasks are determined.
In general, the choice of company objectives is influenced mainly by the following factors:
availability and volume of demand for products;
availability of own material and financial resources;
level of profitability;
the capital intensity of products, which is determined on the basis of two parameters (the minimum amount of initial capital required to organize the production of this type of product and the ratio of the average annual cost of means of production to the cost of products produced during the year);
availability of suppliers of raw materials, materials, components and equipment necessary for the manufacture of products;
availability of engineering solutions for the release of new or modified products;
availability of qualified personnel.
In all cases, each entrepreneur takes into account:
presence of competitors and their intentions;
the degree of international relations in the field of trade in products of interest to him;
availability of land for construction and possible expansion of the enterprise;
type and capacity of transport communications;
Availability of utility and other infrastructure to service the existing enterprise.
Accounting and analysis of the main factors of the enterprise's activity are necessary in order to avoid future losses of funds and time that can lead to bankruptcy.
The success of an enterprise is determined by the knowledge of the needs of the market and the fruitfulness of the entrepreneurial economic initiative of the leaders of the enterprise and its personnel.
An economic initiative is an independent action of the enterprise personnel aimed at obtaining a given result. The initiative, in turn, is a function of the target setting, determined by the enterprise itself or imposed on it from the outside, including by order of a higher economic body or the requirements of shareholders. To achieve this goal, the personnel of the enterprise analyzes the internal potential of the enterprise and the state of the external environment in which it operates.
Based on the data obtained, the most appropriate direction of activity and the development strategy of the enterprise are determined. Firm priorities, short-term tasks and long-term goals of the enterprise as a whole and its divisions are established. The tactics of behavior of specialists and managers is built, aimed at achieving the strategic goal of the enterprise and the formation of its priorities.
A goal is a specific end state or desired result that an enterprise (a group of people or an individual) seeks to achieve. Priorities are the main values adopted by the enterprise in its activities for the period of movement towards the goal, expressed in the form of an idea (for example, the creation and production of a new product) or tactics of behavior in order to conquer sales markets. Most often, priorities are expressed in specific indicators: the qualitative characteristics of the product, financial resources and their distribution. For example, top priorities might be:
1) maximum return on invested capital;
2) minimum costs for the production of specific products;
3) elimination of dependence on some external factors(deliveries of raw materials, materials, services, etc.);
4) high quality products as a guarantor of expansion (or retention) of sales markets.
The choice of priority is largely determined by the goal, as well as the state of the internal and external environment of the enterprise. The chosen priorities necessarily acquire a specific form of cost or technical indicators the work of the enterprise and its divisions or instructions for personnel in the form of instructions, orders. After that, control over compliance with these indicators and orders is established.
Entrepreneurial policy is the forms and methods of tracking and maintaining priorities in order to achieve the main goals of the enterprise. Based on the established goals, priorities and developed policy of the enterprise, the main activities of its structural divisions and officials responsible for obtaining the intended results, and their specific tasks are determined (Appendix B, Fig. 2).
The dominant goal of industrial enterprises is to receive and increase income, since only with the availability of financial and material resources derived from income, the enterprise is able to function normally and solve the problems of maintaining production, increasing output, systematically updating and improving quality, and reducing costs. Solving social issues, such as increasing the level of remuneration of staff and creating favorable conditions work at the enterprise is also associated with additional costs, which can be carried out only with additional income in excess of current costs. Of course, the choice and specification of the goals of the enterprise are largely determined by the interests and needs of its owner (including the state), the size of its capital, as well as the action of various internal and external factors. The interests of private individuals and state bodies can be not only different. The state, unlike a private owner, can cover losses through taxes from other efficiently operating enterprises. However, the behavioral motives of the largest associations may partially or completely coincide with the interests of the state in their close interaction.
In general, the choice of goals of enterprises is influenced mainly by the following factors: Volkova O.I., Devyatkina O.V. Economics of the enterprise (firm): textbook. M.: INFRA-M 2007. p.76
1) the presence and volume of demand for products;
2) availability of own material and financial resources;
3) the level of profitability, which is defined as the ratio of the price of manufactured products to its cost;
4) the capital intensity of products, which is determined on the basis of two parameters ( minimum amount initial capital; the ratio of the average annual cost of means of production to the cost of products produced during the year);
5) availability of suppliers of raw materials, materials, components and equipment necessary for the manufacture of products;
6) availability of engineering solutions for the release of new or modified products;
7) availability of qualified personnel.
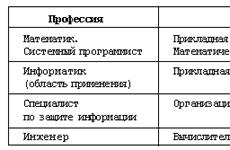
In private entrepreneurship, the choice of the main priorities and goals is significantly influenced by the profession of the entrepreneur, his inclinations and family traditions. In all cases, each entrepreneur takes into account:
1) the presence of competitors and their intentions;
2) the degree of international relations in the field of trade in products of interest to him;
3) availability of land for construction and possible expansion of the enterprise;
4) type and capacity of transport communications;
5) availability of communal and other infrastructure to serve the operating enterprise.
Accounting and analysis of the main factors of the enterprise's activity are necessary to avoid future losses of funds and time that can lead to bankruptcy.
Ketko Natalia Vladimirovna, cand. economy Sciences, Associate Professor, Department of Management, Marketing and Organization of Production, Volgograd State Technical University, Russia
Manaenkova Anna Alexandrovna, Postgraduate Student, Department of World Economy and economic theory, Volgograd State Technical University, Russia
Incentive policy of entrepreneurship: goals, objectives, economic feasibility of development and application
Publish your monograph good quality for only 15 tr!
The base price includes proofreading of the text, ISBN, DOI, UDC, LBC, legal copies, uploading to the RSCI, 10 author's copies with delivery across Russia.
Moscow + 7 495 648 6241
Sources:
1. Androniceanu A. Motivation of the Human Resources for a Sustainable Organizational Development. – Economia: Series Management. - 2011. - 14. - p. 425–438.
2. Shakhovskaya L.S., Ketko N.V. Evaluation of labor motivation of employees in the conditions market economy. - M .: Publishing and Trade Corporation "Dashkov and K0", 2012. - 112 p.
The success of an enterprise is determined by the knowledge of the needs of the market and the fruitfulness of the entrepreneurial economic initiative of the leaders of the enterprise and its personnel.
An economic initiative is an independent action of the enterprise personnel aimed at obtaining a given result. The initiative, in turn, is a function of the target setting, determined by the enterprise itself or imposed on it from the outside, including by order of a higher economic body or the requirements of shareholders. To achieve this goal, the personnel of the enterprise carries out complex analysis the internal potential of the enterprise and the state of the external environment in which it operates, and above all the analysis:
physical and moral depreciation and structure of production capacities of the enterprise;
personnel and their qualifications;
1 Taran V. A. Problems of transformation of the Russian economy. N. NovgorodNGU 1999 S. 99-1 02.
finances of the enterprise and opportunities to attract borrowed capital;
conjuncture of the market segments of interest to the enterprise.
Based on the data obtained, the most appropriate direction of activity and the development strategy of the enterprise are determined. Firm priorities, short-term tasks and long-term goals of the enterprise as a whole and its divisions are established. The tactics of the behavior of specialists and managers is built, aimed at achieving the strategic goal of the enterprise and the formation of its priorities.
A goal is a specific end state or desired result that an enterprise (a group of people or an individual) seeks to achieve. Priorities are the basic values adopted by the enterprise in its activities for the period of movement towards the goal,<енные в форме идеи (например, создание и производство нового товара) или тактики поведения с целью завоевания рынков сбыта. Чаще всего приоритеты вырах<аются в конкретных показателях: качественные характеристики товара, финансовые ресурсы и их распределение. Например, основными приоритетами могут быть:
maximum return on invested capital;
minimum costs for the production of specific products;
elimination of dependence on some external factors (deliveries of raw materials, materials, services, etc.);
high product quality as a guarantee of expansion (or retention) of sales markets.
The choice of priority is largely determined by the goal, as well as the state of the internal and external environment of the enterprise. The selected priorities necessarily acquire a specific form of cost or technical performance indicators of the enterprise and its divisions or instructions for personnel in the form of instructions, orders. After that, control over compliance with these indicators and orders is established.<ений.
Policies are the forms and methods of tracking and maintaining priorities in order to achieve the main goals of the enterprise. Based on the established goals, priorities and developed policy of the enterprise, the main activities of its structural divisions and officials responsible for obtaining the intended results, and their specific tasks are determined (Fig. 3.2).
Let's take a simple example. If, say, the traveler chooses city D as a goal, then the desired result of the trip is arrival in the city. Priorities in this case for him will be), road signs and signs. In this case, specific tasks will include a technical inspection of the vehicle before departure, refueling on the way, processing the necessary documents on the way.
The dominant goal of manufacturing enterprises is to obtain and increase income, since only with the availability of financial and material resources derived from income, the enterprise is able to function normally and solve the problems of maintaining production, increasing output, systematically updating it and improving quality, and reducing costs. The solution of social issues, such as increasing the level of remuneration of personnel and creating favorable working conditions at the enterprise, are also associated with additional costs that can only be carried out with additional income that exceeds current costs.
Of course, the choice and specification of the goals of the enterprise are largely determined by the interests and needs of its owner (including the state), the size of its capital, as well as the action of various internal and external factors. The interests of private individuals and public authorities can be not only different, but even incompatible due to the incompatibility of responsibility for the results of activities and, as a rule, the enormous difference in the amount of resources they have at their disposal. While the state can produce certain types of unprofitable products to ensure the uninterrupted supply of the country's internal needs or maintain an enterprise that does not generate income in order to save jobs for the population, an individual who takes such actions will go bankrupt. The state, unlike a private owner, can cover losses through taxes from other efficiently operating enterprises. However, the behavioral motives of the largest associations may partially or completely coincide with the interests of the state in their close interaction.
In general, the choice of goals of enterprises is influenced mainly by the following factors:
availability and volume of demand for products;
availability of own material and financial resources;
the level of profitability, which is defined as the ratio of the price of manufactured products to its cost;
the capital intensity of products, which is determined on the basis of two parameters (the minimum amount of initial capital required to organize the production of this type of product; the ratio of the average annual cost of means of production to the cost of products produced during the year);
availability of suppliers of raw materials, materials, components and equipment necessary for the manufacture of products;
availability of engineering solutions for the release of new or modified products;
availability of qualified personnel.
In private entrepreneurship, the choice of the main priorities and goals is significantly influenced by the profession of the entrepreneur, his inclinations and family traditions. In all cases, each entrepreneur takes into account:
presence of competitors and their intentions;
the degree of international relations in the field of trade in products of interest to him;
availability of land for construction and possible expansion of the enterprise;
type and capacity of transport communications;
Availability of utility and other infrastructure to service the existing enterprise.
Accounting and analysis of the main factors of the enterprise's activity are necessary to avoid future losses of funds and time that can lead to bankruptcy.