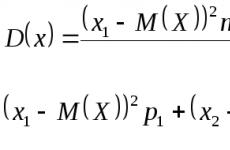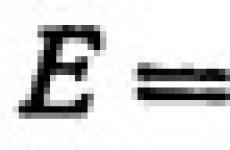Why is PCR diagnostic done in pulmonology. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) - a method of high accuracy in the detection of specific infectious agents
PCR diagnostics - what is it? The essence of the Polymerase Chain Reaction lies in the fact that markers of a special type are used to study biological material, which quickly analyze the DNA of infectious agents. In gynecology, there are different methods of PCR analyzes in women, depending on the material being studied (blood, urine, smears, etc.). After processing the data, the type of pathogen is detected (this is the so-called "PCR qualitative analysis") and / or their concentration - this type of study is called " PCR quantitative analysis".
The delivery of analyzes by PCR allows you to quickly check for pathogens of infectious pathology when it is not possible to do this with other analyzes (immunological, bacteriological, microscopy). In modern laboratory diagnostics, PCR is the most effective and The best way detecting the DNA of microbes and viruses. The test allows the gynecologist and other doctors of the clinic not only to determine the cause of the ailment in women and men, but also to control the course of the process, to correctly assess the result of the therapy.
Prices for PCR diagnostics
| Infection | PCR | Price |
| Chlamydia (Clamidia Trachomatis) | qualitative | 450 |
| Chlamydia | quantitative | 850 |
| Ureaplasma (U. urealiticum / U. parvum) | qualitative | 450 |
| Ureaplasma | quantitative | 750 |
| Mycoplasma (Mycoplasma Hominis) | qualitative | 450 |
| Mycoplasma | quantitative | 750 |
| Mycoplasma (Mycoplasma Genitalium) | qualitative | 450 |
| Mycoplasma | quantitative | 750 |
| Gardnerella (Gardnaerella vaginalis) | qualitative | 450 |
| Trichomonas (Trichomonas vaginalis) | qualitative | 400 |
| Trichomonas | quantitative | 850 |
| qualitative | 500 | |
| Gonococci (Neisseria gohorrhoeae) | quantitative | 650 |
| Cytomegalovirus (CMV) | qualitative | 400 |
| The causative agent of syphilis (Treponema pallidum) | qualitative | 500 |
| Candida (Candida albicans) | qualitative | 450 |
| Candida (Candida albicans / Candida glabrata / Candida crusei) | qualitative | 750 |
| Herpes virus type I and II (HSV) | qualitative | 450 |
| Epstein-Barr virus | qualitative | 500 |
| Varicella-Zoster virus | qualitative | 350 |
| Human papillomaviruses |
WHAT PCR SHOWS
Qualitative PCR analysis indicates the direct presence of the infectious agent in the human or animal body. You can pass both a smear of almost any localization (genitals, urethra, oropharynx, etc.), and PCR blood tests. By smear or scraping in gynecology, they check for chlamydia, urea- and mycoplasmas, herpes virus, HPV and other microbes. The result of the DNA analysis is given to the patient with the conclusion of the laboratory "detected" or "not found". In the case of a blood test, it allows you to identify HIV, hepatitis, herpes, cytomegalovirus and other microorganisms at an early stage, and in some cases, to determine their genotype and shows the number.
Quantitative PCR assays.
The study allows not only to quickly identify the desired genetic material, but also to show the concentration of their DNA (quantitative PCR method). Determination of the type and number of pathogens is important in deciding whether to prescribe treatment, especially if, for example, mycoplasma (DNA quantitation), ureaplasma typing (DNA quantitation) or, most importantly, genotyping and quantification of the viral load in analyzes for HPV infection.
PCR RESULTS
From all that has been said, it is clear what PCR analysis is and what are the advantages of this test in gynecology. Another important nuance of this diagnostic - the decoding of the result is available and convenient for a non-professional. Considering how much PCR analysis is done in the clinic, as well as the timing of the conclusion (the laboratory usually issues information in 1-2 days), this diagnostic method becomes the best choice for determining all major gynecological and other infections.
The laboratory, with a qualitative method for conducting DNA research on female and male smears, makes a conclusion of two types:
- "PCR negative" - no pathogen was found in the test material and
- "PCR positive" - RNA or DNA of a microbe or virus was found in the test.
PCR in gynecology
Indications for passing these tests in women are as follows:
- Suspicion of the possibility of infection with STIs;
- Anonymous survey;
- The presence of secretions from the genital tract, itching;
- Pain in the lower abdomen;
- Discomfort when urinating;
- Pain during sexual intercourse;
- Elevated leukocytes in the smear analysis for flora;
- The presence of erosion on the cervix;
- Planning for pregnancy;
- Problems with conceiving and bearing a child;
- Preparation for gynecological operations, IVF;
- For preventive purposes.
Where is the best place to take PCR tests in Moscow?
This type of diagnostics in gynecology refers to modern and high-tech methods. PCR tests for infections should be done in a clinic that has everything necessary to obtain full results. In our medical center, material is taken by qualified, experienced gynecologists (not average staff in the treatment room), disposable instruments and special laboratory materials are used, and samples received from patients are sent to work daily. This allows not only to obtain PCR results quickly, but also to ensure their reliability. Optionally - complete anonymity of the survey.
How much does PCR cost?
This service is provided by many medical institutions of the capital. The cost is influenced by many factors, ranging from location to internal pricing policy. However, there are objective factors that determine the average minimum figure, below which a quality and reliable service cannot be provided due to the factors mentioned. The price of PCR diagnostics in Moscow clinics for some infections is on average as follows:
- qualitative analysis of a PCR smear - 400 - 500 rubles;
- quantitative analysis of PCR smear - from 600 rubles (1 unit);
- RNA scraping diagnostics - from 1,000 rubles (1 unit);
- PCR blood test qualitative (for example, for herpes, HPV, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus) - 450 - 550 rubles, quantitative - from 2,000 rubles;
- HIV DNA qualitative (denial/confirmation of the presence of HIV in the preclinical period) - from 2,000 rubles, quantitative RNA - from 7,000 rubles, resistance - from 14,000 rubles.
Preparation for PCR
To obtain correct, reliable research results, girls and women should follow certain rules before going to be tested for infections:
1-2 days before the visit to the clinic for testing, refuse sexual intercourse;
- refrain from urinating 1.5 - 2 hours before the smear;
- to carry out hygiene of the external genitalia with plain water, without detergents, exclude douching;
- exclude the use of vaginal tablets, suppositories;
- do not take PCR tests during menstruation;
- Being a virgin, before the examination, warn the gynecologist about this in advance.
How to take PCR tests
Passing PCR in our clinic, including anonymously, is quite simple. Next, we will talk about how PCR is taken from women and men and from where, from which places this study is most informative.
In the case of a woman, the analysis is taken by a gynecologist. This usually happens at the initial appointment with the doctor or when you just turn up to take tests for infections, without prior consultation. Everything according to your desire. You say your wishes, for which infections you would like to be tested, and after that the procedure for taking the material begins directly. The patient undresses below the waist, is located on the chair. Having parted the labia minora, the doctor inserts a speculum of a suitable size into the vagina. Gynecologists take PCR from women, usually from the cervix, as well as the urethra. In the latter case, before the introduction of the probe, a short-term massage of the urethra with a finger inserted into the vagina is performed. In the event that the PCR analysis is taken by teenage girls or virgin girls, then the mirror is not used, and samples of secretions are taken through a hole in the hymen or the vestibule of the vagina. The resulting material is placed in a sealed test tube with a special medium and sent to the laboratory.
Taking this analysis in men is not particularly difficult. The probe is inserted into the urethra at a depth of 3-4 cm, rotated several times clockwise and counterclockwise. The material is also placed in a test tube for further diagnostics.
Federal Agency for Education
State educational institution
Supreme vocational education
"Karelian State Pedagogical Academy"
Coursework on the topic:
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and its application
Completed by: student Koryagina Valeria Alexandrovna
Checked by: Karpikova Natalya Mikhailovna
Petrozavodsk 2013
Introduction
Chapter 1 Literature Review
1.5.4 Plateau effect
1.5.6 Amplification
Conclusion
Introduction
The last twenty years have been marked by the widespread introduction of molecular genetic methods into the biological, medical, and agricultural sciences.
By the early 1970s, it seemed that molecular biology had reached a certain degree of perfection. During this period, microorganisms were the main object of molecular genetic research. The transition to eukaryotes presented researchers with completely new problems that could not be solved using the methods of genetic analysis that existed at that time. A breakthrough in the development of molecular genetics became possible due to the emergence of a new experimental tool - restriction endonucleases. In subsequent years, the number of direct DNA analysis methods based on qualitatively different approaches began to increase rapidly.
Modern technologies in many cases allowed for more deep level start studying the fine structural and functional organization of nuclear and extranuclear genomes of various organisms. This was of particular importance for the development of new methods for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases. No less important was the possibility of using the achievements of molecular genetics in population biology and breeding to identify and analyze the genetic variability of populations, varieties and strains, identify and certify economically valuable individuals, create genetically modified organisms, and solve other issues.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. There is no universal method that could solve all the problems that arise. Therefore, the choice of a specific method for the study is one of the most important stages of any scientific work.
Chapter 1 Literature Review
1.1 History of the discovery of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
In 1983 K.B. Mullis et al. published and patented the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method, which was destined to have a profound impact on all areas of research and application of nucleic acids. The significance of this method for molecular biology and genetics turned out to be so great and obvious that seven years later the author was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
At the beginning of using the method, after each heating-cooling cycle, DNA polymerase had to be added to the reaction mixture, since it was inactivated at the high temperature necessary to separate the DNA helix chains. The reaction procedure was relatively inefficient, requiring a lot of time and enzyme. In 1986, the polymerase chain reaction method was significantly improved. It has been proposed to use DNA polymerases from thermophilic bacteria. These enzymes proved to be thermostable and were able to withstand many reaction cycles. Their use made it possible to simplify and automate PCR. One of the first thermostable DNA polymerases was isolated from bacteria Thermus aquaticusand named Taq-polymerase.
The possibility of amplifying any DNA segment whose nucleotide sequence is known, and obtaining it after PCR in a homogeneous form and preparative amount, makes PCR an alternative method for molecular cloning of short DNA fragments. In this case, there is no need to apply complex methodological techniques that are used in genetic engineering in conventional cloning. The development of the PCR method has greatly expanded the methodological possibilities of molecular genetics, and, in particular, genetic engineering, so much so that it has radically changed and strengthened the scientific potential of many of its areas.
1.2 Varieties of polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
· Nested PCR- used to reduce the number of by-products of the reaction. Use two pairs of primers and carry out two consecutive reactions. The second pair of primers amplifies the DNA region within the product of the first reaction.
· Inverted PCR- is used when only a small area within the desired sequence is known. This method is especially useful when it is necessary to determine neighboring sequences after DNA has been inserted into the genome. For the implementation of inverted PCR, a series of DNA cuts is carried out with restriction enzymes<#"justify">polymerase chain reaction primer
· Group-specific PCR- PCR for relatives<#"center">1.3 Polymerase chain reaction
Discovered in the mid-1980s, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can increase the number of copies of an original sample millions of times within a few hours. During each cycle of the reaction, two copies are formed from the original molecule. Each of the synthesized DNA copies can serve as a template for the synthesis of new DNA copies in the next cycle. Thus, repeated repetition of cycles leads to an increase in the number of copies exponentially. It follows from the calculations that even if there are 30 cycles, the number of copies of the original molecule will be more than 1 billion. Even if we take into account that not all amplicons are duplicated during each cycle, the total number of copies, despite this, is quite a large figure.
Each cycle of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) consists of the following steps:
· Denaturation - An increase in temperature causes a double-stranded DNA molecule to unwind and split into two single-stranded ones;
· Annealing - Lowering the temperature allows primers to attach to complementary regions of the DNA molecule;
· Elongation - The enzyme DNA polymerase completes the complementary strand.
For amplification of the selected fragment, two oligonucleotide primers (seeds) flanking a certain DNA region are used. Primers oriented 3 - ends towards each other and in the direction of the sequence that needs to be amplified. DNA polymerase carries out the synthesis (completion) of mutually complementary DNA chains, starting with primers. During DNA synthesis, primers are physically inserted into the chain of newly synthesized DNA molecules. Each strand of the DNA molecule formed using one of the primers can serve as a template for the synthesis of a complementary DNA strand using the other primer.
1.4 Conducting a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
The polymerase chain reaction is carried out in special thin-walled polypropylene test tubes, compatible in size with the used thermal cycler (amplifier) - a device that controls the temperature and time characteristics of the stages of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
1.5 Principle of the polymerase chain reaction method
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an in vitro DNA amplification method that can isolate and multiply a specific DNA sequence billions of times within a few hours. The ability to obtain a huge number of copies of one strictly defined region of the genome greatly simplifies the study of an existing DNA sample.
To carry out a polymerase chain reaction, a number of conditions must be met:
1.5.1 Presence of a number of components in the reaction mixture
The main components of the reaction (PCR) mixture are: Tris-HCl, KCl, MgCl 2, a mixture of nucleotide triphosphates (ATP, GTP, CTP, TTP), primers (oligonucleotides), analyzed DNA preparation, thermostable DNA polymerase. Each of the components of the reaction mixture is directly involved in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and the concentration of reagents directly affects the course of amplification.
· Tris-HCl - determines the pH of the reaction mixture, creates a buffer capacity. The activity of DNA polymerase depends on the pH of the medium, so the value of the pH directly affects the course of the polymerase chain reaction. Usually the pH value is in the range of 8 - 9.5. The high pH is due to the fact that as the temperature rises, the pH of the Tril-HCl buffer drops.
· KCl - the concentration of potassium chloride up to 50 mm affects the course of the processes of denaturation and annealing, the concentration above 50 mm inhibits DNA polymerase.
· MgCl 2- because DNA polymerase is Mg 2+ - dependent enzyme, then the concentration of magnesium ions affects the activity of the enzyme (Mg 2+forms complexes with NTP - it is these complexes that are the substrate for polymerase). A high concentration leads to an increase in nonspecific amplification, and a low one leads to inhibition of the reaction, the optimum (for various polymerases) is in the region of 0.5 - 5 mM. In addition, the concentration of magnesium salts affects the course of denaturation and annealing processes - an increase in the concentration of Mg 2+causes an increase in the melting temperature of DNA (i.e., the temperature at which 50% of double-stranded DNA strands are broken into single-stranded strands).
· NTP - nucleotide triphosphates are direct monomers of nucleic acids. To prevent chain termination, an equal ratio of all four nucleotide triphosphates is recommended. The low concentration of these components in the reaction mixture increases the probability of errors in the construction of the complementary DNA strand.
· Primers - The most optimal is the use of primers with a melting point difference of no more than 2 - 4 o C. Sometimes during long-term storage at a temperature of 4 o With, or after a large number of freezing - thawing, the primers form secondary structures - dimers, reducing the efficiency of the PCR. The elimination of this problem is reduced to incubation in a water bath (T=95 o C) for 3 minutes and subsequent rapid cooling to 0o FROM.
· DNA preparations - the quantity and quality of the DNA preparation (matrix) directly affects the course and parameters of the polymerase chain reaction. Excess DNA sample inhibits the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). impurities various substances, which are in the DNA preparation, can also reduce the efficiency of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR): sodium acetate, sodium chloride, isopropanol, ethanol, heparin, phenol, urea, hemoglobin, etc.
· DNA polymerase - when using a small amount of DNA polymerase, a decrease in the synthesis of the final product is observed in direct proportion to the size of the fragments. An excess of polymerase by 2–4 times leads to the appearance of diffuse spectra, and by 4–16 times, low molecular weight nonspecific spectra. The range of concentrations used is 0.5 - 1.5 units of activity in terms of 25 µl of the PCR mixture.
In addition to the main components of the PCR mixture, a number of additional substances are used that improve the qualitative and quantitative indicators of PCR: acetamide (5%) - an increase in the solubility of the main components; betaine (sodium salt) - stabilization of DNA polymerase, lowering the melting point of DNA, equalizing the melting point; bovine albumin (10-100 μg / ml) - stabilization of DNA polymerase; dimethyl sulfoxide (1-10%) - increasing the solubility of the main components; formamide (2-10%) - an increase in the specificity of annealing; glycerol (15-20%) - an increase in the thermal stability of the enzyme, a decrease in the temperature of denaturation of a DNA sample; ammonium sulfate - lowering the temperature of denaturation and annealing.
1.5.2 Cycle and temperature
The general view of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) program is as follows:
stage. Prolonged primary denaturation of the DNA preparation.1 cycle
stage. Rapid denaturation of the DNA preparation. Primer annealing. Elongation.30 - 45 cycles.
stage. Prolonged elongation. Cooling of the reaction mixture. 1 cycle.
Each element of the stage - denaturation, annealing, elongation - has individual temperature and time characteristics. The parameters of temperature and flow time of each element are selected empirically, in accordance with the qualitative and quantitative indicators of the amplification products.
Denaturation. During given element The polymerase chain reaction splits a double-stranded DNA molecule into two single-stranded ones. Temperature parameters of denaturation are in the range of 90 - 95 o C, but in the case of a DNA sample with a high content of guanine and cytosine, the temperature should be increased to 98 o C. The temperature of denaturation should be sufficient to completely denature - cleave the DNA strands and avoid "sudden cooling" or rapid annealing, however, thermostable DNA polymerase is less stable at high temperatures. Thus, the selection of optimal denaturation temperature parameters for the primer/sample ratio (DNA preparation) is an important condition for amplification. If the denaturation temperature in the first step is above 95 o C, it is recommended to add DNA polymerase to the reaction mixture after primary denaturation. The duration of this element of the stage during the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) should be sufficient for complete DNA denaturation, but at the same time not significantly affect the activity of DNA polymerase at a given temperature.
Annealing. Annealing temperature (T a ) is one of the most important parameters of the polymerase chain reaction. The annealing temperature for each specific primer is selected individually. It depends on the length and nucleotide composition of the primer. Usually it is lower by 2 - 4 o From the melting point value (T m ) primer. If the annealing temperature of the system is below the optimum, then the number of non-specific amplified fragments increases and, conversely, a higher temperature reduces the number of amplified products. In this case, the concentration of specific amplicons can sharply decrease, up to inhibition of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Increasing the annealing time also leads to an increase in the number of nonspecific amplicons.
Elongation. Typically, each type of thermostable DNA polymerase has an individual temperature optimum of activity. The rate of synthesis of a complementary DNA strand by an enzyme is also a value specific to each polymerase (on average, it is 30–60 nucleotides per second, or 1–2 thousand bases per minute), so the elongation time is selected depending on the type of DNA polymerase and the length of the amplified region.
1.5.3 Basic principles of primer selection
When creating a PCR test system, one of the main tasks is the correct selection of primers that must meet a number of criteria:
Primers must be specific. Particular attention is paid to 3 - the ends of the primers, since it is from them that Taq polymerase begins to complete the complementary DNA chain. If their specificity is insufficient, then it is likely that undesirable processes will occur in the test tube with the reaction mixture, namely, the synthesis of nonspecific DNA (short or long fragments). It is visible on electrophoresis in the form of heavy or light additional bands. This makes it difficult to evaluate the results of the reaction, since it is easy to confuse a specific amplification product with synthesized foreign DNA. Part of the primers and dNTPs is consumed for the synthesis of nonspecific DNA, which leads to a significant loss of sensitivity.
Primers should not form dimers and loops, i.e. no stable double strands should be formed by annealing the primers to themselves or to each other.
1.5.4 Plateau effect
It should be noted that the process of accumulation of specific amplification products exponentially takes only a limited time, and then its efficiency drops critically. This is due to the so-called "plateau" effect.
term effect plateau used to describe the process of accumulation of PCR products in the last cycles of amplification.
Depending on the conditions and the number of cycles of the amplification reaction, at the time the effect is achieved plateau substrate utilization (dNTPs and primers), reactant stability (dNTPs and enzyme), amount of inhibitors, including pyrophosphates and DNA duplexes, competition for reactants by non-specific products or primer-dimers, specific product concentration, and incomplete denaturation at high concentration amplification products.
The lower the initial concentration of the target DNA, the higher the risk of the reaction plateau". This point can occur before the number of specific amplification products is sufficient to be analyzed. Only well-optimized test systems can avoid this.
1.5.5 Sample preparation of biological material
Different techniques are used for DNA extraction, depending on the tasks. Their essence lies in the extraction (extraction) of DNA from a biological product and the removal or neutralization of foreign impurities to obtain a DNA preparation with a purity suitable for PCR.
The method of obtaining a pure DNA preparation, described by Marmur, is considered standard and has already become classical. It includes enzymatic proteolysis followed by deproteinization and DNA reprecipitation with alcohol. This method makes it possible to obtain a pure DNA preparation. However, it is quite laborious and involves working with such aggressive and pungent substances as phenol and chloroform.
One of the currently popular methods is the DNA extraction method proposed by Boom et al. This method is based on the use of a strong chaotropic agent, guanidine thiocyanate (GuSCN), for cell lysis, and subsequent DNA sorption on a carrier (glass beads, diatomaceous earth, glass milk, etc.). After washings, DNA remains in the sample adsorbed on the carrier, from which it can be easily removed using an elution buffer. The method is convenient, technologically advanced and suitable for sample preparation for amplification. However, DNA losses are possible due to irreversible sorption on the carrier, as well as during numerous washes. This is especially important when working with small amounts of DNA in the sample. Moreover, even trace amounts of GuSCN can inhibit PCR. Therefore, when using this method, the correct choice of the sorbent and careful observance of technological nuances are very important.
Another group of sample preparation methods is based on the use of Chilex-type ion exchangers, which, unlike glass, do not adsorb DNA, but vice versa, impurities that interfere with the reaction. As a rule, this technology includes two stages: sample boiling and adsorption of impurities on an ion exchanger. The method is extremely attractive due to its simplicity of execution. In most cases, it is suitable for working with clinical material. Unfortunately, sometimes there are samples with impurities that cannot be removed using ion exchangers. In addition, some microorganisms cannot be destroyed by simple boiling. In these cases, it is necessary to introduce additional stages of sample processing.
Thus, the choice of the sample preparation method should be treated with an understanding of the purposes of the intended analyses.
1.5.6 Amplification
To carry out the amplification reaction, it is necessary to prepare the reaction mixture and add the analyzed DNA sample to it. In this case, it is important to take into account some features of primer annealing. The fact is that, as a rule, in the analyzed biological sample there are various DNA molecules, to which the primers used in the reaction have partial, and in some cases significant, homology. In addition, primers can anneal to each other to form primer-dimers. Both lead to a significant consumption of primers for the synthesis of side (nonspecific) reaction products and, as a result, significantly reduce the sensitivity of the system. This makes it difficult or impossible to read the results of the reaction during electrophoresis.
1.6 Composition of the standard PCR reaction mixture
x PCR buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl solution, pH 9.0, 500 mM KCl solution, 25 mM MgCl2 solution ) …….2.5 µl
Water (MilliQ) ……………………………………………………….18.8 µl
A mixture of nucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs)
mM solution of each………………………………………….……….0.5 µl
Primer 1 (10 mM solution) ………………………………………….….1 µl
Primer 2 (10 mM solution) ………………………………………….….1 µl
DNA polymerase (5 units / µl) ……………………………………………0.2 µl
DNA sample (20 ng/µl) …………………………………………..1 µl
1.7 Evaluation of reaction results
In order to correctly assess the results of PCR, it is important to understand that this method is not quantitative. Theoretically, amplification products of single target DNA molecules can be detected by electrophoresis already after 30–35 cycles. However, in practice this is done only in cases where the reaction takes place under conditions close to ideal, which is not often encountered in life. The degree of purity of the DNA preparation has a particularly great influence on the efficiency of amplification; the presence of certain inhibitors in the reaction mixture, which in some cases can be extremely difficult to get rid of. Sometimes, due to their presence, it is not possible to amplify even tens of thousands of target DNA molecules. Thus, there is often no direct relationship between the initial amount of target DNA and the final amount of amplification products.
Chapter 2: Applications of the Polymerase Chain Reaction
PCR is used in many areas for analysis and in scientific experiments.
Criminalistics
PCR is used to compare so-called "genetic fingerprints". We need a sample of genetic material from the crime scene - blood, saliva, semen, hair, etc. It is compared with the suspect's genetic material. A very small amount of DNA is enough, theoretically - one copy. The DNA is cut into fragments, then amplified by PCR. The fragments are separated by DNA electrophoresis. The resulting picture of the location of the DNA bands is called the genetic fingerprint.
Establishing paternity
Results of electrophoresis of DNA fragments amplified by PCR. Father. Child. Mother. The child inherited some features of the genetic imprint of both parents, which gave a new, unique imprint.
Although "genetic fingerprints" are unique, family ties it can still be installed by making several such prints. The same method can be applied, with slight modifications, to establish evolutionary relationships among organisms.
Medical diagnostics
PCR makes it possible to significantly speed up and facilitate the diagnosis of hereditary and viral diseases. The gene of interest is amplified by PCR using appropriate primers and then sequenced to determine mutations. Viral infections can be detected immediately after infection, weeks or months before symptoms of the disease appear.
Personalized medicine
Sometimes drugs are toxic or allergenic for some patients. The reasons for this are partly in individual differences in the susceptibility and metabolism of drugs and their derivatives. These differences are determined at the genetic level. For example, in one patient, a certain cytochrome may be more active, in another - less. In order to determine what kind of cytochrome a given patient has, it is proposed to perform a PCR analysis before using the drug. This analysis is called preliminary genotyping.
Gene cloning
Gene cloning is the process of isolating genes and, as a result of genetic engineering manipulations, obtaining a large amount of the product of a given gene. PCR is used to amplify a gene, which is then inserted into a vector, a piece of DNA that carries the foreign gene into the same organism or another organism that is easy to grow. As vectors, for example, plasmids or viral DNA are used. The insertion of genes into a foreign organism is usually used to obtain a product of this gene - RNA or, most often, a protein. In this way, many proteins are obtained in industrial quantities for use in agriculture, medicine, etc.
DNA sequencing
In the sequencing method using fluorescently or radioactively labeled dideoxynucleotides, PCR is an integral part, since it is during polymerization that nucleotide derivatives labeled with a fluorescent or radioactive label are inserted into the DNA chain. This stops the reaction, allowing the positions of specific nucleotides to be determined after separation of the synthesized strands in the gel.
Mutagenesis
Currently, PCR has become the main method of mutagenesis. The use of PCR made it possible to simplify and speed up the mutagenesis procedure, as well as to make it more reliable and reproducible.
The PCR method made it possible to analyze the presence of human papillomavirus sequences in sections of biopsies of human cervical neoplasms embedded in paraffin 40 years before this study. Moreover, with the help of PCR, it was possible to amplify and clone fragments of mitochondrial DNA from the fossil remains of the human brain of the age of 7 thousand years!
On lysates of individual human spermatozoa, the possibility of simultaneously analyzing two loci located on different nonhomologous chromosomes was demonstrated. This approach provides a unique opportunity for fine genetic analysis and the study of chromosomal recombination, DNA polymorphism, etc. The method of analyzing individual spermatozoa immediately found practical application in forensic medicine, since HLA typing of haploid cells makes it possible to determine paternity or identify a criminal (the HLA complex is a set of genes of the human major histocompatibility complex; the loci of the HLA complex are the most polymorphic of all known in higher vertebrates: within a species, at each locus, there is an unusually large number of different alleles - alternative forms of the same gene).
Using PCR, it is possible to identify the correctness of the integration of foreign genetic structures in a predetermined region of the genome of the studied cells. Total cellular DNA is annealed with two oligonucleotide primers, one of which is complementary to the site of the host DNA near the insertion point, and the other to the sequence of the integrated fragment in the antiparallel DNA strand. The polymerase chain reaction in the case of an unchanged chromosomal DNA structure at the proposed insertion site leads to the formation of single-stranded DNA fragments of an indefinite size, and in the case of a planned insertion, double-stranded DNA fragments of a known size, determined by the distance between the annealing sites of the two primers. Moreover, the degree of amplification of the analyzed region of the genome in the first case will be linearly dependent on the number of cycles, and in the second - exponentially. The exponential accumulation during PCR of an amplified fragment of a predetermined size makes it possible to visually observe it after electrophoretic fractionation of a DNA preparation and make an unambiguous conclusion about the insertion of a foreign sequence into a given region of chromosomal DNA.
Conclusion
The PCR method is currently the most widely used as a method for diagnosing various infectious diseases. PCR allows you to identify the etiology of the infection, even if the sample taken for analysis contains only a few DNA molecules of the pathogen. PCR is widely used in early diagnosis HIV infections viral hepatitis etc. To date, there is almost no infectious agent that cannot be detected using PCR.
List of used literature
1.Padutov V.E., Baranov O.Yu., Voropaev E.V. Methods of molecular - genetic analysis. - Minsk: Unipol, 2007. - 176 p.
2.PCR "in real time" / Rebrikov D.V., Samatov G.A., Trofimov D.Yu. and etc.; ed. b. n. D.V. Rebrikov; foreword L.A. Osterman and acad. RAS and RAAS E.D. Sverdlov; 2nd ed., rev. and additional - M.: BINOM. Knowledge Laboratory, 2009. - 223 p.
.Patrushev L.I. Artificial genetic systems. - M.: Nauka, 2005. - In 2 tons
.B. Glick, J. Pasternak Molecular biotechnology. Principles and application 589 pages, 2002
5.Shchelkunov S.N.
Edited by A.A. Vorbyeva
Http://ru. wikipedia.org
http://scholar. google.ru
.
.
http://www.med2000.ru/n1/n12. htm
12.http://prizvanie. su/
Tutoring
Need help learning a topic?
Our experts will advise or provide tutoring services on topics of interest to you.
Submit an application indicating the topic right now to find out about the possibility of obtaining a consultation.
PCR diagnostics(polymerase chain reaction) is used to detect the active stage of the disease in combination with already traditional studies, when there is no reaction by immunological and microbiological diagnostic methods.
For a certain period, PCR diagnostics was used only for scientific purposes, and only starting from the end of the 20th century and the beginning of the 21st, this analysis became a kind of “gold standard”, which is of great benefit in various fields of medicine.
What is the essence of PCR diagnostics?
PCR diagnostics, in contrast to the one capable of detecting traces of antibodies (AT), establishes not only the root causes of the pathological condition, but also detects the presence of DNA or RNA on a specific specific site using enzymes in the laboratory.
PCR analysis is highly accurate, eliminating the possibility of false reactions and it is not necessary to take blood from a vein for examination, a small amount of tissue samples, biological fluid is sufficient.
To the above variant of the biological environment of the material for testing containing the alleged infectious agent, several options can be assigned at once by the decision of the doctor, including this may be:
- smear(discharge from the genitals);
- scraping from the mucosa(mouth, nose, genitals);
- saliva, sputum or pleural fluid;
- prostate juice, the study of prostate secretion for the presence of a pest;
- placental tissue or amniotic fluid;
- general urine analysis to study the sediment (after centrifugation), if necessary, to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- cerebrospinal fluid for the detection of infectious lesions of the central nervous system;
- collection of cells or tissues(biopsy) from the liver, duodenum, stomach, etc.
These samples are placed in a special reactor and analyzed by repeated doubling (amplification) of the studied DNA fragments, by repeated cycles of replication and denaturation with the addition of specific enzymes for synthesis. According to the type of chain reaction, this method identifies the type and individual characteristics of DNA or RNA. Ultimately, the PCR process comparative analysis cloned genetic material allows you to identify even single cells of a live virus, easily distinguishing ureaplasma from mycoplasma or.
Advantages and disadvantages of PCR diagnostics
This PCR diagnostic has both advantages and several disadvantages.
Benefits of diagnostics:
- the definition of the pathogen gives a direct indication of the presence in the genetic material of an atypical section of DNA or RNA;
- PCR diagnostics gives 100% accuracy due to the presence in the test material of nucleic acid particles (DNA or RNA fragments) characteristic only of a specific virus or bacterium;
- high sensitivity of the PCR system, in comparison with other diagnostic methods. PCR analysis to determine the presence of a pathogen is sufficient for one cell of a live virus (10-100 cells in a sample), which makes it possible to detect a pathogenic microorganism at an early stage of the disease in the absence of severe symptoms, and in advanced forms;
- high-tech automated PCR amplification increases the speed of analysis by testing on the day of sampling (allocating no more than 4-6 hours for diagnosis). This increases productivity and gives superiority over culture methods of research;
- the versatility of the analysis makes it possible, using the genetic material of DNA or RNA, taken in various ways, to detect several pathogens from one biological sample.
Speaking of disadvantages, then, given the sensitivity of the PCR system, one of the unpleasant moments is:
- variability of microorganisms. The disadvantage is that a mutation is inherent in microorganisms, leading to a change in the studied genotype of the pathogen. And the PCR test system in the amplified region of the genome cannot catch the hybrid of an already evolving pathogen, just as the human immune system does not recognize it, so there will be no reaction to determining the presence of an infectious disease. But for this, various developments are underway to improve the PCR method;
- the possibility of obtaining a false positive or false negative result. In order not to encounter false results at one of the stages of PCR diagnostics, it must be carried out carefully, without violating the process, observing the rules for taking the material. Samples can change their structure or even break down, which can lead to a false negative or false positive result. It should be understood that such a result can be when the infection has already been killed, but the dead cells have not had time to renew themselves and were taken into account during cloning. Therefore, on early dates after the treatment, other methods are used (for example,), and after the complete elimination of inactive pathogens from the body, an analysis-control by PCR is carried out. And already the attending physician makes the final decision on the appropriateness of therapy, taking into account all the arguments "for" and "against".
Preparation for PCR diagnostics and conditions for testing
It is worth paying attention to the simple preparation for PCR, for this it is necessary to strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending physician and observe at least a few undeniable conditions for a more accurate result.
Depending on the method of sampling material for examination, it must be remembered that:
- for diagnostics with venous blood the patient must be tested on an empty stomach, excluding even the use of liquid;
- to give a smear it is necessary to refrain from sexual contact for at least a couple of days, it is allowed to carry out hygiene of the genital organs in the evening, but not on the day of the test. It is worth choosing the optimal time for the study, taking into account: two days before or after the menstrual cycle;
- for any sampling method should stop a couple of weeks before the delivery of the use of antibacterial medicines, having previously consulted with your doctor, as this may affect the reliability of the result;
- for urinalysis to determine the presence of pathogens, it is necessary not only to observe sterility and hygiene, but also the quality of the collected material for research, which carries more accurate information. Therefore, it is acceptable to wait 2-3 hours from the last urination to the collection of urine, or to use a morning sample, which gives a higher probability of showing the presence of an inflammatory process.
PCR use and detected diseases
To search for the causative agents of many diseases, the above recommendations should not be ignored, and the prescribed examination by a doctor using the PCR diagnostic method can protect not only an adult, but also a small, unborn child in the womb from serious complications.
Indeed, it is the female half of the population that most often suffers from certain types of viruses (HPV), significantly increasing the possibility of cervical cancer or infertility. And, in view of the possibility negative impact on the course of pregnancy and on the development of the fetus, it should be borne in mind that various groups of microorganisms transmitted sexually or with immunodeficiency are difficult to attribute to one or another group of the pathogen, since they are very interconnected (for example, TORCH infections and STIs). But the polymerase chain reaction is able to find a foreign structure by determining the specific type of viral DNA in the female body.
Deciphering the results of the analysis allows you to confirm or refute the presence of diseases. Covering a wide range of pathogens, such an analysis is very relevant for the timely detection of many infections, such as:
- detection of HIV infection. Severe impairment of immunity by an infection that primarily affects immunocompetent cells present on the surface of the immune system on CD4 receptors, subsequently losing their ability to defend themselves against infections and stop responding to the presence of virus RNA in the blood plasma. In case of a positive result during an anonymous examination, it is repeated with the addition of additional studies;
- viral hepatitis, most often hepatitis C(containing RNA pathogen), which, due to its easy tolerance, is difficult to diagnose by other methods, because the PCR method is more optimal for recognizing the pathogen in the blood or liver biopsy. manifests itself at a late stage, forming a malignant inflammatory process. However, it is worth considering that if the result is positive during the test for the presence of antibodies in the blood (AT), and the PCR test gives a negative result, this may indicate the presence of a virus in the body in a very low amount, or the affected cells are in a pending stage in genome of liver cells without access to the bloodstream. In such cases, a number of repeated studies will be carried out for the final diagnosis and treatment methods;
- oncogenic viruses such as HPV(human papillomavirus) having more than 100 various types a virus transmitted sexually or during medical procedures, a newborn is infected through the birth canal from the mother if she is a carrier of papillomavirus infection;
- STI(sexually transmitted infections);
- suitable for detecting all STDs(, gardnerellosis,) and TORCH infections;
- indicates with a high degree of accuracy having a mononucleosis infection, characterized by damage to the lymphatic and reticuloendothelial systems (enlarged lymph nodes, spleen, liver), can be detected using PCR diagnostics, taking blood serum as the test material. Filatov's disease, according to external parameters, can manifest itself as rashes, biliousness skin, white coating on the tongue.
- , penetrating into the blood of AIDS patients and organ transplant recipients with the use of drugs to suppress the immune system;
- herpetic infection, representing one or another type of herpes that can affect the genitals, the mucous membrane of the eyes or the skin;
- tuberculosis. In the presence of the main symptoms of the disease, a PCR analysis is prescribed after the results of bronchoscopy, allowing you to diagnose the active stage of tuberculosis much faster than using a bacteriological or bacterioscopic method;
- viral infectious disease such as tick-borne encephalitis(Borreliosis). Characterized by cell damage nervous system, intoxication, inflammation of the brain and subsequently the development of paralysis. To detect the antigen using PCR diagnostics, blood and cerebrospinal fluid are taken to isolate the RNA virus.
- detection of Helicobacter pylori infection(leading to chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, stomach tumors) by PCR diagnostics allows detecting Helicobacter pylori DNA (genetic material) in a biopsy, feces, saliva, distinguishing strains according to the degree of malignancy.
PCR diagnostics of infections is developing at an accelerated pace and is successfully used in oncology, gynecology, urology, gastroenterology, virology, and the list is constantly updated, but is not limited to the search for pathogens of infectious diseases. Among other practical applications of the PCR method, one can also single out the use of research to establish paternity and identify a person.
PCR diagnostics is a technique based on the use of polymerase chain reaction, which can be used to examine a person for infectious and hereditary diseases. PCR analyzes for 12 infections show a result, regardless of whether the disease is acute or chronic. Some experts consider PCR 12 a mandatory analysis and do not make a final diagnosis without it. The results can be positive even long before the onset of symptoms of the disease.
In the 20th century, Cary Mullis from the USA discovered the phenomenon of the polymerase chain reaction. Currently, the PCR method is the gold standard in some areas of medicine. The method is the most effective for detecting a disease in the active stage, since there are cases when conventional methods do not give such an accurate result in the active stage.
Diagnosis of infectious processes using PCR is quite relevant in modern world. The advantages of this type of examination are as follows:
- Detection of an infectious agent in analyses. The analysis involves the identification of DNA or RNA of an infectious agent.
- False and erroneous reactions are practically excluded.
- The PCR method 12 is the most sensitive. Thanks to this method, even single cells of infectious agents can be detected.
- The result of PCR for hidden pathogens is ready within 4 hours after the procedure.
- The ability to detect infectious agents without the absence of characteristic symptoms for the disease. The method is quite effective in the event of a specific disease.
In the modern world, PCR diagnostics of infections is developing at an accelerated pace. The technique is being actively improved. New varieties appear PCR examinations. Thanks to the development this method examination, it becomes as accessible as possible to a wide range of people, while the cost is gradually changing.
Basis of the polymerase chain reaction
 The PCR method is carried out exclusively in the laboratory. For its implementation, special enzymes are used, which increase several times the structure of the DNA and RNA of the patient. Such a quantity of DNA and RNA should be formed so that visual analysis can be carried out. During the examination, a copy of the RNA or DNA section is copied, which ideally fits the required conditions.
The PCR method is carried out exclusively in the laboratory. For its implementation, special enzymes are used, which increase several times the structure of the DNA and RNA of the patient. Such a quantity of DNA and RNA should be formed so that visual analysis can be carried out. During the examination, a copy of the RNA or DNA section is copied, which ideally fits the required conditions.
The laboratory maintains a database that lists the exact structure of various infectious agents. Thanks to the PCR method, you can not only see the pathogen, but also calculate its quantitative ratio.
PCR diagnostics also involves certain innovations, among which the following can be distinguished:
- introduction of mutations;
- connection of individual DNA fragments;
- determination of paternity, etc.
Infections detected by PCR analysis
PCR diagnostics can reveal the following infectious processes:
- hepatitis of the following varieties: A, B, C, G;
- Epstein-Barr virus, the causative agent of infectious mononucleosis;
- cytomegalovirus;
- mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- herpes 1 and 2 types;
- many sexually transmitted infections: ureaplasmosis, gardnerellosis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis.
- HPV and its oncogenic subspecies;
- tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis;
- candida infection;
- listeriosis;
- Helicobacter pylori infection.
And these are just some of the most common infections that can be detected using PCR. PCR blood test is actively used in the gynecological field of medical practice, as well as in areas such as:
- pulmonological;
- phthisiatric;
- gastroenterological;
- oncological;
- many other branches of medicine.
Rules for collecting material for analysis
Foreign DNA and RNA can be detected by examining a variety of body fluids of a particular person. In order to examine a person for the presence of certain sexually transmitted infections, it is necessary to take a sample of discharge from the genital organs (smear or scraping) of the patient and his urine.
 If it becomes necessary to examine a person for various kinds of infections (HIV, herpes, hepatitis, and others), then a PCR analysis is taken, for which the patient's blood is used.
If it becomes necessary to examine a person for various kinds of infections (HIV, herpes, hepatitis, and others), then a PCR analysis is taken, for which the patient's blood is used.
To diagnose a herpetic lesion, mononucleosis, you need to take a smear from the patient's oral cavity. To confirm CMVI, the patient's urine is taken for analysis. There are cases when the cerebrospinal fluid is examined to determine the causes of the neurological abnormalities that have arisen.
At the same time, a pulmonologist examines the sputum and fluid from the pleura of a particular patient using the PCR method.
If a newborn baby has a suspicion of intrauterine infection, doctors take an analysis of amniotic fluid from a pregnant woman and a piece of placental tissue.
Delivery of analysis: features of the procedure and interpretation of the results
All patients examined by the PCR method receive the most reliable result. In this case, the occurrence of errors is practically excluded. The results of this analysis are prepared quickly enough, which facilitates the diagnosis and ensures the timely appointment of therapeutic measures.
The reliability of the PCR result directly depends on the correctness of the delivery of the material for examination. The material must not be contaminated, otherwise the result of the study will not be objective. The most important recommendations before taking a PCR test include the following requirements:
- It is forbidden to have sexual activity a day before the analysis.
- A blood test for infections must be taken on an empty stomach in the morning.
- Urine is given in the morning in a sterile container.
The result of the analysis will be ready in 1.5-2 days after the procedure in question. There are situations when the result can be prepared on the same day.
Deciphering the results
The result of this type of examination can be positive or negative. A negative result of a blood test indicates that there are no infectious elements in the submitted material. A large number of PCR tests performed show a negative analysis.
 A positive PCR analysis confirms the fact that infectious agents were found in the submitted material and high-quality, most effective treatment of the patient is necessary.
A positive PCR analysis confirms the fact that infectious agents were found in the submitted material and high-quality, most effective treatment of the patient is necessary.
The result may be positive, but there are no manifestations of the disease. This indicates either the onset of the disease, or its carriage. If the carrier of the disease is detected, then no therapeutic measures are required. You just need to see a specialist. Examples of such diseases are:
- papillomavirus infection;
- herpes, etc.
Usually they are found in saliva, scrapings from the cervical canal, urethra. However, it must be remembered that a sick person can infect absolutely healthy people, despite the fact that this disease does not bother him in any way. The disease can become chronic. It should be noted that in cases where the PCR blood test showed positive result, the appointment of therapeutic measures is simply necessary.
PCR analysis also has a quantitative characteristic. The quantitative result is evaluated only by a specialist, it is individual for different infections. Based on the quantitative characteristics, the doctor is able to understand how active this pathological process is, to put the exact stage of development of a particular disease. By analyzing the results obtained, the specialist can choose the necessary drug and, possibly, reconsider the dosage of the drug.
Accuracy of PCR diagnostics
Specialists are given PCR 3 most important characteristics, among which are:
- Accuracy.
- Specificity.
- Sensitivity.
Diagnosis of infections by PCR has a high probability of detecting infectious agents. PCR analysis of blood and other fluids is highly specific. With its help, you can easily identify a specific infectious process. PCR diagnostics is highly sensitive. If the test material contains a minimum amount of infectious agents, the PCR method will always be positive.
The most rare is a false positive result. If there is no infection, then the result is negative.
PCR for latent infectious process
If an STI is suspected in a person, then a blood test for latent infections is prescribed. Sexual diseases can be detected only by examining the patient. Diseases such as:
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasmosis;
- gonorrhea;
- herpes;
- gardnerellosis;
- mycoplasma.
The above sexual infections are quite common and at the same time insidious. At the initial stage of the development of the disease, they do not give bright symptoms, and patients do not seek help. PCR blood test, scrapings from the mucous membrane of the urethra and cervical canal are required if these infections are suspected.
STIs have a very negative impact on reproductive system. They can cause infertility or malformations in the fetus. In this regard, before planning a pregnancy, you need to take a PCR test.
PCR for 12 infections is popular. Diagnosis by PCR 12 is carried out through the delivery of swabs from the genitals. The material is taken 2 hours after the act of urination. 2 days before the study, suppositories should not be inserted into the vagina and douching should not be performed. The result of the analysis will be ready in 2 days.
The cost of PCR varies depending on the infection being studied. The price ranges from 200 to 500 rubles for each infection. You can enter and be examined in a private laboratory on your own, without a doctor's referral.
The polymerase chain reaction has been known for 30 years. It is widely used in many fields, from archeology to genetics.
It is the PCR method that helps to establish paternity, but it is most often used to detect various infectious diseases in the human body.
How is PCR analysis carried out, and what is it? We will try to answer these questions in detail.
PCR analysis - what is it?
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a highly accurate method of molecular genetic diagnostics, which makes it possible to detect various infectious and hereditary diseases in humans, both in the acute and chronic stages, and long before the disease can manifest itself.
The PCR method is absolutely specific and, performed correctly, cannot give a false positive result. That is, if there is no infection, then the analysis will never show that it is. Therefore, now very often, in order to confirm the diagnosis, an additional PCR analysis is taken to determine the pathogen and its nature.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was developed in 1983 by Cary Mullis (USA), for which he was awarded in 1993 Nobel Prize in the field of chemistry.
What is the advantage of this method?
Diagnosis by this method allows you to find the pathogen directly in the gene contained in the studied materials. This is the most accurate analysis for sexual infections, latent infections, various sexually transmitted diseases.
Differences between PCR diagnostics and other laboratory research methods are as follows:
- the method is aimed at identifying the pathogen itself;
- diagnostics by PCR is versatile: to detect several pathogens;
- diseases, only one biological sample of the patient is sufficient;
- the method is highly sensitive and is not accompanied by other cross-reactions.
In addition, the advantage of PCR diagnostics is that any biological material of the patient is suitable for analysis: blood, secretions from the genital organs, urine, semen.
What infections can be detected by a PCR smear?
The body may have a large number of causative agents of infections, this includes the “hidden”, which do not manifest themselves for a long time.
PCR smear analysis makes it possible to detect such infections:
- ureplasmosis of the genital organs;
- candidiasis ();
- herpes;
- the presence of cancer cells;
- assess the hormonal state;
The studied material for PCR is usually sputum, saliva, urine, blood. Before carrying out the analysis, it is necessary to carefully prepare for it, having received a preliminary consultation with a doctor.
Blood for PCR is usually donated on an empty stomach. Good results are shown by analysis when the material for research is taken from the cervical canal or urethra. In this case, it is best to carry out PCR diagnostics no later than one day after intercourse.
Varieties of PCR
PCR is used in many areas for analysis and in scientific experiments. There are different analysis methods:
- reverse transcription PCR(Reverse Transcription PCR, RT-PCR (English)) - used to amplify, isolate or identify a known sequence from an RNA library.
- Inverted PCR(Inverse PCR (English)) - is used if only a small area within the desired sequence is known. This method is especially useful when it is necessary to determine neighboring sequences after DNA has been inserted into the genome.
- Nested PCR is used to reduce the number of side products of a reaction. Use two pairs of primers and carry out two consecutive reactions.
- Asymmetric PCR(English Asymmetric PCR) - is carried out when it is necessary to amplify mainly one of the chains of the original DNA. Used in some sequencing and hybridization analysis techniques.
- Quantitative PCR(Quantitative PCR, Q-PCR (English)) or real-time PCR - used to directly observe the measurement of the amount of a particular PCR product in each reaction cycle.
- Stepped PCR (Touchdown PCR (English)) - using this approach, the influence of non-specific binding of primers is reduced.
- Group-specific PCR(English group-specific PCR) - PCR for related sequences within one or between different types using conservative primers for these sequences.
If the nucleotide sequence of the template is partially known or not known at all, degenerate primers can be used, the sequence of which contains degenerate positions in which any bases can be located. For example, the primer sequence could be: …ATH… where H is A, T, or C.

What biological materials are being studied?
Various biological media and human fluids can serve as a material for PCR research, in which foreign DNA of a bacterium or DNA or RNA of a virus can be detected:
- Urine. It can be used for infectious lesions of the genitourinary tract in men and urinary organs in women (in men, the use of urine as a material replaces epithelial scraping).
- Phlegm. It is used for the diagnosis of tuberculosis and less often for the diagnosis of respiratory forms of chlamydia and mycoplasmosis. Sputum in the amount of 15-20 ml is collected in a sterile (disposable) vial.
- biological fluids. Prostate juice, pleural, cerebrospinal, amniotic fluid, articular fluid, bronchoalveolar lavage, saliva are taken according to indications.
- Epithelial scrapings from mucous membranes. Usually used to diagnose sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, gardnerellosis, herpetic and other infections that affect the mucous membranes.
- Biopsies. Most often, biopsy specimens of the stomach and duodenum are used to detect Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Blood, plasma, serum. Used for PCR analysis of hepatitis B, C, D, G viruses, herpes, CMV, HIV, human genes.
How to prepare for the analysis?
The reliability of the PCR result directly depends on the correctness of the delivery of the material for examination. The material must not be contaminated, otherwise the result of the study will not be objective. The most important recommendations before taking a PCR test include the following requirements:
- Urine is given in the morning in a sterile container.
- A blood test for infections must be taken on an empty stomach in the morning.
- You should not be sexually active the day before the test.
The result of the analysis will be ready in 1.5-2 days after the procedure in question. There are situations when the result can be prepared on the same day.

Deciphering the analysis of the PRP
The process of interpreting the presented study is notable for its simplicity. results pcr analysis can be received in 1.5-2 days after the delivery of the material. In some cases, the result is ready on the first day, and this is what they can mean:
- Negative result shows that the material being diagnosed does not contain the desired infectious agent.
- PCR positive indicates that DNA or RNA of the pathogen is present in the human body.
In some cases, quantitative determination of microorganisms is carried out. This is especially true in diseases caused by opportunistic pathogens. Since these bacteria show their negative effects only when they are in excess.
Also, quantitative PCR analysis is important for the choice of therapeutic tactics and for the purpose of monitoring the treatment of viral infections such as HIV and hepatitis viruses.
How accurate is PCR in diagnosing infections?
The PCR method is characterized by high accuracy, specificity and sensitivity. This means that this analysis is capable of:
- accurately determine the presence or absence of infection;
- specify exactly what kind of infection it is (specificity);
- detect infection even at a very low content of microbial DNA in biological material,
- which has been tested (sensitivity).
PCR analysis: price and terms
The price of a specific analysis will depend on which infection you will be tested for. Approximate prices and terms:
- STI: 300-500 rubles, terms - 1 day;
- Epstein-Barr virus, human papillomavirus, herpes, cytomegalovirus: 300-500 rubles, terms - 1 day;
- Hepatitis A, B, C, D, G: qualitative analysis 650 rubles, quantitative analysis 2000 rubles. Terms - up to 5 days;
- Antibodies to the hepatitis C virus, total (Anti-HCV) - 420 rubles;
- Antibodies to the hepatitis C virus, IgM (Anti-HCV IgM) - 420 rubles;
- Helicobacter pylori (Helicobacter pylori): 300-400 rubles, terms - 1 day;
- HIV (antibodies and antigens) - 380 rubles;
- HIV RNA, qualitatively - 3,500 rubles;
- HIV RNA, quantitatively - 11,000 rubles.
To save money, you can choose a fixed package of analyzes. This service is provided by most clinics where you can take an analysis using the PRC method (in vitro, onclinic, etc.).