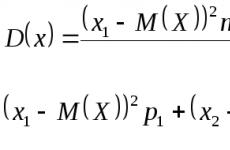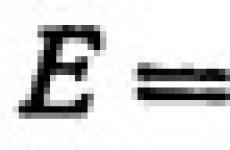Seismic zoning of the Crimea. How seismically dangerous is the construction of the Crimean NPP? The wall material must be structurally connected to the reinforced concrete frame, and not only fill it
The Crimean peninsula and the entire coast of the Krasnodar Territory are located in a seismically hazardous zone, the formation of the relief is still ongoing here. In addition, scientists report that even with the final formation of the terrain, the movement of tectonic plates never stops. Therefore, the risk of earthquakes in the zone of seismic activity cannot be reduced to zero. Therefore, going on vacation to the Crimea, familiarize yourself with the main before, during, and after the earthquake. If we are in a seismically dangerous region, then we must take this into account in our lives.

Earthquakes for Crimea are a common thing, in numerous historical treatises that have survived to this day, some especially destructive cataclysms on the peninsula are described. The oldest known Crimean earthquake occurred in BC. e .. This event was reported by the Roman chronicler Dion Cassius and the Christian historian Paul Orosius. The first left records of the destruction of several cities in the affected area, the second spoke in more detail about what happened. Paul Orosius wrote about the feast of Ceres, arranged by the king, in the midst of which a strong earthquake began. The result of a terrible natural phenomenon was terrible destruction in cities and fields.
Another ancient catastrophe occurred in 480 AD. This earthquake became known from an inscription in Tauric Chersonesos, according to these data, the event lasted about 40 days and left behind great damage in the ancient policy. Later historians testify to earthquakes in 1292, 1471. The cataclysm of 1341 came to the Crimea with the power of tremors with a force of 8-9 points and a strong storm. The Byzantine chronicler George Kedrin described the sea that overflowed its banks for 10 versts, flooding all the buildings in this zone. The earthquake of 1471 is known from the memoirs of the Russian traveler Pavel Sumarokov. The power of the earth's vibrations reached 9 points, as a result, the mountain and the fortress in Yalta collapsed, and its frightened inhabitants went to live in other villages.
In 1615, a resident of Feodosia Khachatur Kafaetsi, which caused the destruction of the city wall, many houses, overflowing the shores of the sea.
In February 1786, Simon Pallas witnessed a catastrophe in the village of Kuchuk-koy, near Yalta. Residents of the surrounding villages in fear left their homes, taking away their livestock. Until the end of February, the earth's landscape was collapsing, revealing to people a huge sinkhole with a depth of 10 to 20 sazhens.
In 1802, an earthquake overtook Sumarokov in Sevastopol, who left detailed evidence about him. The strength of the tremors then reached 6 points. Fluctuations in the earth's firmament in 1838 alarmed the inhabitants of Simferopol and the South Bank. In October 1869, a magnitude 7 earthquake destroyed some buildings in Sudak and Taraksha. The epicenter of this event was near Foros.
Earthquakes in 1875, 1902, 1908, 1919 were no less destructive and terrible for the population. The most powerful and destructive. The greatest damage was caused to the South Bank, in total, more than 60 people died during this earthquake. 
Nuclear power plants belong to the category of especially critical structures; to select their locations, it is necessary to carry out activities of a special complex of geological, geophysical and seismological surveys. This should also take into account low-probability seismic events that occur once every ten thousand years.
As shown by studies conducted by the Institutes of Geophysics of the Academy of Sciences of the Ukrainian SSR, the current level of seismic activity in the northern part of the Kerch Peninsula is commensurate with the activity of the southern coastal zone of Crimea, where in 1927 a well-known destructive earthquake occurred with an intensity of 9 points at the epicenter.
The Kazantip seismic station, opened in 1982 at a distance of 5 km from the NPP, recorded about 100 weak seismic events over 6 years, which occurred at epicentral distances of less than 100 km.
The most significant, which caused alarm among the population and the public, were the earthquakes that occurred on April 8, 1987 in the Sea of Azov near Cape Kazantip. In the village of nuclear scientists Shchelkino and the village of Mysovoye, the intensity of the shaking reached 4 points, in 10 other settlements of the Lenensky district - up to 3 points. total area sensitivity was 900 sq. km.
Earthquakes of similar strength (in terms of the amount of released energy) have repeatedly occurred in the southern part of the Sea of Azov, in particular, in 1968, 1981 and 1988. Their epicenters are confined to the zone of the South-Azov deep fault, which passes in the immediate vicinity of the nuclear power plant.
The working groups of the Government Commission, which worked in September 1988 in the area of the nuclear power plant, also assigned the sources of alleged earthquakes of the 1st century BC to the zone of the South Azov fault. BC e. and III c. n. e., according to archaeological evidence, they twice destroyed the city of Zenonov Chersonese (cape Zyuk in the north of the Kerch Peninsula). The intensity of these earthquakes is estimated at 9 points. It is authentically known and no one doubts the earthquake that occurred in the Kerch Strait in 63 BC. e. and destroyed many cities of the Bosporus state. Based on the totality of data on modern seismicity and ancient historical earthquakes, the Government Commission adopted an estimate of MSE (maximum design earthquake) at the NPP site of 9 points on soils of category II. During the construction and operation of nuclear power plants, the seismic properties of soils can change significantly (due to flooding) and move from category II to category III, which is seismically unfavorable. At the same time, it is necessary to add an increment due to soil conditions of at least 1 point to the calculated SSE intensity of 9 points.
In the pre-war period, 4 stations of the Institute of Seismology of the USSR Academy of Sciences operated on the territory of Crimea. The stations monitored the seismic situation, recorded vibrations of the earth's surface, and carried out work on seismic zoning. Seismic microzoning of the southern coast of Crimea was carried out by the Yalta seismological station. In 1940, after many years of observations, seismologists came to the conclusion that the southern coast of Crimea is located in an eight-point seismicity zone, and deviations of one point in one direction or another are allowed in the zone, depending on the nature of the soil and the conditions of their occurrence in individual microdistricts.
On June 26, 1927, the Crimean seismologists registered strong tremors. The earthquake lasted about 5 seconds. The newspaper "Krasny Krym" in those days wrote that the tremors were felt in all cities and regions of Crimea. In Simferopol, the earthquake reached 5 points. In towns and villages, "many buildings received cracks." Several mountain falls have been recorded, resulting in the destruction of a number of houses. The western part of Mount Ai-Petri has sunk somewhat. Chimney blocks came off the ridge. The rocks broke off into the sea between Simeiz and the Swallow's Nest. The Monk Rock collapsed... On Mount Castel, as a result of an earthquake, the Devil's Finger rock fell. Workers of the Crimean Vodkhoz conducting observations on Besh-Terek during the earthquake felt strong vibrations of the soil, accompanied by a rumble of considerable strength. The shocks were repeated throughout the day.
On the night of June 28-29, 1927, the Crimeans felt new shocks. They lasted about 3 seconds and were much weaker than on June 26th. Before the earthquake, a strong rumble was heard.
Two and a half months later, on September 12, 1927, another strong earthquake occurred in the Crimea. Its epicenter was in the sea, in the Yalta region, and the strength of the oscillations reached 9 points. On this day, residents of the southern coast of Crimea felt tremors with a force of more than 7 points. In Simferopol, Evpatoria, Dzhankoy, their intensity reached 6 points, in Odessa - 4 points, Novorossiysk and Chisinau - 3 points. Weak fluctuations were recorded that day in Poland.
Crimean seismologists warned residents of the peninsula and tourists about a strong earthquake in the region in the near future. On Tuesday, July 18, the Izvestia newspaper was told by the director of the Crimean State Expert Council for Seismic Hazard Assessment and Earthquake Forecast Yulian Burym.
View of the Swallow's Nest in the village of Gaspra. Photo: Vladimir Smirnov / TASS
As reported, the tremors will be felt on the peninsula, although the epicenter of the disaster is in the Black Sea, 30-50 km from the southern coast of Crimea.
"An earthquake is expected within a day. We have one of the signs. I will not give you specific numbers. Yes, strong, tangible. But it may not happen at all," the specialist said.
This message has caused a serious stir. As a result, comments about the upcoming natural disaster poured in from various interested departments. Thus, in the Main Directorate of the Ministry of emergencies in the Republic of Crimea noted that they had checked the report of the expert council. According to Vladimir Ivanov, head of the press service of the Crimean Ministry of Emergency Situations, there were no signs of an earthquake.
"After receiving the message, we began to check this information through the network of seismic stations of the Republic of Crimea, which did not record any changes in the seismic activity of the peninsula and the adjacent water area," Ivanov told the Kryminform agency.
It also turned out that the animals of the Crimean zoos do not show any concern about the elements.
"Information was collected from all the zoo corners and zoos of the Crimea in order to change the behavior of animals - similarly: there are no anomalies in the behavior of animals," said the head of the press service of the regional department of the Ministry of Emergency Situations.
In turn, the head of the laboratory of continental seismicity and seismic hazard prediction of the Institute of Physics of the Earth RAS Alexei Zavyalov, commenting on the news from the peninsula, suggested the possible destruction of buildings or the occurrence of a tsunami.
"Scenarios can be different. According to the first, houses can be destroyed. If the earthquake source is located in the Black Sea, a tsunami may occur," the seismologist said.
Now, in his opinion, the Crimean authorities should carry out certification of buildings for their seismic stability during earthquakes.
"Exactly 90 years ago - in July and September 1927 - the famous Yalta earthquakes occurred, so it's time to prepare for this. Strong earthquakes occur in Crimea, but, of course, not as often as in Kamchatka and Japan," he stressed. seismologist.
In 1927, the elements destroyed 70% of all buildings on the peninsula, the Kryminform portal recalls. Then the architectural monument "Swallow's Nest" was seriously damaged - due to a push of 8 points, the tower collapsed, a crack passed through the entire building. According to geologists, before that, in the Crimea, tremors of the same magnitude occurred during the time of Catherine II. As a result, the hypothesis of a 100-year cycle arose. In the near future, a new devastating earthquake is not expected on the peninsula, but they are preparing.
Today I want to touch on a rather interesting and exciting topic for many - about earthquakes in the Crimea. Periodically, information slips in the media that an earthquake is coming in Crimea. People, having learned about this, quickly pass this information on to each other, unrest begins in society, periodically developing into panic. But in the vast majority of cases, information about upcoming earthquakes in the Crimea is absolutely unfounded, simply sucked out of thin air. That is why I want to talk about this in more detail today. I will also touch upon the history of earthquakes in the Crimea, their nature, scale and possibility of occurrence. I will also try to explain intelligibly what your actions should be in case of an earthquake.
I must say right away - do not trust anyone, with the exception of official sources about the exact day and even the hour of the coming earthquake. Do not use rumors and do not spread them. Seismologists have emphasized more than once that there are no reliable methods, no reliable prediction of the time of an earthquake today, either in our country or abroad. A scientific search is underway for ways to solve this extremely complex theoretical problem, which is still poorly supported by an experimental basis. That's why different kind rumors about the known exact time of the earthquake in Crimea are nothing but a deliberate provocation to destabilize public life, create nervousness and panic among the population. False rumors are sometimes more dangerous than the earthquake itself. We should talk about something else - about a reliable forecast of the place and strength of possible future disasters for carrying out preventive preventive measures and the readiness of the population, all relevant services of Crimea to resist them.
CRIMEA IS A SEISMICLY DANGEROUS REGION: FROM THE HISTORY OF EARTHQUAKES OF THE CRIMEA
Crimea is one of the seismically dangerous territories. In terms of seismicity, our peninsula is not inferior to such active regions as the Caucasus, Central Asia, and Siberia. Strong earthquakes of the Crimea in terms of released energy are comparable to well-known earthquakes, for example, Spitak (Armenia, 1988), Dagestan (1970), San Francisco (1989). The Tashkent earthquake of 1966 was 1000 times weaker than the Crimean earthquake of September 11, 1927.
However, destructive earthquakes in Crimea occur relatively rarely, on average, less often than the life of one generation of people, and therefore the memory of them is erased very quickly, vigilance is lost, and the experience of previous tragedies is poorly taken into account.
Every year in the Crimea, on average, about a hundred weak tremors occur, which are mainly recorded by seismic stations located in several settlements of the Crimean peninsula.
The sources of most earthquakes are located in the earth's crust in the area of the steep continental slope of the Black Sea at depths from 10 to 40 km. The main seismogenic structures stretch along the entire southern coast of Crimea from Sevastopol to Kerch and the southern part of the Sea of Azov. The centers of the devastating earthquakes of 63 BC are associated with these structures. e., 480, 1292, 1341, 1471, 1615, 1875, 1919, 1297 with an intensity of up to 8 points. Seismic instruments registered weak earthquakes in the steppe and foothill parts of the peninsula (in 1975 in the Dzhankoy region, 1976 - Belogorsk, 1988 - Stary Krym). Strong earthquakes also occurred in the area of the Black Sea deep basin. Geological and archaeological traces of the strongest ancient seismic catastrophes were noted on Mount Demerdzhi, on the southern coast of Crimea, in the regions of Sevastopol, on the Kerch Peninsula and Taman.
Consequences of the Crimean earthquake of 1927 Balaklava
HOW IS THE POWER OF EARTHQUAKES MEASURED IN THIS PLACE?
The strength (intensity) of vibrations of the earth's surface is measured in points on a 12-point Richter scale.
Earthquakes can be conditionally divided into imperceptible (1), perceptible (2), destructive (3) and catastrophic (4).
1 - earthquakes with a magnitude of 1-2 points, in which ground vibrations are noted by seismic instruments and, in rare cases, by individuals in a calm state.
2 - earthquakes 3, 4, 5 points. At 3 points - vibrations are noted by few people, at 4-5 the earthquake is felt by many people, there is rattling of glasses, swinging of hanging objects. Starting from 5 points, many sleepers wake up.
3 - 6, 7 points: 6 points - noticed by most people, many of them are frightened. Light damage appears in buildings, thin cracks in the plaster. 7- cracks in the plaster and chipping of individual pieces of buildings, cracks in the main walls.
4 - with a force of 8-12 points, 8 points - through cracks in the walls, falling cornices, chimneys, individual parts of buildings; 9 points - there are collapses in some buildings, collapse of walls, ceilings, roofs; 10 points - collapses in many buildings, cracks in the soil up to a meter wide; 11 points - collapses of the vast majority of buildings of good construction, numerous cracks on the surface of the Earth, large collapses in the mountains; 12 points - large-scale changes in the relief, complete destruction.
In the range from 2 to 5 points, mainly people's sensations are used to determine the intensity, since buildings and objects do not yet show significant reactions. The basis for determining the intensity from 6 to 10 points is damage to buildings, more than 10 points - landscape changes, since the buildings are so destroyed that it is almost impossible to use them for classifying the intensity, and eyewitnesses are in severe panic and their information also becomes of little use.
WHAT IS THE EARTHQUAKES OF THE CRIMEA DANGEROUS? ON THE EXAMPLE OF THE EARTHQUAKE OF 1927
Yalta, 1927
The most fully studied are two earthquakes in 1927 (June 26 and September 11), which occurred in the Black Sea at a distance of about 30 km from the South Coast. Shaking with a force of up to 8 points was felt along the entire coast of Crimea. 11 people died. Many houses and buildings were destroyed. 70 percent of buildings were damaged. Telegraph and telephone communications were interrupted. The losses amounted to about 35 million rubles (according to 1927 data). There were landslides in the mountains, scree, landslides, rock falls, heavy rockfalls, cracks in the ground, ruptures in communication pipes, knockouts on the highway, road blockages. Water sources appeared and disappeared, their chemical composition. Clouds of caustic dust rose along the Yaylinsky ridge, causing lacrimation and inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nasal and oral cavities. Fire and smoke columns up to 500 m high and up to 2.5 km wide were noted in the Black Sea. The gases released from the bottom of the sea burned for several hours. Tidal and ebb waves with a maximum height of up to 1 m were noted in Balaklava.
The consequences of the 1927 earthquake include a sharp increase in cardiovascular diseases, general panic, mass neuroses and psychoses.
The modern urbanized civilized Crimea is becoming even more vulnerable to earthquakes due to the high population density (especially in summer), destruction and flooding of the soil in major cities, construction of high-risk facilities (storage facilities for toxic materials, dams, gas and oil pipelines, etc.) often without additional surveys on the degree of seismic risk. The danger of catastrophically rapid erosion of slopes during earthquakes, prepared by active human activity, is increasing: cutting slopes during the construction of roads and large structures, flooding slopes and destroying vegetation on them, erecting heavy buildings.
Such severe consequences as loss of life, leakage of gas and oil, emissions chemical elements can be significantly reduced, subject to absolute compliance normative documents transmitted by seismologists construction organizations and ensure High Quality construction.
Well, the next blog entry will be again devoted to earthquakes, namely, what should be the behavior of a person during this natural disaster(read HERE>>). Everyone should know how to behave during an earthquake just in case.
yourcrimea.org
The seismicity of Crimea is about three earthquakes a year, as strong as the one that occurred in early May in Alushta, Yulian Burym, director of the Crimean Expert Council for Seismic Hazard Assessment and Earthquake Prediction, told RG. - Once a year fluctuations exceed four points. Then there are seismic events with a frequency of tens and hundreds of years. An earthquake like the one that happened in 1927 happens once every 400-500 years.
Today, the seismic situation on the peninsula and adjacent areas is continuously monitored by seven stationary stations.
All of them are located along the coast from Kerch to Sevastopol, as well as in the center of the peninsula, - the director of the Institute of Seismology and Geodynamics of KFU named after V.I. Vernadsky Yuri Wolfman. - The data obtained at the stations form the basis for improving the methodology for predicting seismic hazard for areas prone to it, including Crimea.
In Ukraine, although earthquake monitoring was included in a special budget item, no funds were provided for the reconstruction of the observation system at all. For this reason, all seismic stations on the peninsula still have Soviet sensors that have been operating for more than a quarter of a century.
It was assumed that we should ensure the operability of the stations without specially allocated funds for the reconstruction of the observation network. Therefore, we tried in every possible way to modernize the network on our own, - said Yuri Volfman. - For example, we had to make blocks of analog-to-digital converters for seismic stations ourselves, we assembled them literally on our knees.
Now the Institute of Seismology has become integral part KFU them. Vernadsky, thanks to the support of the university, we purchased five new domestic converter units for stationary stations.
With a margin of safety
Alas, in the 21st century, scientists still cannot predict earthquakes. In 1975, a successful forecast was made in China, which made it possible to avoid many of the negative consequences of this natural disaster. However, a year later, a terrible earthquake occurred in the same region, in which about 250 thousand people died. Nobody could predict it.
If someone makes a so-called "accurate" forecast of the time, place and strength of an earthquake, then these are most likely not scientists, but astrologers or psychics, says Yulian Burym. - More than 20 years ago, the international scientific community adopted a declaration on the ban on issuing forecasts to the media, since they are of a probabilistic nature. More or less successful attempts were made after 1975, but on the whole the problem has not been solved.
The modern concept of seismic safety is not to predict as accurately as possible the place, time and force of the impact of the elements, but to comply with building codes to avoid devastating consequences. For example, in Yalta, in order for residents to feel safe, buildings must be ready for an eight-point seismic. Specialists carry out microseismic zoning, since the soil in each specific area can both weaken and increase the destructive impact. Microzoning saves money, or vice versa - adds millions of rubles to builders in expenses, because according to the law, absolutely all projects must undergo an examination for seismic safety. However, in reality this is not always the case.
We know many cases when modern construction is carried out in violation of the norms, including seismic, - says Yulian Burym. - In the center of Yalta there are candles built in the 2000s without any seismic expertise.
The water is mixed
The Crimean earthquake of 1927, in addition to destruction, had many other consequences. Among other things, the chemical composition and debit of springs have changed on the South Coast. Today, artesian water is the peninsula's second most important source of water supply.
In our region, pumping groundwater from artesian horizons will not lead to an increase in seismic activity, - says Yuri Volfman. - Groundwater reserves are replenishable, one should not think that if we took water from the depths, then it will no longer be there. At one time, these sources were an alternative to the North Crimean Canal.
Another thing is that wells must be drilled very carefully, under the supervision of specialists. Alas, experts admit, today this is often done with gross violations, which leads to the mixing of fresh and salty aquifers, and there is practically no control over these processes.
Previously, we monitored the state of artesian waters at five wells, today only one remained under observation, - says Doctor of Geological and Mineralogical Sciences, Professor Anatoly Lushchik. - Naturally, such data will not be representative.
mud volcanoes
In addition to water, hydrocarbon production is actively conducted in Crimea. That is why on the Tarkhankut peninsula, where gas wells are operated, two temporary seismic observation points have appeared. The second region requiring increased attention of seismologists is the Kerch Peninsula.
The management of the university applied to the Crimean government with a proposal to create an integrated East Crimean geodynamic test site, - says Yuri Volfman. - All communications connecting us with the mainland flock to Kerch. This is an additional intensive impact on the environment, which increases the risks caused by the already unfavorable engineering, seismological and geological and structural factors.
Mud volcanism, high seismicity, difficult ground conditions - all these phenomena are in Kerch, and only one seismic station monitors them. Experts were seriously concerned about the eruption that occurred in December last year. mud volcano in the village of Novoselovka, Leninsky district, which almost flooded the village. The bridge under construction passes near several mud volcanoes that form at a depth of 13-15 kilometers.
Now experts have prepared maps of the seismic zoning of Crimea for inclusion in the building codes of the Russian Federation. Appendix to maps - a list of more than 200 settlements of the peninsula.
Help "RG"
Like seas, Crimea is surrounded on all sides seismic zones. The one that caused tremors in the South Coast is located at a distance of 20-40 kilometers from the coast and stretches to Kerch. Another zone extended from Sevastopol towards Odessa. The seismic activity of the peninsula is not stable. There were years when instruments recorded up to 250 local earthquakes per year. In other periods, their number did not exceed 50. Now the "norm" is considered to be 70-80 shocks of various strengths per year.