Forms and types of credit. Basic forms of credit
Credit classification is primarily carried out according to the following criteria:
1) in the form in which a specific loan is provided;
3) by the term of provision.
Classification on these grounds allows you to identify the main forms of credit.
In addition, it is possible to classify a loan in more detail using additional characteristics, while talking about the types of loans within one form or another.
Loan type- This is a more detailed description of the main form of credit by highlighting additional features. The detailed classification is based on the principles of lending, therefore, many specific types of loans reflect the specifics of the movement of credit, that is, they characterize certain aspects of the organization of the credit process.
The primary forms of credit include: commodity; monetary and mixed.
Commodity form- This is a form of credit, which is characterized by the provision by the creditor of things, goods on the terms of the counter transfer of an equal number of other things, goods of the same kind and quality.
Such transactions were widely used in ancient society. Roman law regulated such credit relations and defined them as a loan agreement. Roman jurists distinguished between a loan and a loan. With a loan, not every such thing was subject to return, but precisely the one that was borrowed (the same horse that was taken for plowing). In case of a loan, any similar thing was subject to return, i.e., a thing with the same generic characteristics (grain of the same grade).
On the basis of the commodity form of credit received a comprehensive development of its monetary form - is a form of credit, which is characterized by the transfer of money on a repayment basis .
In the modern economy, this form has become predominant. From the very moment of its appearance, it was destined for a special role, since money is an absolutely liquid and easily replaceable asset.
Along with these forms, there is mixed form credit, which combines a number of properties of the first two.
Indeed, credit can be provided both by transferring goods, which is characteristic of the commodity form, and by transferring money, which is characteristic of its monetary form. In this case, repayment will be carried out in the reverse order - in cash or in goods.
Depending on who is the lender and borrower in the transaction, the following loans are allocated:
1) commercial (economic);
2) banking;
3) civil (personal);
4) state;
5) international;
6) consumer.
Commercial loan.
A commercial loan can be described as a loan provided by one legal entity (seller) to another legal entity (buyer) in the form of a deferred payment for goods sold or by buyers to sellers in the form of an advance or prepayment for goods delivered.
Commercial lending is the main financial instrument for marketing products in wholesale trade. Sale of goods on credit has become a common way for industrial companies to sell them, it becomes an important tool of competition due to additional attraction of customers. The main reason for the widespread use of this form of credit is the expansion and strengthening of economic ties between business entities.
In modern conditions, in practice, there are mainly three varieties (types) of commercial credit:
1) with a fixed maturity;
2) with the payment of the price only after the actual sale by the borrower of the goods delivered in installments (consignment);
3) lending on an open account.
In the first case, after delivery of the goods, the buyer transfers the promissory note to the seller as a promissory note to pay for the goods after a certain period of time. Or the seller himself issues a bill of exchange (draft) to the buyer, who, having received commercial documents, accepts it, that is, agrees to pay within the period indicated on it.
In the second case, we are dealing with consignment. It is a method of trading on credit, in which the retailer receives goods without the obligation to pay for them. This trade is often referred to as the transfer of goods for sale. If the goods are sold, then payment will be made to the manufacturer, and if not, then the retailer can return the goods to the manufacturer without paying a penalty. Consignment is usually used when selling new, atypical goods, the demand for which is difficult to predict.
Under an open account agreement, once accepted by both parties, the buyer acquires the right to make periodic purchases without applying for credit on a case-by-case basis. The usual procedure for the transaction is as follows: when the buyer orders the goods, it is immediately shipped, and payment for it is made within the specified time after receipt of the invoice.
The use of commercial credit requires the seller to have sufficient capital in case of a slowdown in receipts from debtors. Therefore, in the modern economy, a commercial loan is actively used primarily by large companies that have the most favorable conditions for obtaining financial resources through the accounting and pledge of bills and through bank refinancing of a commercial loan (for example, factoring).
Bank loan.
This is a loan, the main form of which is the transfer of funds. It is provided exclusively by specialized credit organizations that have a license to carry out such operations from the Central Bank. The role of the borrower can be legal entities, state or local authorities. Credit relations are formalized by a credit agreement or credit agreement.
A bank loan differs from a commercial loan in the following ways:
a) specialized credit and financial organizations, and not any legal entities associated with the production or sale of goods, act as a creditor for a bank loan;
b) the average interest on a commercial loan, as a rule, is lower than the average bank interest rate for a given period of time. The fee for commercial credit is included in the price of the goods, and is not determined specifically through a fixed percentage of the base amount;
c) the term of a commercial loan, as a rule, is much shorter than that of a bank loan.
A bank loan is classified according to a number of criteria.
Method of issuing (providing) a loan:
a) cash or non-cash loans (by transferring funds from account to account or by issuing cash from an account);
b) refinancing (rediscount of bills, purchase of resources on the interbank market, issue of bonds and other debt obligations by a commercial bank);
c) re-registration (debt restructuring);
d) bill credits.
Loan currency. Loans are provided in the national currency, in the currency of the creditor's country, in the currency of a third country.
Number of participants. Bilateral and multilateral transactions are possible (crediting by a banking consortium, syndicated loans).
Purpose of the bank loan.
Loans are provided:
a) to increase the fixed capital (renewal of production assets, new construction, expansion of production volumes);
b) for temporary replenishment of working capital
c) for the implementation of investment projects;
d) mortgage loans, etc.
Giving technique:
a) one-time loans, i.e., issued in one amount;
b) limited loans (overdraft; credit lines).
Credit line involves the use of borrowed funds within the established limit. Within its framework, enterprises can receive funds for the purposes stipulated by the agreement and return them during the term of the credit line agreement. There are the following types of credit lines: seasonal; revolving, i.e. the client, after repaying the debt on the loan, has the right to receive a loan again within the established limit; a credit line with a notification to the client about the upper limit of lending, the excess of which is unacceptable, or involves the payment of increased interest for exceeding it; confirmed line - each time the client is obliged to agree on the conditions for providing a specific amount within the credit line.
Overdraft is the elimination of a temporary shortage of working capital for the enterprise to make current payments by crediting the current account of the bank's client at the expense of the bank's funds in the amount of not more than 10-15% of the monthly turnover on the client's current account. It is provided, as a rule, against the receipt of funds to the client's current account, which are immediately written off to repay the overdraft, that is, in fact, without collateral (although it can be provided under an agreement with the bank).
By criterion security loans are divided into secured and unsecured. The only form of securing the repayment of unsecured loans is a loan agreement. Secured loans are the main type of modern bank credit, in which one of the basic principles of lending finds its practical expression. The role of collateral can be any property owned by the borrower on the basis of ownership, most often real estate or securities. If the borrower violates its obligations, this property is sold in order to compensate for the losses incurred. The amount of the loan issued is usually less than the average market value of the proposed security and is determined by agreement of the parties.
Maturity.
Depending on the repayment terms, loans are divided into short-term, medium-term and long-term.
A) Short term loans are provided, as a rule, to replenish working capital (current lending to working capital) of the borrower. The most actively used in the stock market, trade and services. The repayment period for this type of loan usually does not exceed one year.
b) medium-term loans are provided for a period of one to three years for both industrial and purely commercial purposes. The most widespread in the agricultural sector and with partial modernization of production.
V) Long term loans are used, as a rule, for investment purposes. Like medium-term loans, they serve the movement of fixed assets, differing in large volumes of transferred credit resources. They are used in lending for reconstruction, technical re-equipment, new construction at enterprises in all sectors of the economy. The average repayment period is usually between three and five years, but can be up to 25 years or more, especially if appropriate financial guarantees are received from the state.
By repayment methods Loans are divided into:
1) loans repaid in one amount at the end of the term;
2) loans repaid in installments;
3) loans repaid in unequal shares during the loan term (as a rule, with a grace period).
Loans repayable lump sum(payment) on the part of the borrower, is a traditional form of repayment of short-term loans, which is very functional from the standpoint of legal registration, since it does not require the use of a differentiated interest calculation mechanism.
Specific conditions (procedure) for the repayment of loans repaid in installments during the entire term of the loan agreement, are determined by the agreement, are used, as a rule, for medium-term loans. For long-term loans for investment purposes, a grace period (up to a year) is often applied, during which the borrower does not pay any interest or part of the debt. During this time, the borrower manages to install equipment and start production.
By type of interest rate loans are divided into: loans with a fixed interest rate and loans with a floating interest rate.
According to different methods of charging interest There are several types of loans:
a) loans, the interest on which is paid at the time of its total repayment. The traditional form of payment for short-term loans for a market economy, which has the most functional character from the standpoint of ease of calculation.
b) loans, the interest on which is paid in equal installments by the borrower during the entire term of the loan agreement. The traditional form of payment for medium and long-term loans, which is quite differentiated depending on the agreement of the parties (for example, for long-term loans, interest payments can begin both at the end of the first year of using the loan, and after a longer period).
c) loans, the interest on which is withheld by the bank at the time of their direct issuance to the borrower. For a developed market economy, this form is absolutely uncharacteristic and is used only when inflation is high.
Civil (personal) credit.
This basic form of credit is characterized by the participation of individual citizens in credit relations. They act as each other's lenders and borrowers in borrowing money or goods for personal rather than business purposes. In general, these relations are of a local (family, related) nature, and are not formalized by a loan agreement.
State loan.
The main feature of this form of credit is the indispensable participation of the state in the person of central and local executive authorities. The subjects of the state loan are legal entities and individuals, on the one hand, and central and local authorities, on the other. The state acts as a borrower or lender. Traditionally, this form of credit is associated with the issuance of government bonds or other securities and is called a government loan. Much less often, the state acts as a creditor, providing loans to legal entities and individuals.
State credit also includes the provision by the state of guarantees for loan obligations of legal entities and individuals.
State loans can be divided into types according to the following criteria:
1) by deadlines for providing loans: short-term (with a maturity of up to 1 year), medium-term (from 1 to 5 years) and long-term (over 5 years) loans;
2) by location: internal and external (international) loans;
3) by subjects of relations: loans placed by central and local authorities;
4) by market status: market (freely placed on the stock market) and non-market - loans that are not subject to circulation on the market. They are designed for certain (target) categories of investors;
5) by yield: interest rate or zero coupon.
Interest-bearing loans involve (from 2 to 4 times a year) the payment of income on coupons - tear-off receipts of a bond. Short-term loans usually do not have coupons. They are sold at a discount from the face value indicated on the bonds, and are redeemed at face value. The difference is the amount of income on the bond.
6) by income determination method: fixed income and floating income.
International credit.
International credit is a credit that characterizes the form of credit relations between states or between economic entities of different countries.
It is used in the form:
1) commercial (intercompany);
2) banking;
3) interstate credit.
At the same time, in credit relations with the participation of states and international institutions, it always acts in monetary form, in foreign trade activities - in monetary and commodity form (as a kind of commercial credit to an importer or exporter).
The borrowers and lenders are private enterprises (including banks), government agencies (ministries and departments) and international (IMF, IBRD) and regional (EBRD) financial organizations.
Specific types of international credit can be classified according to a number of criteria:
1) by intended purpose: commercial or cash loans, including funds for the acquisition of fixed capital, new construction, other investment needs;
2) by due date: short-term, medium-term and long-term loans;
3) by provision currency: a loan in the currency of the borrowing country or
creditor country, in the currency of a third country.
A characteristic feature of an international loan is its additional legal or economic protection in the form of private insurance and state guarantees.
Consumer credit.
This is a form of lending to individuals. The goal is to meet the consumer needs of the population - for the acquisition of land, housing, cottages, cars, durable goods. It is provided under a mortgage (mortgage) of land plots, housing, pledge of a car, securities, guarantee of third parties.
Both specialized financial and credit organizations and banks, as well as any legal entities engaged in the sale of goods or services, can act as a creditor.
Typically, with the help of such a loan, durable goods (cars, refrigerators, furniture, household appliances) are sold. The term of the loan is up to 3 years, the percentage is from 10 to 25. The population in industrialized countries spends from 10 to 20% of their annual income to cover consumer credit. In case of non-payment on it, the property is seized by the creditor.
To date, life in installments and doing business on credit have become quite relevant and very popular phenomenon. Banks are in a tough uncompromising struggle for each client, and every day lending is becoming more affordable. At the same time, various forms and types of credit appear, and the conditions for obtaining it are becoming more and more simplified.
How necessary is it?
As you know, a market economy cannot do without loans. On the one hand, some participants in commodity-money relations need additional funds, in addition to those that are currently available. On the other hand, individuals, enterprises or organizations have an excess of money supply, for example, due to a mismatch in the timing of production and sale of a certain product, accumulated savings or unplanned income.
A certain contradiction arises, which is quite successfully resolved with the help of the credit market (loan capital market). Actually, the very concept of "credit" means the movement of loan capital, subject to the obligatory condition of its payment and repayment. Any credit system characterizes the movement of the money supply, i.e., the accumulated funds, capitals and incomes of various segments of the population are loaned to individuals, various enterprises or the state itself. It is the various options for the interaction of participants in the credit market that give rise to various forms of credit.
Credit functions
The relationship between the borrower and the lender involves the adoption of a number of obligations that are prescribed in the contract. The loan agreement defines the obligations of the bank or other person providing the loan, terms, amount and terms of repayment. Based on this, three main functions of a loan can be defined:
- Distribution - is revealed during the concentration of funds and their subsequent distribution on a returnable basis. This function is fully traced in the allocation of funds to organizations to meet urgent needs and expand production.
- Emission - manifests itself when non-cash forms of payment are used. That is, there is a replacement of cash by commodity forms.
- Controlling - allows you to monitor the economic activities of entities. In this regard, borrowers and lending structures are encouraged to use various forms and types of loans, which will make it possible to use borrowed funds to the fullest extent for development and increasing profitability.
Loan depending on the structure
The composition of any loan is quite simple and includes the borrower, the lender and the loan value. Depending on the type of the latter, the following forms of credit are distinguished:
- monetary;
- commodity;
- commodity-money;
A few hundred years ago, the commodity form of lending was the most common in Rus' and was expressed, for example, in lending grain to peasants for sowing or other agricultural products. In the modern world, the commodity form of credit is no longer the main one and is expressed only in the sale of goods in installments or, for example, in leasing.

In the current realities, the most applicable are monetary and mixed forms of credit. In the first case, money is a universal instrument of payment, while the mixed form is used when the delivery of goods on an installment basis is accompanied by a gradual return of their value in monetary terms.
Types of lending
Studying the concept of "credit" in more detail, one can single out several organizational and economic features used to classify it.
Depending on the economic orientation, there are several main types of lending:
- industrial;
- trade;
- agricultural.
You can also divide loans into direct and indirect, depending on the objects of lending, that is, what exactly the loan is taken for. Of course, most often credit funds are used to purchase goods, but sometimes it happens that funds are needed to satisfy non-material needs, for example, paying salaries to staff, paying necessary taxes and fees, etc. In this case, the loan does not have a material and material forms, but covers a gap in the payment turnover.
Depending on the degree of security, loans can be:
- with full collateral - the value of collateral fully covers the cost of the loan itself and reduces the financial risks of the lender to almost zero;
- incomplete collateral - the collateral value of the collateral does not fully cover the amount of the loan;
- without collateral (blank) - the collateral value is completely absent, the lender's risks are maximum.

To classify a loan by type, you can also apply the charge for its use. Here you can select an interest-free and interest-bearing loan (free and paid), cheap and expensive, which completely depends on the size of the interest rate.
Another point on which loans are divided may be the term of the loan. A loan that serves the current needs of the borrower and taken for a period of not more than six months is considered short-term, up to one year or more - medium-term and long-term, respectively. It should be noted that such a distribution is typical, for example, for Russia, in other countries the distribution depending on the terms of lending may be different.
And who are the creditors?
In addition to those listed above, depending on other indicators, many other types of loans can be distinguished. For example, you can divide them depending on the participants in the transaction, the source of the return of credit funds, etc.
For example, the main forms of credit can be distinguished depending on the participants in the credit relationship. And so further let's look at loans in this perspective:
- banking;
- commercial;
- state;
- international;
- consumer;
- usurious;
- mortgage, etc.
Bank lending
The most common, of course, is bank lending. With this form, the owners of free funds provide them to borrowers using the intermediary of banks.

Depending on the subject of lending, the following forms of bank loans are distinguished:
- lending to legal entities - in the case when funds are spent on paying off various debts and making various payments - this is a loan of money, and if they are used to expand production capacities, as well as to replenish the main and working capital of the enterprise - a loan of capital;
- lending to individuals - funds are provided for the intended use of individuals. persons - treatment, training, repair, construction, recreation, prosthetics, etc.;
- interbank loans - to consolidate correspondent relations between banks, as well as to maintain the proper level of profitability of banking structures.
Commercial lending
Considering other forms of lending, one can single out an equally profitable loan - economic or commercial. In this form, enterprises provide loans (or goods) to each other, without the participation of banks. Commercial credit is the fundamental principle of commodity-money relations, as it allows you to level the contradiction, when some enterprises have already produced goods and are ready to sell them, while others have not yet sold their own and therefore do not have the means to buy. Economic credit contributes to the sale of goods and profits embedded in them. That is why rates on commercial loans are much lower than those of banks.

A business loan debt is a promissory note, which can be simple or "bearer" - which provides for a written order from the lender to pay a specified amount to a third party. This feature of the bills makes it possible to transfer them, while an endorsement is placed on it - a special endorsement. The more endorsements, the more likely it is to be redeemed.
State lending
Considering the main forms of credit, it is impossible not to dwell on the state loan. This is a form of lending in which one of the subjects of relations (borrower or lender) is the state. Such a loan is fundamentally different from other types. When providing, for example, a bank loan, certain material assets belonging to the borrower act as collateral, and in the case of a state loan, all property owned by a territorial unit, or all of its income for a certain period, is collateral. The main purpose of this form of credit is to solve all kinds of problems on a national scale - covering the state budget deficit, financing various programs.
In cases where the state itself is a creditor, through the Treasury or the Central Bank, lending occurs to a certain industry or commercial banks and non-banking organizations as a result of auction trading in credit resources in the interbank loan market.
International lending
One of the latest forms is international lending, which arose when economic relations went beyond the state framework.
Forms of an international loan are practically no different from an internal loan. The subjects of international lending are almost identical to the domestic economy: the population, enterprises, banks, the state. The only difference is that the borrower and the lender are citizens of different countries. Thus, international lending can be defined as the flow of loan capital between countries. Traditionally, there are such forms of international credit:
- corporate (entrepreneurial) loan;
- bank loan;
- government loan.
Consumer
A form of loan in which credit funds are not used to produce new value, but are aimed at satisfying certain needs, is a consumer loan. Lenders in this case can be commercial organizations that offer for retail sale - most often in installments - durable goods, medical services, direct cash lending for the intended purpose. A feature of this type of lending is that the borrowers are individuals who have taken money to meet purely personal needs.

Consumer credit is very closely related to banking, as financial companies use the debt obligations of their customers to obtain cash loans from banking structures. That is why the concept of consumer lending can be interpreted much more broadly - as a set of cash and commodity loans provided to the population by banks, financial organizations and directly by the state. Such a loan can be used not only for current needs, but also for investment purposes. However, in this case, the borrower will be required to report and documentary evidence of the use of the loan.
Usurious
The most ancient and primitive type of lending is usurious credit. Its distinguishing feature is inflated interest rates on loans and not entirely legal methods of collecting amounts from an irresponsible payer. Most often, such services are provided by organizations that do not have an official license to conduct commercial activities. Leaving aside the black lending market, the most prominent representative of legal usurious lending in our time are pawnshops. It is there that short-term loans are provided, at extremely high interest rates, and highly liquid collateral is required, which is transferred to the lender for safekeeping.
Mortgage
One of the most common loans in Russia is a mortgage loan. It is provided for the purchase of real estate, as well as for the construction and overhaul of residential and industrial premises. The loan is secured either by the subject of mortgage itself or by other equivalent property owned by the borrower at the time of conclusion of the contract. A mortgage loan is exclusively targeted and long-term.

The development of the mortgage market implies the existence of a certain system, the participants of which are directly the borrower, lender, investor and various intermediaries - insurers, appraisers, registrars, regulators, etc. Investors in this case can be financial market entities that purchase securities secured by mortgage loans - financial and credit organizations, funds, including pension funds, just the population.
Conclusion
No matter how economists classify a loan, using common sense, it can be divided into two most important categories: a profitable loan and one that is not worth messing with. Since any loan assumes that you take other people's money for a while, and you have to give your own forever, this is perhaps the most important classification that you should get acquainted with.
By the nature of the loaned value credit is divided into three forms:
Commodity form credit historically precedes the monetary form. In this form of credit, goods are loaned. At the same time, the goods that are the object of the loan ensure its return. Goods are used in economic circulation, and are most often repaid in cash. Goods become the property of the borrower only after repayment of the loan and payment of interest.
Monetary form loan - the classic form of credit, which means that temporarily free cash is being loaned. The monetary form is the most typical due to the fact that money is the universal equivalent in the exchange of commodity values, a universal means of circulation and payment. This form of credit largely depends on the situation in the economy, inflation, unemployment, etc. This form of credit is used by both the state and individuals both within the country and in foreign economic turnover.
Mixed (commodity-money) form loan. In this case, the loan is provided in the form of a commodity, and is returned in cash or vice versa. It is widespread in developing countries when borrowed funds at the international level are returned through commodity deliveries.
Bank loan
With this form of credit, only money capital is used. This loan is provided exclusively by financial and credit institutions licensed by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation to conduct such types of operations. The scope of this loan is much wider than commercial.
The banking form of the loan has the following features:
the bank, as a rule, operates not so much with its own capital as with attracted resources;
the bank lends idle capital;
the bank lends not just money, but money as capital.
The price for using bank loans is loan interest, determined on a mutually beneficial basis between the subjects of credit relations and fixed in the loan agreement.
commercial loan means that the lender is not a credit institution, but the loan is provided in the course of a commercial transaction, therefore it is also called a commercial one. A loan can be provided by any entity that has temporarily free cash at its disposal.
Commercial credit is one of the first forms of credit relations in the economy, which gave rise to bill circulation and thereby actively contributed to the development of non-cash money circulation, finding a practical expression of financial and economic relations between legal entities in the form of sales of products or services by deferred payment. The main purpose of this form of credit is to accelerate the process of selling goods and, consequently, extracting the profit embedded in them.
The commercial loan instrument is traditionally bill of exchange, expressing the financial obligations of the borrower in relation to the lender. Two forms of a bill of exchange are most widely used - a simple bill containing a direct obligation of the borrower to pay a fixed amount directly to the lender, and a transferable (draft), representing a written order to the borrower from the lender to pay a fixed amount to a third party or to the bearer of the bill. In modern conditions, the function of a bill is often taken over by a standard agreement between the supplier and the consumer, which regulates the procedure for paying for products sold on the terms of a commercial loan. A commercial loan is fundamentally different from a bank loan:
the role of the creditor is not specialized financial institutions, but any legal entities associated with the production or sale of goods or services;
provided exclusively in commodity form;
loan capital is integrated with industrial or commercial, which in modern conditions has found practical expression in the creation of financial companies, holdings and other similar structures, including enterprises of various specializations and activities;
the average cost of a commercial loan is always lower than the average bank interest rate for a given period of time;
when the transaction is legally executed between the lender and the borrower, the fee for this loan is included in the price of the goods, and is not determined specifically, for example, through a fixed percentage of the base amount.
In foreign practice, commercial credit is extremely widespread. For example, in Italy, up to 85% of the amount of transactions in wholesale trade is carried out on the terms of a commercial loan, and the average period for it is about 60 days, which significantly exceeds the period of actual sale of goods to direct consumers. In Russia, this form of lending has until recently been limited to the scope of circulation. In other industries, such factors as high inflation rates, the crisis of non-payments, the unreliability of partnerships, and the shortcomings of specific law, objectively impeded its spread.
In modern conditions, in practice, there are mainly three types of commercial loans:
a loan with a fixed repayment period;
a loan with a return only after the actual sale by the borrower of the goods delivered in installments;
crediting on an open account, when the delivery of the next batch of goods on the terms of a commercial loan is carried out until the debt on the previous delivery is paid off.
State loan
The main feature is the participation of the state or local authorities at various levels. State credit is provided at the expense of budgetary funds.
Acting as a creditor, the state, through the central bank, lends:
specific industries or regions experiencing a special need for financial resources, if the possibilities of budget financing have already been exhausted, and loans from commercial banks cannot be attracted due to the action of market factors;
commercial banks in the process of auction or direct sale of credit resources in the interbank credit market;
target programs of international relations.
The state acts as a borrower in the process of placing government loans or in carrying out operations in the government short-term securities market. The main form of credit relations in the state credit are such relations in which the state acts as a borrower of funds. It should be noted that in the transitional period it should be used not only as a source of attracting financial resources, but also as an effective tool for centralized credit regulation of the economy.
International credit - a set of credit relations operating at the international level, the direct participants of which are the state and international financial institutions (IMF, IBRD, etc.). A distinctive feature is the belonging of one of the participants in credit relations to another country.
In relations with the participation of states as a whole and international institutions, credit always acts in monetary form, in foreign trade activities - also in commodity form (as a kind of commercial credit to the importer). It is classified according to several basic features:
by the nature of loans - interstate, private;
in form - state, banking, commercial;
by place in the foreign trade system - export crediting, import crediting.
A characteristic feature of an international loan is its additional legal or economic protection in the form of private insurance and state guarantees.
When regimes change, new authorities do not always recognize the obligations of their predecessors. On the Day of Assistance to States and Commercial Creditors in solving this problem, clubs of international creditors were created: the Paris Club unites creditor states, the London Club includes international commercial creditors.
Civil form of credit(private, personal, usurious). This form of credit was the first in the history of credit and existed in commodity form, then it was developed in monetary form. It is usurious. This loan is implemented by issuing loans to individuals, as well as business entities that do not have an appropriate license from the central bank. It is characterized by ultra-high interest rates and often criminal methods of recovery from the non-payer.
This form of credit can also be of a friendly nature. It is based on mutual trust and is not accompanied by the conclusion of a contract. Promissory notes with notarial certificates are used.
Production credit provided for entrepreneurial purposes: expansion of production volume, works, services, assets. Production credit directly affects the increase in the supply of goods, works, services, assets, factors of production, and the increase in the standard of living of the population.
Consumer credit. A characteristic feature of consumer credit is the relationship of both monetary and commodity capital, and individuals are potential borrowers.
Unlike the production form, this credit is used by the population for the purpose of consumption; it is not aimed at creating new value.
Both specialized credit organizations and any legal entities selling goods or services can act as a creditor. In monetary form, a consumer loan is provided as a bank loan to an individual to purchase real estate, pay for expensive medical treatment, etc., in commodity form - in the process of retail sale of goods with deferred payment. In Russia, this type of loan is only gaining distribution, it is used to a limited extent for lending secured by real estate (most often housing). In foreign practice, consumer credit covers all segments of the working population, mainly through various credit card systems.
Other forms of credit
In addition, the loan can be classified according to other criteria. Thus, there is a financial form of credit, direct and indirect, explicit and hidden, basic and additional, developed and undeveloped.
financial loan used to conduct transactions with financial assets: securities, currency, various instruments of the loan capital market. It contributes to satisfying the demand for speculative capital.
Direct form of credit reflects the direct issuance of a loan to the user without intermediaries.
Indirect form of credit provides for taking loans for lending to other entities. It is usually used when lending for the purchase of agricultural products.
Under explicit form of credit refers to a loan with a predetermined purpose. New forms of credit include leasing loan and a number of others.
The main form of credit is this is a money loan, while a commodity loan is its additional form.
Developed and undeveloped forms of credit characterize the degree of its development. Lombard credit can be attributed to an undeveloped form of credit.
Credit in per. from Latin (creditium) has two meanings - “I believe, trust”, “debt, loan”. A loan is an economic category and expresses economic relations between business entities associated with the redistribution of temporarily free cash on terms of urgency, payment and repayment.
A way of organizing credit relations is a loan. The totality of funds transferred for temporary use for a fee in the form of interest is called loan capital. Loan capital is capital in the form of money provided by its owner to the borrower under certain conditions. A loan is a movement of loan capital.
Credit principles: 1. Urgency.
2. Return. Banks use the free funds of enterprises and individuals and, upon request, they must be returned.
3. Payment. The implementation of this principle in practice is carried out through the mechanism of bank interest. The payment of the loan stimulates the borrower to its most productive use.
4. Target nature of loans, i.e. loans are provided for specific purposes.
5. Loan security. This principle expresses the need to ensure the protection of the lender's property interests in the event of a possible violation by the borrower of its obligations and finds practical expression in such forms of lending as loans secured or secured by financial guarantees.
6. Efficiency of loans, i.e. providing at cost-effective commercial promotions.
7. Differentiation of lending - the choice of the most reliable borrowers. The practical implementation of this principle may depend both on the individual interests of a particular bank, and on the centralized policy pursued by the state to support certain industries or areas of activity (for example, small business, etc.).
Credit in the country's economy performs the following functions:
1. Promotes the redistribution of capital between sectors of the economy and the formation of an average rate of profit.
2. Stimulates labor efficiency.
3. Expands the market for goods.
4. Accelerates the process of selling goods and making a profit.
5. It is a powerful tool for the centralization of capital.
6. Accelerates the process of accumulation and concentration of capital.
7. Provides a reduction in distribution costs associated with the circulation of money and the circulation of goods (non-cash money, bills are used). It is necessary to note the regulatory function of the loan.
Types of loans
1. By terms, they distinguish:
a) short-term loans (up to 1 year);
b) medium-term (over a year to 3 years);
c) long-term (over 3 years).
2. By the nature of the security:
Unsecured (blank);
Secured (pledge of property, bank guarantees and guarantees, assignment of the borrower's claims to a third party in favor of the bank, provision with travel and commodity documents, bills of exchange - accounting of bills).
3. By means of provision:
3.1. Loan in one amount (based on a loan agreement);
3.2. Open credit line. The loan is granted within a certain period within the agreed limit, each loan is issued as necessary in stages, on time and in the amount determined by agreement of the parties. The credit line is:
a) simple (non-renewable);
b) renewable (revolving) loan;
c) on-call (on demand).
3.3. Overdraft - short-term lending to the current account of the borrower as payment documents arrive to him within the limit of lending;
3.4. Combined options.
4. By order of repayment (one-time payment, evenly, according to an individual schedule).
5. By the nature of the interest rate (fixed or floating).
6. By the method of paying interest (monthly, at the time of loan repayment).
7. By lending methods. A lending method is a set of methods by which a loan is issued and repaid. Two methods are applied:
a) target loan, incl. term loan, revolving and non-revolving credit line;
b) overdraft.
8. By loan currency (in national currency, in foreign currency, in several currencies).
9. By the number of creditors (one bank; syndicated; parallel).
10. By types of borrowers:
a) loans to commercial enterprises;
b) industrial enterprises;
c) individuals;
d) commercial banks;
e) agricultural loans;
f) secured by real estate (mortgage);
g) loans secured by securities.
11. Services of a credit nature:
§ bank acceptance of bills of exchange and checks - the bank pays for the obligations of the client, having previously received funds from him;
§ Availability loan – the bank makes payment only in case of bankruptcy of the debtor;
§ factoring – collection of accounts receivable of clients and receipt of payments due in their favor;
§ leasing is the acquisition of ownership of property and its subsequent transfer for temporary use.
Mortgage loans are provided for the construction, reconstruction or acquisition of residential or industrial premises.
Their advantages:
· low risk when issuing a loan;
· loans are long-term, which frees the CB from frequent negotiations;
a stable clientele
· Mortgages are traded on the secondary market, which allows the CB to diversify its risk by selling the mortgage after the loan is issued.
Negative aspects of mortgages for CB:
§ the need to have narrow specialists in the real estate appraisal;
§ distraction of funds for a long time;
§ it is difficult to forecast earnings and market interest rates.
Mortgage types:
a) mortgages with a fixed interest rate (every month the borrower pays% and repays the loan, the amount of deductions is constant);
b) with a floating interest rate (adjusted once a year);
c) mortgages with differentiated payments (payments are gradually increasing);
d) guaranteed mortgages (insurance).
consumer credit- This is a loan provided to individuals by lenders (banks and various credit organizations). Consumer credit serves as a means of meeting various consumer needs of the population.
According to the economic content, there are:
1. Commodity consumer loans - car loans, commodity express loans, loans for the purchase of various services.
2. Financial consumer loans (or personal loans) - standard loans (including overdrafts) and credit cards.
According to the objects of lending, consumer loans are divided into two types: for current purposes and for capital expenditures.
Loans for current purposes, in turn, are divided into:
1) loans for the purchase of durable goods - furniture, household appliances, etc. (including "shop" express loans);
2) loans for urgent needs (unsecured cash loans);
3) car loans (classic car loans, express car loans, car loans with buyback under the trade-in scheme);
4) educational credit and credit for recreation, for medical services;
5) purchase of credit cards.
Capital expenditure loans include loans for the renovation of apartments and houses, the purchase and construction of housing and land for construction. Such a loan requires 100% collateral in the form of guarantors, movable or immovable property. A special case of such a loan is a mortgage.
According to the intended purpose, they distinguish: targeted loan (credit funds are spent on strictly defined purposes) and non-purpose loan (used at your own discretion). General purpose loans include emergency loans and overdrafts.
Distinguish according to the method of delivery one-time loans And revolving or revolving loans (credit cards and overdraft).
A consumer loan by repayment method can be:
a loan with a one-time repayment (the borrower returns the entire amount to the bank with interest after a certain period of time); a loan with installment payment (the amount and interest are paid by the borrower monthly for some time).
Loans against securities issued for the purchase of securities. The users of such loans are dealers (operate with securities) and brokers (finance the purchase of securities for their clients). These loans are on-call.
On-call loans (from the English on call - on demand) - bank loans that can be claimed at any time (demand loans). Such loans in world banking practice are secured by promissory notes, goods and securities.
A mortgage is an encumbrance of property rights to a property.
Mortgage credit lending- this is lending secured by real estate, that is, lending using a mortgage as a security for the repayment of loan funds.
When considering a mortgage as an element of the economic system, it is necessary to highlight its three most characteristic features.
1. Pledge of real estate acts as a tool to attract the necessary financial resources for the development of production.
2. A mortgage is able to ensure the realization of property rights to objects when other forms (for example, purchase and sale) are inappropriate under these specific conditions.
3. Creation of fictitious capital on the basis of a security with the help of a mortgage (when the owner of a real estate object issues primary, secondary, etc. mortgages, working capital increases by the amount of fictitious capital formed).
You can identify the following distinctive features of a mortgage loan:
1. Mandatory security(moreover, the property for the purchase of which a mortgage loan is taken can also act as collateral).
This means that, in case of default by the borrower of obligations, foreclosure on housing is carried out with its subsequent sale in order to repay the debt of the borrower on the loan to the creditor. The amount remaining after repayment of the loan, minus the costs associated with the foreclosure procedure and the sale of housing, is returned to the former borrower. The borrower and all adult members of his family give a notarized consent to the release of the mortgaged dwelling in the event of foreclosure. Mortgaged housing must be free from any restrictions (encumbrances), must not be pledged to secure another obligation.
2. The duration of the loan. Long-term mortgage housing loans are provided for a period of 3 or more years (optimally 20-25 years). Due to the long repayment period, the size of the monthly payments of the borrower is reduced.
3. Most mortgage loans are targeted.
4. A mortgage loan is considered a relatively low-risk banking operation.
The main requirements include the following:
The loan amount, as a rule, is no more than 60-70% of the market value of the purchased housing;
The amount of the monthly payment on the loan should not exceed 30% of the total income of the borrower and co-borrowers (if any) for the relevant billing period;
When assessing the probability of loan repayment, the lender uses officially confirmed information about the current income of the borrower and co-borrowers.
Credit Services
1. Availability loan. Payment under a bill of exchange can be secured in full or in part of the bill amount by means of aval (bill surety). This security is given by a third party or even by one of the signatories of the bill. Aval is given on a bill of exchange or on an additional sheet; it can also be given on a separate sheet, indicating the place of issue. It is expressed by the words "count as aval", signed by those who give aval. The avalist is responsible in the same way as the one for whom he gave the aval. His undertaking is valid even if the undertaking which he guaranteed should be invalid for any reason whatsoever.
By paying a bill of exchange, the avalier acquires the rights arising from the bill of exchange against the one for whom he gave the guarantee, and against those who, by virtue of the bill of exchange, are obliged to this latter.
2. Acceptance credit. Used in foreign trade. It consists in lending to the importer through the acceptance by the bank of drafts (bills of exchange) issued to him by the exporter.
3. Factoring. This is the collection of accounts receivable of its customers and the receipt of payments due in their favor. In factoring operations, invoices and payment requests are sold.
Open factoring - in this case, the payer is notified that the supplier is assigning invoices to the bank (factor). Closed (confidential) factoring - the payer is not notified. By agreement of the parties, the right of recourse may be provided, i.e. the right to return unpaid invoices to the factor with the requirement to reimburse the credit to the factor. But in world practice this is rarely used, factoring companies bear the entire risk of non-payment.
4. Forfaiting. This is such a credit operation in which the exporter, having received from the importer the bills of exchange (drafts) accepted by the importer, sells them at a discount to the bank. When the due date for payment of the drafts, the importer usually repays his debt in semi-annual installments. The transaction is formalized by the appropriate endorsement.
Currently, forfaiting operations are developing in the field of international trade and represent the purchase of bills and other obligations from exporting firms to advance their commercial activities, i.e. receipt of payments from debtors. Specialized firms and banks act as buyers of export debt. The advantages of forfaiting include: acceleration of capital turnover due to advance payments from buyers, release of exporters from currency risks of non-payments, increase in the liquidity of exporting enterprises by reducing receivables and increasing the level of cash, the possibility of making new capital investments.
5. Bills of exchange operations in the bank, in whatever form they are carried out, begin with the receipt of a bill of exchange by the client. Loans in the form of accounting for bills of exchange and in the form of a special loan account secured by bills of exchange are opened separately. Bill credits are divided into permanent and one-time. Credits for the accounting of bills can be bearer And promissory notes. The first one is opened for accounting of bills of exchange transferred by clients to the bank. Economic agencies that have a large number of bills of sale use bearer loans.
A promissory note loan is provided to customers who issue promissory notes against this loan to pay for inventory items, works and services shown to other economic bodies, enterprises and individuals. The latter present such bills to the bank, which sends them for accounting to the drawer's bank at the expense of the loan opened to him by the drawer. Loans are opened on demand. An application for a bill of exchange loan is usually submitted to a bank in which the main accounts of enterprises and economic agencies are opened, including a settlement (current) account.
6. Lombard loan- A loan secured by securities. Upon default, the securities become the property of the bank.
7. Leasing. The objects of leasing are machines, mechanisms and vehicles, and the subjects are equipment manufacturers, lessors, lessees and banks involved in leasing operations.
Depending on the composition of the participants, direct and indirect leasing are distinguished. At direct leasing property is rented without intermediaries with direct transfer of values to the lessee on a bilateral basis. At indirect leasing the lease is organized by several parties, one of which may act as a consignor, another as a lessor, and a third as a creditor.
According to the degree of commercial complexity, irreversible and returnable leasing are distinguished. Irreversible leasing involves the use of property without the right to sell or transfer it to another tenant. At leaseback the equipment manufacturer first sells it to its counterparty, and then receives it under leasing, which makes it possible to mobilize additional funds to expand production.
Leasing with a full payback of property - financial leasing, which differs in that during the term of the contract there is a full payment of the cost of the leased equipment.
Leasing with incomplete payback of property - operational or partial leasing, at which the term of the contract is less than the standard shelf life of the property.
"Leverage - leasing", or separate leasing - leasing with the attraction of borrowed funds from the investor, which involves the participation of several companies providing financing. The main lessor becomes the owner of the property, with all the ensuing consequences, but he can grant the right to receive lease payments to his lenders.
Net leasing – All maintenance of the property is taken over by the lessee. This is typical for financial leasing.
"Wet" leasing- the costs of mandatory maintenance of property, repair, insurance are borne by the lessor. This is typical for operational leasing.
Leasing with a full range of services – with complex maintenance of property by the lessor.
Leasing with a partial set of services – if the lessor accounts for only a certain proportion of property maintenance work.
Also exists revolving lease , or leasing with successive replacement of property.
Source - T.A. Frolova Banking: lecture notes Taganrog: TTI SFU, 2010.
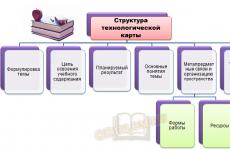
Forms of credit are varieties arising from the essence of credit relations.
Loan classification is carried out according to such basic features as the nature of the loaned value, the categories of creditors and borrowers, the form of provision, and the directions of borrowers' needs.
Rice. 5.1. Classification of loan forms
Forms of credit by the nature of the loaned value
By the nature of the loaned value credit is divided into three forms:
Commodity form credit historically precedes the monetary form. In this form of credit, goods are loaned. At the same time, the goods that are the object of the loan ensure its return. Goods are used in economic circulation, and are most often repaid in cash. Goods become the property of the borrower only after repayment of the loan and payment of interest.
The first creditors were entities that had surpluses of commodities. Currently, the commodity form of credit is used in the sale of goods by installments, leasing and rental, and is often accompanied by a monetary form.
Monetary form loan - the classic form of credit, which means that temporarily free cash is being loaned. The monetary form is the most typical due to the fact that money is the universal equivalent in the exchange of commodity values, a universal means of circulation and payment. This form of credit largely depends on the situation in the economy, inflation, unemployment, etc. This form of credit is used by both the state and individuals both within the country and in foreign economic turnover.
Mixed (commodity-money) form loan. In this case, the loan is provided in the form of a commodity, and is returned in cash or vice versa. It is widespread in developing countries when borrowed funds at the international level are returned through commodity deliveries.
Bank loan
With this form of credit, only money capital is used. This loan is provided exclusively by financial and credit institutions licensed by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation to conduct such types of operations. The scope of this loan is much wider than commercial.
The banking form of the loan has the following features:
- the bank, as a rule, operates not so much with its own capital as with attracted resources;
- the bank lends idle capital;
- the bank lends not just money, but money as capital.
The price for using bank loans is loan interest, determined on a mutually beneficial basis between the subjects of credit relations and fixed in the loan agreement.
commercial loan
commercial loan means that the lender is not a credit institution, but the loan is provided in the course of a commercial transaction, therefore it is also called a commercial one. A loan can be provided by any entity that has temporarily free cash at its disposal.
Commercial credit is one of the first forms of credit relations in the economy, which gave rise to bill circulation and thereby actively contributed to the development of non-cash money circulation, finding a practical expression of financial and economic relations between legal entities in the form of sales of products or services by deferred payment. The main purpose of this form of credit is to accelerate the process of selling goods and, consequently, extracting the profit embedded in them.
The commercial loan instrument is traditionally bill of exchange, expressing the financial obligations of the borrower in relation to the lender. The most widespread are two forms of a bill of exchange - a simple bill containing a direct obligation of the borrower to pay a fixed amount directly to the creditor, and a transferable (draft), representing a written order to the borrower from the lender to pay a fixed amount to a third party or to the bearer of the bill. In modern conditions, the function of a bill is often taken over by a standard agreement between the supplier and the consumer, which regulates the procedure for paying for products sold on the terms of a commercial loan. A commercial loan is fundamentally different from a bank loan:
- the role of the creditor is not specialized financial institutions, but any legal entities associated with the production or sale of goods or services;
- provided exclusively in commodity form;
- loan capital is integrated with industrial or commercial, which in modern conditions has found practical expression in the creation of financial companies, holdings and other similar structures, including enterprises of various specializations and activities;
- the average cost of a commercial loan is always lower than the average bank interest rate for a given period of time;
- when the transaction is legally executed between the lender and the borrower, the fee for this loan is included in the price of the goods, and is not determined specifically, for example, through a fixed percentage of the base amount.
In foreign practice, commercial credit is extremely widespread. For example, in Italy, up to 85% of the amount of transactions in wholesale trade is carried out on the terms of a commercial loan, and the average period for it is about 60 days, which significantly exceeds the period of actual sale of goods to direct consumers. In Russia, this form of lending has until recently been limited to the scope of circulation. In other industries, such factors as high inflation rates, the crisis of non-payments, the unreliability of partnerships, and the shortcomings of specific law, objectively impeded its spread.
In modern conditions, in practice, there are mainly three types of commercial loans:
- a loan with a fixed repayment period;
- a loan with a return only after the actual sale by the borrower of the goods delivered in installments;
- crediting on an open account, when the delivery of the next batch of goods on the terms of a commercial loan is carried out until the debt on the previous delivery is paid off.
State loan
The main feature is the participation of the state or local authorities at various levels. State credit is provided at the expense of budgetary funds.
Acting as a creditor, the state, through the central bank, lends:
- specific industries or regions experiencing a special need for financial resources, if the possibilities of budget financing have already been exhausted, and loans from commercial banks cannot be attracted due to the action of market factors;
- commercial banks in the process of auction or direct sale of credit resources in the interbank credit market;
- target programs of international relations.
The state acts as a borrower in the process of placing government loans or in carrying out operations in the government short-term securities market. The main form of credit relations in the state credit are such relations in which the state acts as a borrower of funds. It should be noted that in the transitional period it should be used not only as a source of attracting financial resources, but also as an effective tool for centralized credit regulation of the economy.
International credit
International credit - a set of credit relations operating at the international level, the direct participants of which are the state and international financial institutions (IMF, IBRD, etc.). A distinctive feature is the belonging of one of the participants in credit relations to another country.
In relations with the participation of states as a whole and international institutions, credit always acts in monetary form, in foreign trade activities it also acts in commodity form (as a kind of commercial credit to the importer). It is classified according to several basic features:
- by the nature of loans - interstate, private;
- in form - state, banking, commercial;
- by place in the foreign trade system - export crediting, import crediting.
A characteristic feature of an international loan is its additional legal or economic protection in the form of private insurance and state guarantees.
When regimes change, new authorities do not always recognize the obligations of their predecessors. On the Day of Assistance to States and Commercial Creditors in solving this problem, clubs of international creditors were created: the Paris Club unites creditor states, the London Club includes international commercial creditors.
Civil form of credit
Civil form of credit(private, personal, usurious). This form of credit was the first in the history of credit and existed in commodity form, then it was developed in monetary form. It is usurious. This loan is implemented by issuing loans to individuals, as well as business entities that do not have an appropriate license from the central bank. It is characterized by ultra-high interest rates and often criminal methods of recovery from the non-payer.
This form of credit can also be of a friendly nature. It is based on mutual trust and is not accompanied by the conclusion of a contract. Promissory notes with notarial certificates are used.
Consumer and industrial credit
Production credit provided for entrepreneurial purposes: expansion of production volume, works, services, assets. Production credit directly affects the increase in the supply of goods, works, services, assets, factors of production, and the increase in the standard of living of the population.
Consumer credit. A characteristic feature of consumer credit is the relationship of both monetary and commodity capital, and individuals are potential borrowers.
Unlike the production form, this credit is used by the population for the purpose of consumption; it is not aimed at creating new value.
Both specialized credit organizations and any legal entities selling goods or services can act as a creditor. In monetary form, a consumer loan is provided as a bank loan to an individual for the purchase of real estate, payment for expensive treatment, etc., in commodity form - in the process of retail sale of goods with deferred payment. In Russia, this type of loan is only gaining popularity, it is used to a limited extent for lending secured by real estate (most often housing). In foreign practice, consumer credit covers all segments of the working population, mainly through various credit card systems.
Other forms of credit
In addition, the loan can be classified according to other criteria. Thus, there is a financial form of credit, direct and indirect, explicit and hidden, basic and additional, developed and undeveloped.
financial loan used to conduct transactions with financial assets: securities, currency, various instruments of the loan capital market. It contributes to satisfying the demand for speculative capital.
Direct form of credit reflects the direct issuance of a loan to the user without intermediaries.
Indirect form of credit provides for taking loans for lending to other entities. It is usually used when lending for the purchase of agricultural products.
Under explicit form of credit refers to a loan with a predetermined purpose. New forms of credit include leasing loan and a number of others.
The main form of credit is this is a money loan, while a commodity loan is its additional form.
Developed and undeveloped forms of credit characterize the degree of its development. Lombard credit can be attributed to an undeveloped form of credit.
Having considered the forms of credit, you can analyze their types.
Loan types
As a result of the relationship between the lender and the borrower, six independent general forms of credit can be distinguished.
Bank loan - one of the most common forms of credit relations in the economy, the object of the transaction is cash. Operations are carried out by specialized credit institutions that have a license from the central bank. The bank operates not so much with its own capital as with borrowed resources. He disposes of idle capital, temporarily free cash placed in bank accounts. The bank provides a loan on a fee basis (the loaned value acts as capital: the money brings a profit to the borrower, which should be enough at least to pay the loan interest). The role of the borrower is played by legal entities and individuals who conclude an appropriate agreement with a credit institution. The bank interest rate is determined by agreement of the parties, taking into account the refinancing rate, the cost of credit resources and credit conditions.
By deadlines Loans are divided into:
- oncol- the loan is repayable within a fixed period after notification of the lender, is currently used quite rarely;
- short-term loans are provided to compensate for a temporary shortage of own working capital (usually up to one year). Short-term loans are most actively used in the stock market, trade and services, in the mode of interbank lending. In domestic banking practice, such loans are the most common form and are characterized by the fact that they are usually provided for up to 6 months and serve the sphere of circulation;
- medium-term loans granted for a period of one to three years. In the conditions of Russia, loans up to one year, in addition to a trade and commercial nature, have a production direction;
- long-term loans are provided for a period of more than one year, in some countries - more than three years and are used, as a rule, for investment purposes, serve the movement of fixed assets. They are especially common for lending to capital construction, the fuel and energy complex, and the raw materials industries. In Russia, they are practically not used due to economic instability, lack of long-term credit resources.
By repayment methods bank loans are divided into:
- loans with a one-time payment from the borrower, which do not require the use of the differentiated interest mechanism;
- installment loans for the entire term of the contract used in the repayment of medium-term and long-term loans. The agreement provides for anti-inflationary measures for the creditor.
By retention method loan interest:
- interest paid at the time of total loan repayment(short-term);
- interest paid equal contributions during the entire term of the contract;
- interest is paid in moment of loan disbursement, is very rare with ultra-short loans up to five days.
By availability of collateral:
- trust loans - the loan agreement is the only form of security. Used for lending to regular and reliable customers. Thus, banks can lend to each other; in case of medium-term lending, it is obligatory to insure the loan at the expense of the borrower;
- secured loans - any property owned by the borrower by right of ownership, most often real estate, liquid goods, securities, acts as collateral. If the borrower violates the terms of the contract, the security passes to the bank. When concluding a contract, it is very important to evaluate the collateral;
- loans guaranteed by others- the guarantor draws up an obligation to compensate the bank for the damage incurred if the borrower violates the terms of the loan agreement.
For the intended purpose:
- general loans, used by the borrower at its own discretion;
- targeted loans are used for the purposes stipulated by the terms of the loan agreement, the violation of which entails the application of financial sanctions.
By categories of potential borrowers: for the development of agriculture; commercial loans for the sphere of circulation; loans to intermediaries on the stock exchange; mortgage loans for property owners; interbank loans (the current rate on interbank loans is an important factor in determining the credit policy for other types of loans).
Commercial loan - one of the first historical forms of credit, which gave rise to bill circulation. The parties to the transaction are legal entities - economic entities. Promotes the development of non-cash turnover. The loaned value circulates between legal entities in the form of product sales, provision of services with deferred payment.
Promissory note - is a traditional commercial loan tool that happens simple- a direct obligation of the borrower to pay the lender a certain amount, transferable - an order from a creditor to a borrower to pay a debt to a third party or to the bearer of a bill. The differences between a commercial loan and a bank loan are as follows: a legal entity acts as a creditor; if credit is granted in the form of a commodity, then it is not a temporarily free value that is lent, but an ordinary commodity; property as an object of transfer passes from the lender to the borrower; if the loan is issued in cash, then its source is temporarily free cash; the ownership of the loaned value accordingly remains with the creditor. The average rate on a commercial loan issued in a commodity form is lower than the bank loan rate, because the loan fee is included in the price of the goods. Currently, three forms of commercial credit are used: a loan with a fixed repayment period; credit return after the actual sale of goods delivered in installments; delivery of the next consignment of goods is carried out until the moment of repayment of the debt on the previous consignment.
State loan - the state acts as a creditor in the person of state authorities and provides loans through the Central Bank of the Russian Federation to specific industries and regions, commercial banks when selling credit resources on the interbank market, as well as at the international level. The state acts as a borrower in the process of placing government loans or in carrying out transactions with government securities.
International credit - it is a set of credit relations at the global level. The participants in the transactions are international financial and credit institutions, governments, banks, monopolies. It acts mainly in the form of money, in foreign trade operations - in the form of commodities. Loans are subject to private insurance (depending on the nature of the loan) and state guarantees.
Private loan - a credit transaction between individuals based primarily on IOUs. The term of the transaction is often not strictly agreed, the interest is set at a lower rate than in a bank; is friendly in nature, acts both in monetary and in commodity forms.
usurious loan - is currently illegal, characterized by ultra-high interest rates and often criminal methods of debt collection.
Depending on the target needs of the borrower, there are productive(the loan is used for the purpose of production and circulation) and consumer forms of credit (this is a form of lending to individuals, provided in the form of money or goods, limitedly used secured by real estate, widely used abroad through the credit card system; not used to create new value, aims to satisfy the consumer needs of the borrower).
Forms of credit are not isolated from each other.